Advanced Bandwidth Management enables administrators to manage specific classes of traffic based on their priority and maximum bandwidth settings. Advanced Bandwidth Management consists of three major components:
|
•
|
Classifier – classifies packets that pass through the firewall into the appropriate traffic class.
|
|
•
|
Estimator – estimates and calculates the bandwidth used by a traffic class during a time interval to determine if that traffic class has available bandwidth.
|
|
•
|
Scheduler – schedules traffic for transmission based on the bandwidth status of the traffic class provided by the estimator.
|
This graphic illustrates the basic concepts of Advanced Bandwidth Management.
Advanced Bandwidth Management concepts
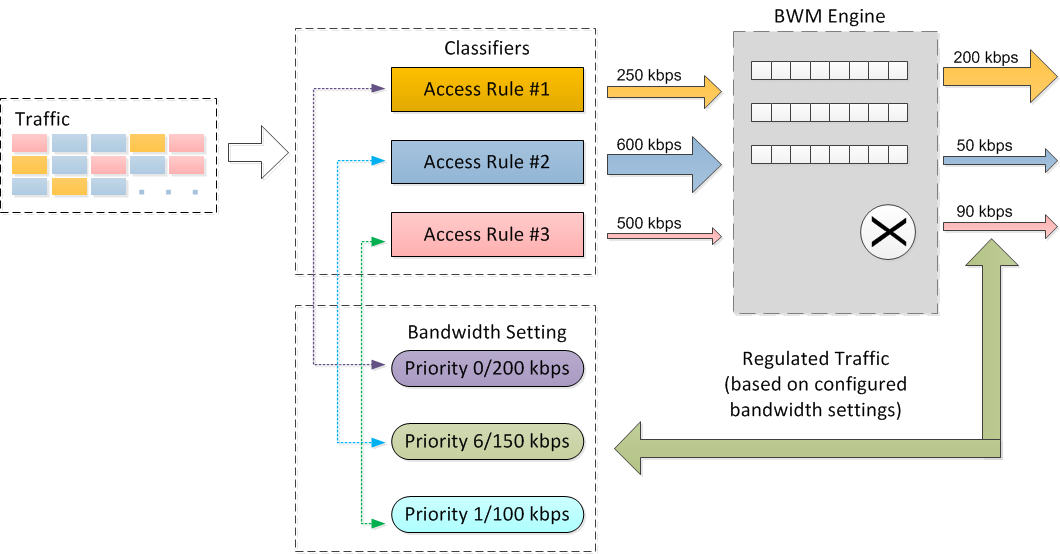
Bandwidth management configuration is based on policies which specify bandwidth limitations for traffic classes. A complete bandwidth management policy consists of two parts: a classifier and a bandwidth rule.
A classifier specifies the actual parameters, such as priority, guaranteed bandwidth, and maximum bandwidth, and is configured in a bandwidth object. Classifiers identify and organize packets into traffic classes by matching specific criteria.
A bandwidth rule is an access rule or application rule in which a bandwidth object is enabled. Access rules and application rules are configured for specific interfaces or interface zones.
The first step in bandwidth management is that all packets that pass through the SonicOS firewall are assigned a classifier (class tag). The classifiers identify packets as belonging to a particular traffic class. Classified packets are then passed to the BWM engine for policing and shaping. The SonicOS uses two types of classifiers:
The following table shows the classifiers that are configured in a bandwidth object:
After packets have been tagged with a specific traffic class, the BWM engine gathers them for policing and shaping based on the bandwidth settings that have been defined in a bandwidth object, enabled in an access rule, and attached to application rules.
Classifiers also identify the direction of packets in the traffic flow. Classifiers can be set for either the egress, ingress, or both directions. For Bandwidth Management, the terms ingress and egress are defined as follows:
For example, a client behind Interface X0 has a connection to a server which is behind Interface X1. The following table shows:
To be compatible with traditional bandwidth management settings in WAN zones, the terms inbound and outbound are still supported to define traffic direction. These terms are only applicable to active WAN zone interfaces.
