ADSL is an acronym for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (or Loop). The line is asymmetric because, when connected to the ISP, the upstream and downstream speeds of transmission are different. The DSL technology allows non-voice services (data) to be provided on regular single copper wire-pair POTS connections (such as your home phone line). It allows voice calls and data to pass through simultaneously by using higher band frequencies for data transmission.
The SonicWall ADSL module cards support only one subscriber ADSL line (one port). Two types of ADSL module cards are supported:
The ADSL standards shown in Supported ADSL Standards are supported.
The ADSL module card uses 2 LEDs to indicate connectivity status. The upper green LED is the ADSL link. Its status is as follows:
The lower green LED shows the system and ADSL module activity.
The ADSL module card is detected on boot, and assigned an interface name of M0 or M1. The interface name is based to it based on the expansion slot hosting the module card. You will see the assigned entry when you log into the Network Interfaces page.
The ADSL interface is never unassigned. When plugged in, it is always present in the WAN zone and zone assignment cannot be modified.
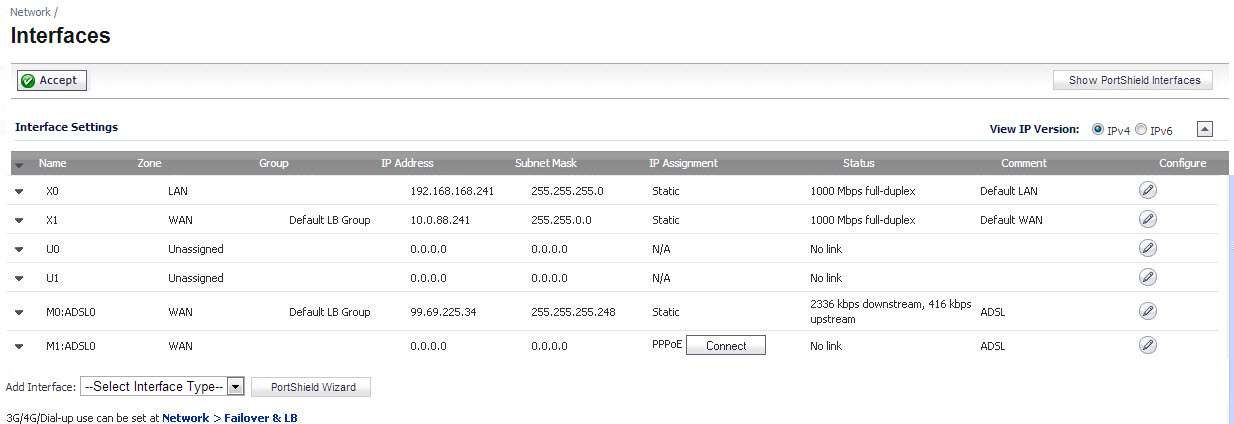
Click on the Configure icon to the right of the interface entry. You will see a menu with three tabs: General, Advanced, and DSL Settings. The DSL Settings tab allows you to configure ISP-specific settings for the ADSL connection.
It displays the configurable DSL fields:
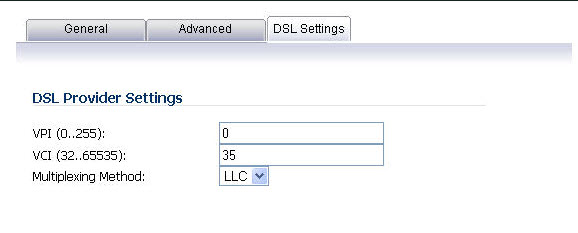
The values for these parameters should match the settings on the ISP DSLAM, and are provided by the ISP. These values vary from one ISP to another, and from country to country.
The SNWL default uses the most common values in the USA. The VPI and VCI settings are used to create the Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) from the NSA2400MX to the ISP DSLAM.
When finished configuring these ISP settings, click OK.
The Ethernet-specific settings on the Advanced tab, even if set, do not apply to the ADSL module. The Link Speed field in the Advanced tab has a fixed "N/A" selection, since it does not apply to ADSL. The ADSL link speed can't be customized but is predetermined by the DSL Provider.
The standard WAN ethernet settings are not affected by the presence of the ADSL module.
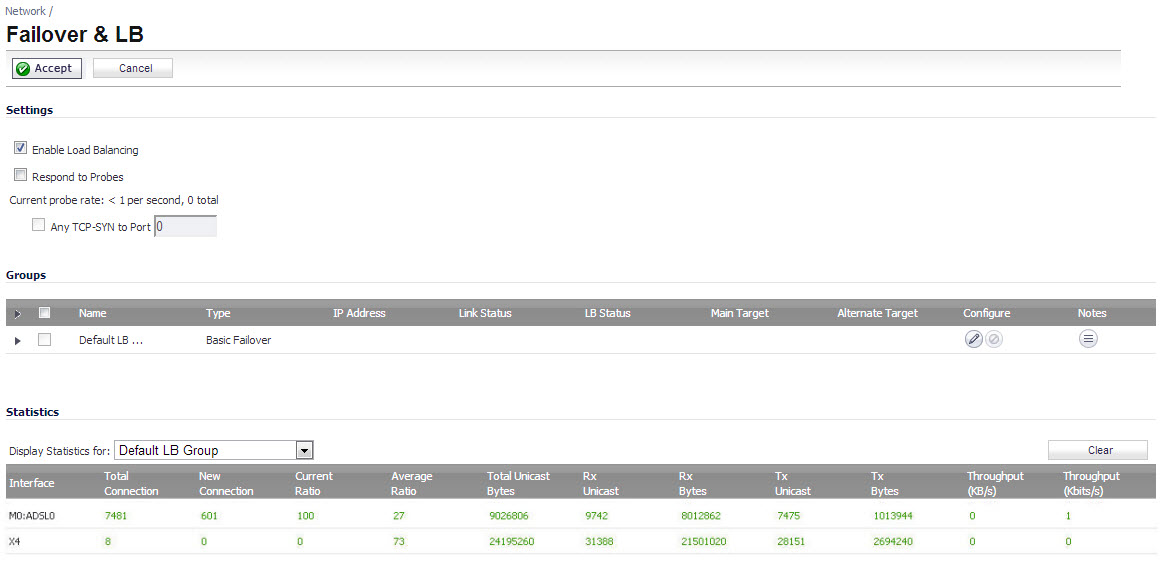
When the ADSL module is first plugged in, it should be added to the WAN Load Balancing default group so that the ADSL module can be used to handle default route traffic. Go to the Failover & LB page and click the Configure icon to edit the settings.
On the General tab, add the ADSL interface to the Load Balancing group. If the default primary WAN, X1, is unused or unconfigured, it can be removed for a cleaner interface configuration.
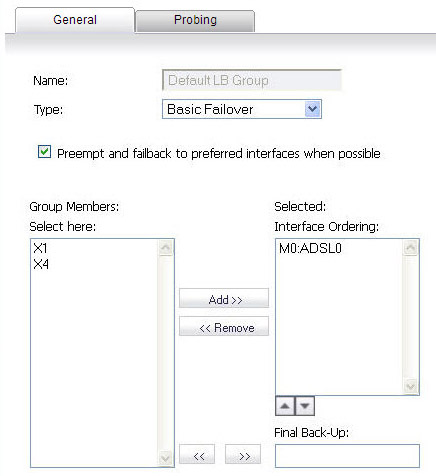
When done, click OK, and the ADSL module will be added to the group.
