Table 24 summarizes the key functional differences between modes of interface configuration:
|
Active/Active Clustering 1
|
|||||
|
Yes 2
|
|||||
|
Link-State Propagation 3
|
|||||
|
TCP Handshake Enforcement 4
|
|||||
Link State Propagation is a feature whereby interfaces in a Wire Mode pair will mirror the link-state triggered by transitions of their partners. This is essential to proper operations in redundant path networks.
|
1
|
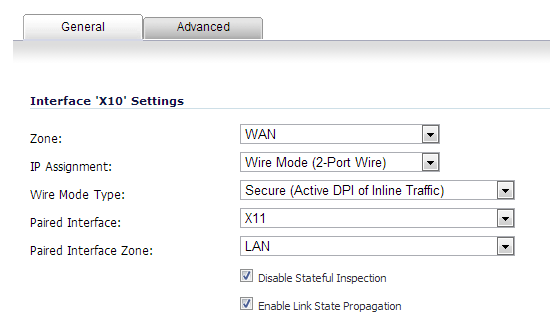
On the Network > Interfaces page, click the Configure icon for the interface you want to configure for Wire Mode.
|
|
2
|
In the Zone drop-down menu, select any zone type except WLAN.
|
|
3
|
To configure the Interface for Tap Mode, in the Mode / IP Assignment drop-down menu, select Tap Mode (1-Port Tap).
|
|
•
|
To configure the Interface for Wire Mode, in the Mode / IP Assignment drop-down menu, select Wire Mode (2-Port Wire).
|
|
4
|
In the Wire Mode Type drop-down menu, select the appropriate mode:
|
|
5
|
In the Paired Interface drop-down menu, select the interface that will connect to the upstream firewall. The paired interfaces must be of the same type (two 1 GB interfaces or two 10 GB interfaces).
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
Wire Mode can be configured on WAN, LAN, DMZ, and custom zones (except wireless zones). Wire Mode is a simplified form of Layer 2 Bridged Mode, and is configured as a pair of interfaces. In Wire Mode, the destination zone is the Paired Interface Zone. Access rules are applied to the Wire Mode pair based on the direction of traffic between the source Zone and its Paired Interface Zone. For example, if the source Zone is WAN and the Paired Interface Zone is LAN, then WAN to LAN and LAN to WAN rules are applied, depending on the direction of the traffic.
In Wire Mode, administrators can enable Link State Propagation, which propagates the link status of an interface to its paired interface. If an interface goes down, its paired interface is forced down to mirror the link status of the first interface. Both interfaces in a Wire Mode pair always have the same link status.
In Wire Mode, administrators can Disable Stateful Inspection. When Disable Stateful Inspection is selected, Stateful Packet Inspection is turned off. When Disable Stateful Inspection is not selected, new connections can be established without enforcing a 3-way TCP handshake. Disable Stateful Inspection must be selected if asymmetrical routes are deployed.
|
1
|
|
2
|
Click the Add Interface button.
|
Click the Configure button for the interface you want to configure.
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Select the Disable Stateful Inspection option.
|
|
7
|
Select the Enable Link State Propagation option.
|
|
8
|
Click the OK button.
|