The following attributes can be used to configure the BGP path selection process.
The weight command assigns a weight value, per address-family, to all routes learned from a neighbor. The route with the highest weight gets preference when the same prefix is learned from more than one peer. The weight is relevant only to the local router.
The weights assigned using the set weight command override the weights assigned using this command.
When the weight is set for a peer-group, all members of the peer-group will have the same weight. The command can also be used to assign a different weight to a particular peer-group member.
The following example shows weight configuration:
The Local Preference attribute is used to indicate the degree of preference for each external route in an appliance’s routing table. The Local Preference attribute is included in all update messages sent to devices in the same AS. Local Preference is not communicated to outside AS. The following figure shows a sample topology illustrating how Local Preference affects routes between neighboring ASs.
BGP Local Preference Topology
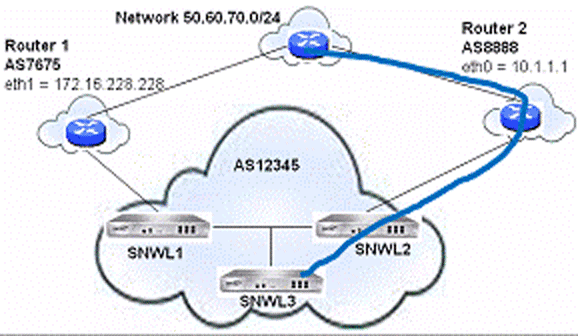
The following BGP configurations are entered on SNWL1 and SNWL2. The higher Local Preference on SNWL2 leads to SNWL2 being the preferred route advertised by AS 12345 (the SonicWall AS) to outside ASs.
Route Maps are similar to Access Control Lists. They consist of a series of Permit and/or Deny statements that determine how the appliance processes the routes. Route maps are applied to inbound traffic—not outbound traffic. The following diagram shows a sample topology that uses a route map to configure local preference.
BGP Local Preference topology with Route Maps

The following BGP configurations are entered on SNWL1 and SNWL2.
The Route Map configured on SNWL2 (rmap1) is configured to apply to inbound routes from neighbor 10.1.1.1. It has two permit conditions:
