|
•
|
|
Click Start Capture to begin capturing all packets except those used for communication between the firewall and the management interface on your console system.
|
|||||||||
|
Stop:
|
Click Stop Capture to stop the packet capture.
|
||||||||
|
Click Clear to clear the status counters that are displayed at the top of the Packet Monitor page.
|
|||||||||
|
Click Refresh to display new buffer data in the Captured Packets window. You can then click any packet in the window to display its header information and data in the Packet Detail and Hex Dump windows.
|
|||||||||
|
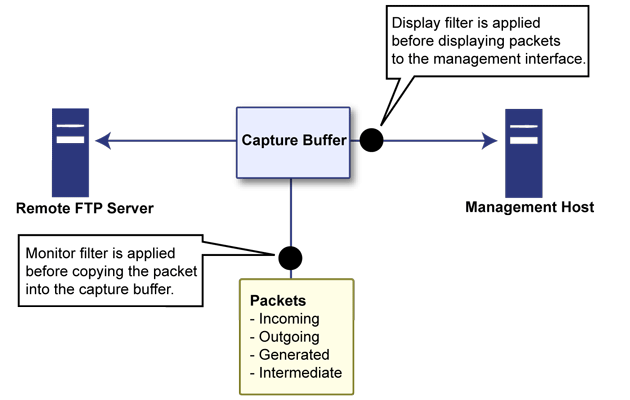
Figure 2. Packet monitor subsystem showing filters
Classification – Refers to identifying a selected set of packets to be mirrored. Incoming and outgoing packets to and from an interface are matched against a filter. If matched, the mirror action is applied.
Action – Refers to sending a copy of the selected packets to a port or a remote destination. Packets matching a classification filter are sent to one of the mirror destinations. A particular mirror destination is part of the action identifier.
Classification is performed on the Monitor Filter and Advanced Monitor Filter tab of the Packet Monitor Configuration window.
A local Sonicwall firewall can be configured to receive remotely mirrored traffic from a remote SonicWALL firewall. At the local firewall, received mirrored traffic can either be saved in the capture buffer or sent to another local interface. This is configured in the Remote Mirror Settings (Receiver) section on the Mirror tab of the Packet Monitor Configuration window.