|
•
|
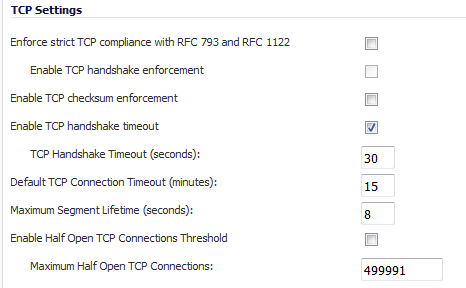
Enforce strict TCP compliance with RFC 793 and RFC 1122 – Ensures strict compliance with several TCP timeout rules. This setting maximizes TCP security, but it may cause problems with the Windows Scaling feature for Windows Vista users. This option is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Enable TCP handshake enforcement – Requires a successful three-way TCP handshake for all TCP connections. This option, available only if the Enforce strict TCP compliance with RFC 793 and RFC 1122, is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Enable TCP checksum enforcement – If an invalid TCP checksum is calculated, the packet is dropped. This option is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Enable TCP handshake timeout – Enforces the timeout period (in seconds) for a three-way TCP handshake to complete its connection. If the three-way TCP handshake does not complete in the timeout period, it is dropped. This option is selected by default.
|
|
•
|
TCP Handshake Timeout (seconds): The maximum time a TCP handshake has to complete the connection. The default is 30 seconds.
|
|
•
|
Default TCP Connection Timeout – The default time assigned to Access Rules for TCP traffic. If a TCP session is active for a period in excess of this setting, the TCP connection is cleared by the firewall. The default value is 15 minutes, the minimum value is 1 minute, and the maximum value is 999 minutes.
|
|
•
|
Maximum Segment Lifetime (seconds) – Determines the number of seconds that any TCP packet is valid before it expires. This setting is also used to determine the amount of time (calculated as twice the Maximum Segment Lifetime, or 2MSL) that an actively closed TCP connection remains in the TIME_WAIT state to ensure that the proper FIN / ACK exchange has occurred to cleanly close the TCP connection. The default value is 8 seconds, the minimum value is 1 second, and the maximum value is 60 seconds.
|
|
•
|
Enable Half Open TCP Connections Threshold – Denies new TCP connections if the high-water mark of TCP half-open connections has been reached. By default, the half-open TCP connection is not monitored, so this option is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Maximum Half Open TCP Connections – Specifies the maximum number of half-open TCP connections. The default maximum is half the number of maximum connection caches.
|
The following sections detail some SYN flood protection methods:
SonicOS provides several protections against SYN Floods generated from two different environments: trusted (internal) or untrusted (external) networks. Attacks from untrusted WAN networks usually occur on one or more servers protected by the firewall. Attacks from the trusted LAN networks occur as a result of a virus infection inside one or more of the trusted networks, generating attacks on one or more local or remote hosts.
|
•
|
SYN Proxy (Layer 3) – This mechanism shields servers inside the trusted network from WAN-based SYN flood attacks, using a SYN Proxy implementation to verify the WAN clients before forwarding their connection requests to the protected server. You can enable SYN Proxy only on WAN interfaces.
|
|
•
|
SYN Blacklisting (Layer 2) – This mechanism blocks specific devices from generating or forwarding SYN flood attacks. You can enable SYN Blacklisting on any interface.
|
The internal architecture of both SYN Flood protection mechanisms is based on a single list of Ethernet addresses that are the most active devices sending initial SYN packets to the firewall. This list is called a SYN watchlist. Because this list contains Ethernet addresses, the device tracks all SYN traffic based on the address of the device forwarding the SYN packet, without considering the IP source or destination address.
Each watchlist entry contains a value called a hit count. The hit count value increments when the device receives the an initial SYN packet from a corresponding device. The hit count decrements when the TCP three-way handshake completes. The hit count for any particular device generally equals the number of half-open connections pending since the last time the device reset the hit count. The device default for resetting a hit count is once a second.
Because the responder has to maintain state on all half-opened TCP connections, it is possible for memory depletion to occur if SYNs come in faster than they can be processed or cleared by the responder. A half-opened TCP connection did not transition to an established state through the completion of the three-way handshake. When the firewall is between the initiator and the responder, it effectively becomes the responder, brokering, or proxying, the TCP connection to the actual responder (private host) it is protecting.
|
1
|
Go to the Layer 3 SYN Flood Protection - SYN Proxy section of the Firewall Settings > Flood Protection page.
|
|
2
|
From the SYN Flood Protection Mode drop-down menu, select the type of protection mode:
|
|
•
|
Watch and Report Possible SYN Floods – Enables the device to monitor SYN traffic on all interfaces on the device and to log suspected SYN flood activity that exceeds a packet count threshold. The feature does not turn on the SYN Proxy on the device so the device forwards the TCP three-way handshake without modification.
|
|
•
|
Proxy WAN Client Connections When Attack is Suspected – Enables the device to enable the SYN Proxy feature on WAN interfaces when the number of incomplete connection attempts per second surpasses a specified threshold. This method ensures the device continues to process valid traffic during the attack and that performance does not degrade. Proxy mode remains enabled until all WAN SYN flood attacks stop occurring or until the device blacklists all of them using the SYN Blacklisting feature.
|
|
•
|
Always Proxy WAN Client Connections – Sets the device to always use SYN Proxy. This method blocks all spoofed SYN packets from passing through the device.
|
|
3
|
Select the SYN Attack Threshold configuration options to provide limits for SYN Flood activity before the device drops packets. The device gathers statistics on WAN TCP connections, keeping track of the maximum and average maximum and incomplete WAN connections per second. Out of these statistics, the device suggests a value for the SYN flood threshold.
|
|
•
|
Suggested value calculated from gathered statistics – The suggested attack threshold based on WAN TCP connection statistics.
|
|
•
|
Attack Threshold (Incomplete Connection Attempts/Second) – Enables you to set the threshold for the number of incomplete connection attempts per second before the device drops packets at any value between 5 and 200,000. The default is the Suggested value calculated from gathered statistics.
|
|
4
|
Select the SYN-Proxy options to provide more control over the options sent to WAN clients when in SYN Proxy mode.
|
|
NOTE: The options in this section are not available if Watch and report possible SYN floods is selected for SYN Flood Protection Mode.
|
|
•
|
All LAN/DMZ servers support the TCP SACK option – Enables SACK (Selective Acknowledgment) where a packet can be dropped and the receiving device indicates which packets it received. This option is not enabled by default. Enable this checkbox only when you know that all servers covered by the firewall accessed from the WAN support the SACK option.
|
|
•
|
Limit MSS sent to WAN clients (when connections are proxied) – Enables you to enter the maximum MSS (Minimum Segment Size) value. This sets the threshold for the size of TCP segments, preventing a segment that is too large to be sent to the targeted server. For example, if the server is an IPsec gateway, it may need to limit the MSS it received to provide space for IPsec headers when tunneling traffic. The firewall cannot predict the MSS value sent to the server when it responds to the SYN manufactured packet during the proxy sequence. Being able to control the size of a segment, enables you to control the manufactured MSS value sent to WAN clients. This option is not selected by default.
|
If you specify an override value for the default of 1460, a segment of that size or smaller is sent to the client in the SYN/ACK cookie. Setting this value too low can decrease performance when the SYN Proxy is always enabled. Setting this value too high can break connections if the server responds with a smaller MSS value.
|
•
|
Maximum TCP MSS sent to WAN clients. The value of the MSS. The default is 1460, the minimum value is 32, and the maximum is 1460.
|
|
•
|
Always log SYN packets received. Logs all SYN packets received.
|
|
•
|
Threshold for SYN/RST/FIN flood blacklisting (SYNs / Sec) – Specifies he maximum number of SYN, RST, FIN, and TCP packets allowed per second. The minimum is 10, the maximum is 800000, and default is 1,000. This value should be larger than the SYN Proxy threshold value because blacklisting attempts to thwart more vigorous local attacks or severe attacks from a WAN network.
|
|
NOTE: This option cannot be modified unless Enable SYN/RST/FIN/TCP flood blacklisting on all interfaces is enabled.
|
|
•
|
Enable SYN/RST/FIN/TCP flood blacklisting on all interfaces – Enables the blacklisting feature on all interfaces on the firewall. This option is not selected by default. When it is selected, these options become available:
|
|
•
|
Never blacklist WAN machines – Ensures that systems on the WAN are never added to the SYN Blacklist. This option is recommended as leaving it cleared may interrupt traffic to and from the firewall’s WAN ports. This option is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Always allow Dell SonicWALL management traffic – Causes IP traffic from a blacklisted device targeting the firewall’s WAN IP addresses to not be filtered. This allows management traffic and routing protocols to maintain connectivity through a blacklisted device. This option is not selected by default.
|
The WAN DDOS Protection (Non-TCP Floods) section is a deprecated feature that has been replaced by UDP Flood Protection and ICMP Flood Protection as described in UDP Tab and ICMP Tab , respectively.
|
IMPORTANT: Dell SonicWALL recommends that you do not use the WAN DDOS Protection feature, but that you use UDP Flood Protection and ICMP Flood Protection instead.
|
Table 72 describes the entries in the TCP Traffic Statistics table. To clear and restart the statistics displayed by a table, click the Clear Stats icon for the table.