|
•
|
The Anti-Spam service determines that an email fits only one of the following threats: Spam, Likely Spam, Phishing, Likely Phishing, Virus, or Likely Virus. It uses the following precedence order when evaluating threats in email messages:
|
•
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
If the Anti-Spam service determines that the message is not any of the above threats, it is judged as good email and is delivered to the destination server.
|
•
|
|
•
|
Destination Mail Server Public IP Address – The IP address to which external MTAs will be connecting by SMTP.
|
|
•
|
Destination Mail Server Private IP Address – The internal IP address of the Exchange or SMTP server (behind the firewall).
|
|
•
|
Zone Assignment – The zone to which the Exchange server is assigned.
|
|
•
|
Inbound Email Port – The TCP service port number to which emails will be sent, also known as the inbound SMTP port.
|
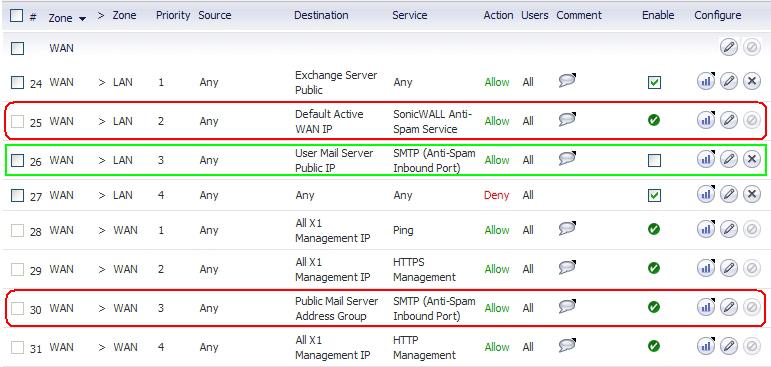
Figure 28. Generated access rules
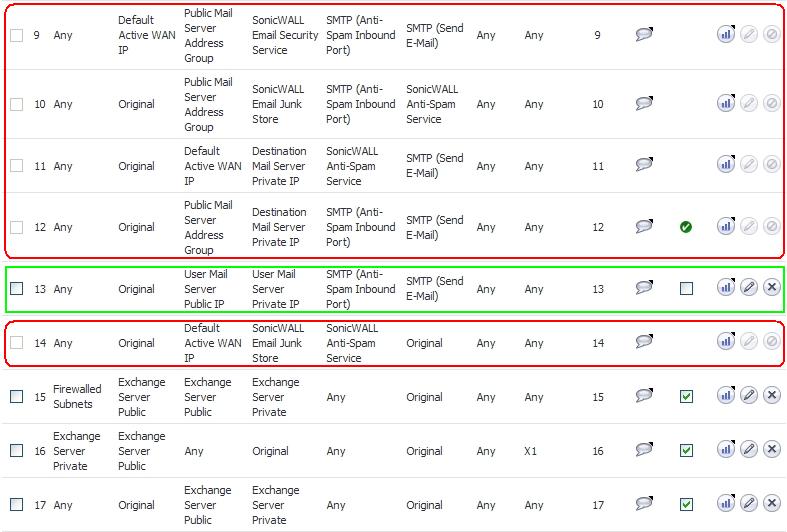
Figure 29. Generated anti-spam service object
Figure 30. Generated NAT policies
|
•
|
A system Address Group Object called the Public Mail Server Address Group is created as a default for the original destination for generated policies. This group contains the Address Object, Destination Mail Server Public IP, which takes the IP address value provided during the wizard.
|
|
•
|
If the existing policy’s original destination is a host type Address Object, then the generated policies use the Public Mail Server Address Group object as their original destination.
|
|
•
|
If there is more than one public IP address for SMTP, the administrator can manually add Address Objects to the Public Mail Server Address Group.
|
In the diag.html page, the Reset GRID Name Cache button can be used to clear all the entries in the GRID name cache.
The Delete Policies and Objects button can be used to remove Anti-Spam Address and Service Objects and policies that are not deleted when the service is turned off. When this button is clicked, SonicOS attempts to remove all the automatically generated objects and policies. This operation is only allowed when the Anti-Spam service is off.
|
•
|
Disable SYN Flood Protection for Anti-Spam related connections – SYN Flood protection by default is turned on for SMTP (25) and Anti-Spam service (10025) ports. This disables the protection.
|
|
•
|
Use GRID IP reputation check only – When selected, this overrides the probing result and simulates the Anti-Spam service being unavailable (admin down). When an email is sent, it still goes through both the SYN FLOOD check and GRID IP check, but other email scanning is not performed.
|