This section provides network administrators advanced firewall settings for configuring detection prevention, dynamic ports, source routed packets, connection selection, and access rule options. To configure advanced access rule options, select Firewall Settings > Advanced under Firewall.
The Firewall Settings > Advanced page includes the following firewall configuration option groups:
|
•
|
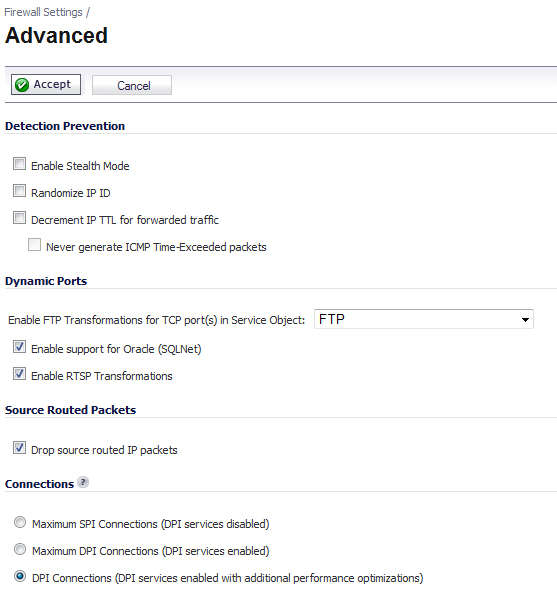
Enable Stealth Mode - By default, the security appliance responds to incoming connection requests as either “blocked” or “open.” If you enable Stealth Mode, your security appliance does not respond to blocked inbound connection requests. Stealth Mode makes your security appliance essentially invisible to hackers.
|
|
•
|
Randomize IP ID - Select Randomize IP ID to prevent hackers using various detection tools from detecting the presence of a security appliance. IP packets are given random IP IDs, which makes it more difficult for hackers to “fingerprint” the security appliance.
|
|
•
|
Decrement IP TTL for forwarded traffic - Time-to-live (TTL) is a value in an IP packet that tells a network router whether or not the packet has been in the network too long and should be discarded. Select this option to decrease the TTL value for packets that have been forwarded and therefore have already been in the network for some time.
|
|
•
|
Never generate ICMP Time-Exceeded packets - The firewall generates Time-Exceeded packets to report when it has dropped a packet because its TTL value has decreased to zero. Select this option if you do not want the firewall to generate these reporting packets.
|
|
•
|
Enable FTP Transformations for TCP port(s) in Service Object - Select from the service group drop-down menu to enable FTP transformations for a particular service object. By default, service group FTP (All) is selected.
|
FTP operates on TCP ports 20 and 21 where port 21 is the Control Port and 20 is Data Port. When using non-standard ports (for example, 2020, 2121), however, Dell SonicWALL drops the packets by default as it is not able to identify it as FTP traffic. The Enable FTP Transformations for TCP port(s) in Service Object option allows you to select a Service Object to specify a custom control port for FTP traffic.
|
a
|
On the Network > Address Objects page, create an Address Object for the private IP address of the FTP server with the following values:
|
|
•
|
Name: FTP Server Private
|
|
•
|
Zone: LAN
|
|
•
|
Type: Host
|
|
•
|
IP Address: 192.168.168.2
|
|
b
|
On the Network > Services page, create a custom Service for the FTP Server with the following values:
|
|
•
|
Name: FTP Custom Port Control
|
|
•
|
Protocol: TCP(6)
|
|
•
|
Port Range: 2121 - 2121
|
|
c
|
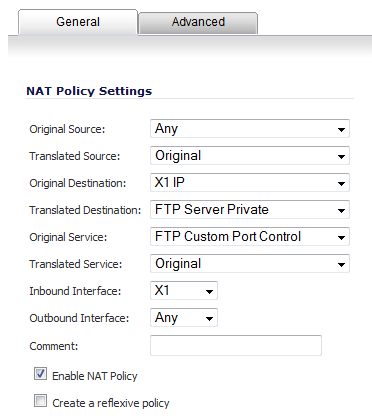
On the Network > NAT Policies page, create the following NAT Policy:
|
|
d
|
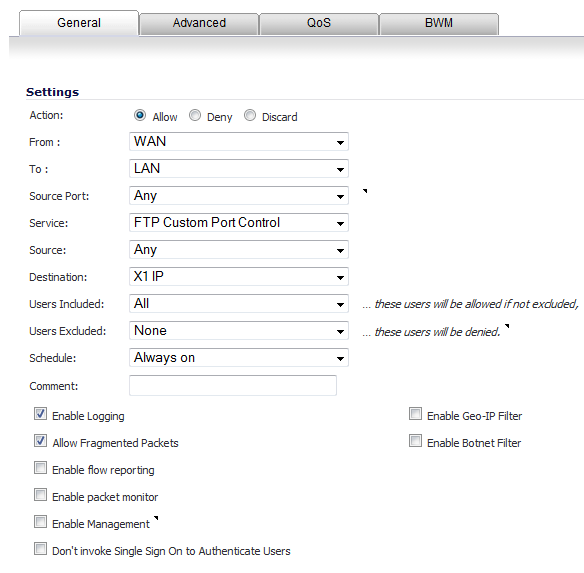
On the Firewall > Access Rules page, create the following Access Rule:
|
|
e
|
Lastly, on the Firewall Settings > Advanced page, from the Enable FTP Transformations for TCP port(s) in Service Object drop-down menu, select the FTP Custom Port Control Service Object.
|
|
•
|
Enable support for Oracle (SQLNet) - Select this option if you have Oracle9i or earlier applications on your network. For Oracle10g or later applications, it is recommended that this option not be selected.
|
|
•
|
Enable RTSP Transformations - Select this option to support on-demand delivery of real-time data, such as audio and video. RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) is an application-level protocol for control over delivery of data with real-time properties.
|