|
2
|
|
3
|
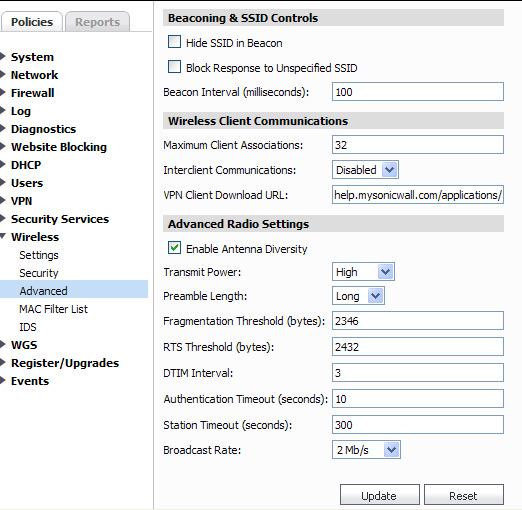
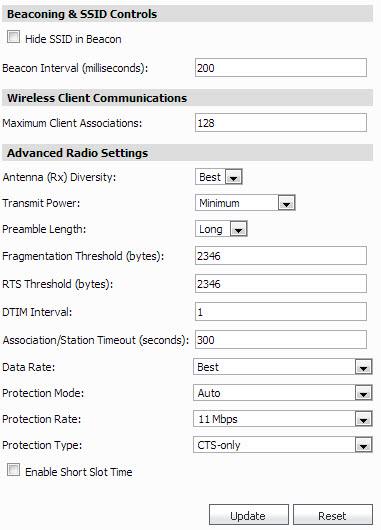
Select Hide SSID in Beacon. If you select Hide SSID in Beacon, your wireless network is invisible to anyone who does not know your SSID. This is a good way to prevent “drive by hackers” from seeing your wireless connection.
|
|
4
|
Enter how often (in milliseconds) a beacon will be sent in the Beacon Interval field. Decreasing the interval time makes passive scanning more reliable and faster because Beacon frames announce the network to the wireless connection more frequently.
|
|
5
|
To specify the maximum number of wireless clients, enter the limit in the Maximum Client Associations field. Wireless clients are devices that attempt to access the wireless SonicWALL appliance.
|
|
•
|
The Antenna Diversity setting determines which antenna the SonicWALL Wireless uses to send and receive data. You can select:
|
|
•
|
Best: This is the default setting. When Best is selected, the SonicWALL Wireless automatically selects the antenna with the strongest, clearest signal. In most cases, Best is the optimal setting.
|
|
•
|
1: Select 1 to restrict the SonicWALL Wireless to use antenna 1 only. Facing the rear of the SonicWALL, antenna 1 is on the left, closest to the console port. You can disconnect antenna 2 when using only antenna 1.
|
|
•
|
2: Select 2 to restrict the SonicWALL Wireless to use antenna 2 only. Facing the rear of the SonicWALL, antenna 2 is on the right, closest to the power supply. You can disconnect antenna 1 when using only antenna 2.
|
|
•
|
Select High from the Transmit Power menu to send the strongest signal on the WLAN. For example, select High if the signal is going from building to building. Medium is recommended for office to office within a building, and Low or Lowest is recommended for shorter distance communications.
|
|
•
|
Select Short or Long from the Preamble Length menu. Short is recommended for efficiency and improved throughput on the wireless network.
|
|
•
|
The Fragmentation Threshold (bytes) is 2346 by default. Increasing the value means that frames are delivered with less overhead but a lost or damaged frame must be discarded and retransmitted.
|
|
•
|
The RTS Threshold (bytes) is 2432 by default. If network throughput is slow or a large number of frame retransmissions is occurring, decrease the RTS threshold to enable RTS clearing.
|
|
•
|
The default value for the DTIM Interval is three. Increasing the DTIM Interval value allows you to conserve power more effectively.
|
|
•
|
The Station Timeout (seconds) is 300 seconds by default. If your network is very busy, you can increase the timeout by increasing the number of seconds in this field.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, select the wireless transmission rate from the Data Rate pull-down list. You can select Best or a value between 1 and 54 megabits per second (Mbps). The default is 48Mbps.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, in the Protection Mode pull-down list, select None, Always or Auto. Use Always or Auto to prevent transmission frame collisions when you have multiple wireless nodes.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, in the Protection Rate pull-down list, select 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 5Mbps or 11Mbps. The Protection Rate specifies the transmission rate for the Request-To-Send (RTS) and Clear-To-Send (CTS) frames. The default is 5Mbps.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, in the Protection Type pull-down list, select RTS-CTS or CTS-only. RTS-CTS is the mechanism used by the 802.11 wireless networking protocol to reduce frame collisions. The node wishing to transmit data sends an RTS frame. The destination node replies with a CTS frame. Other wireless nodes within range refrain from sending data for a specified time to avoid collisions. The default is RTS-CTS.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, in the CCK OFDM Power Delta pull-down list, select 0dBm, 1dBm or 2dBm. Complementary Code Keying (CCK) and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) are digital modulation techniques used in wireless networks using the 802.11 specifications. This field specifies the change in power used in the modulation, expressed in decibels per milliwatt (dBm). Zero dBm equals one milliwatt. Two dBm is less than two milliwatts.
|
|
•
|
For SonicOS Standard 3.8 and above, select Enable Short Slot Time to minimize the time to wait before transmitting. Slot time is the time required for a transmission to reach the destination. The default is to enable a short slot time.
|
|
7
|
When you are finished, click Update. The settings are changed for the selected SonicWALL appliance. To clear all screen settings and start over, click Reset.
|