|
1
|
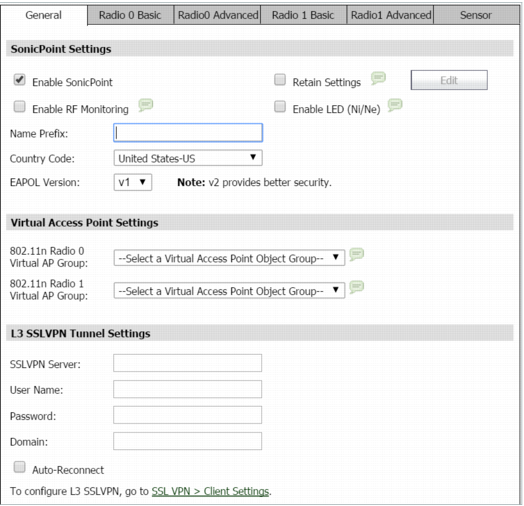
Navigate to SonicPoint > SonicPoints page.
|
|
2
|
To add a new SonicPoint AC profile, click Add a new SonicPoint ACe/ACi/N2 Profile.
or To edit an existing AC profile, click the Configure icon on the same row as the profile you want to edit. |
The Add/Edit SonicPoint Profile dialog appears.
The Add/Edit SonicPoint Profile General tab.
In the General tab, configure the desired settings:
|
1
|
Select Enable SonicPoint to enable each SonicPoint AC automatically when it is provisioned with this profile. This option is selected by default.
|
|
2
|
Optionally, select Retain Settings to have the SonicPoint ACs provisioned by this profile retain customized settings until system restart or reboot. This option is not selected by default.
|
If you select this option, Edit becomes active and the Retain Settings window displays. To specify the settings to retain:
|
a
|
If you are editing an existing SonicPoint AC profile, click Edit. The Retain Settings window displays.
|
|
•
|
Click Retain All Settings; all the other options become dimmed.
|
|
c
|
Click OK.
|
|
3
|
Optionally, select Enable RF Monitoring to enable wireless RF Threat Real Time Monitoring and Management. This option is not selected by default.
|
|
4
|
Enter a prefix for the names of all SonicPoint ACs connected to this zone in the Name Prefix field. This prefix assists in identifying SonicPoint AC on a zone. When each SonicPoint AC is provisioned, it is given a name that consists of the name prefix and a unique number, for example: SonicPoint AC 126008.
|
|
5
|
Select the country where you are operating the SonicPoint ACs from the Country Code drop-down menu. The country code determines which regulatory domain the radio operation falls under.
|
|
6
|
From the EAPOL Version drop-down menu, select the version of EAPoL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) to use: v1 or v2. The default is v1, but v2 provides better security.
|
|
1
|
Optionally, select an 802.11n Virtual Access Point (VAP) group to assign these SonicPoint ACs to a VAP from the Radio 0 Basic Virtual AP Group and Radio 1 Basic Virtual AP Group drop-down menus. The drop-down menus allow you to create a new VAP group. For more information on VAPs, see Using and Configuring Virtual Access Points .
|
|
1
|
In the SSL VPN Server field, enter the IP address of the SSL VPN server.
|
|
2
|
In the User Name field, enter the User Name of the SSL VPN server.
|
|
3
|
In the Password field, enter the Password for the SSL VPN server.
|
|
4
|
In the Domain field, enter the domain that the SSL VPN server is located in.
|
|
5
|
Click Auto-Reconnect for the SonicPoint to auto-reconnect to the SSL VPN server.
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
Select Enable Radio to automatically enable the 802.11ac radio bands on all SonicPoint ACs provisioned with this profile. This option is selected by default.
|
|
•
|
From the Enable Radio drop-down menu, select a schedule for when the 802.11n radio is on or create a new schedule; default is Always on. You can create a new schedule by selecting Create new schedule.
|
|
2
|
Select your preferred radio mode from the Mode drop-down menu. The wireless security appliance supports the following modes:
|
|
3
|
Optionally, select Enable DFS Channels to enable the use of Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) that allows wireless devices to share the same spectrum with existing radar systems within the 5GHz band.
|
|
4
|
In the SSID field, enter a recognizable string for the SSID of each SonicPoint AC using this profile. This is the name that appears in clients’ lists of available wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
Auto - Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. This is the default setting. Use Auto unless you have a specific reason to use or avoid specific channels.
|
|
7
|
For (802.11n only): from the Radio Band drop-down menu, select the band for the 802.11n radio:
|
|
•
|
Auto - Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. Both the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel are set to Auto also. This is the default setting.
|
|
•
|
Standard - 20MHz Channel—Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the standard 20MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Standard Channel drop-down menu is displayed instead of the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel options.
|
|
•
|
Standard Channel—This drop-down menu only displays when the 20MHz channel is selected. By default, this is set to Auto, which allows the appliance to set the optimal channel based on signal strength and integrity.
|
|
•
|
Wide - 40MHz Channel—Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the wide 40MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel drop-down menus are active:
|
|
•
|
Primary Channel—By default this is set to Auto. Optionally, you can specify a specific primary channel. The available channels are the same as for 802.11a in <Blue XRef>5.
|
|
•
|
Secondary Channel—Is set to Auto regardless of the setting of Primary Channel.
|
|
8
|
Enable Short Guard Interval—Specifies the short guard interval of 400ns (as opposed to the standard guard interval of 800ns).
|
|
9
|
Select Enable Aggregation to enable 802.11n frame aggregation that combines multiple data frames in a single transmission to reduce overhead and increase throughput.
|
|
10
|
The Enable MIMO option enables/disables MIMO (multiple-input multiple output). Enabling this option increases 802.11n throughput by using multiple-input/multiple-output antennas. This option is enabled by default for all 802.11n modes and is dimmed to ensure it is not disabled. The option is activated and selected by default if 5GHz 802.11a Only or 2.4GHz 802.11g Only mode is selected.
|
|
NOTE: If a VAP was selected in the 802.11n Radio Virtual AP Group drop-down menu on the Settings tab, this section is not available. Instead, the Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings section is displayed. Go to Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings .
|
The Wireless Security sections of both Radio 0 Basic and Radio 1 Basic tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the Wireless Security settings, see Wireless Security .
|
NOTE: This section displays only if a VAP was selected from the Radio 0 Basic/1 Virtual AP Group drop-down menus in the Virtual Access Point Settings section of the General tab.
|
The Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings section of both Radio 0 Basic and Radio 1 Basic tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings settings, see Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings .
The ACL Enforcement section of both Radio 0 Basic and Radio 1 Basic tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the ACL Enforcement settings, see ACL Enforcement .
|
1
|
The options on the Radio 0 Advanced and Radio 1 Advanced tabs are the same except that Radio 0 Advanced has the Fragmentation Threshold (bytes) field.
|
1
|
Select Hide SSID in Beacon to have the SSID send null SSID beacons in place of advertising the wireless SSID name. Sending null SSID beacons forces wireless clients to know the SSID before connecting. By default, this option is unchecked.
|
|
2
|
From the Schedule IDS Scan drop-down menu, select a schedule for the IDS (Intrusion Detection Service) scan. Select a time when there are fewer demands on the wireless network to minimize the inconvenience of dropped wireless connections. You can create your own schedule by selecting Create new schedule or disable the feature by selecting Disabled, the default.
|
|
3
|
From the Data Rate drop-down menu, select the speed at which the data is transmitted and received. Best (default) automatically selects the best rate available in your area given interference and other factors. Or you can manually select a data rate, from a minimum of 1 Mbps to a maximum of 54 Mbps.
|
|
4
|
From the Transmit Power drop-down menu, select the transmission power. Transmission power effects the range of the SonicPoint.
|
|
•
|
Full Power (default)
|
|
•
|
|
5
|
From the Antenna Diversity drop-down menu, select the method that determines which antenna the SonicPoint uses to send and receive data.
|
|
•
|
Best: This is the default setting. When Best is selected, the SonicPoint automatically selects the antenna with the strongest, clearest signal. In most cases, Best is the optimal setting.
|
|
•
|
1: Select 1 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 1 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 1 is on the left, closest to the power supply.
|
|
•
|
2: Select 2 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 2 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 2 is on the right, closest to the console port.
|
|
6
|
In the Beacon Interval (milliseconds) field, enter the number of milliseconds between sending wireless SSID beacons. The minimum interval is 100 milliseconds, the maximum is 1000 milliseconds, and the default is 100 milliseconds.
|
|
7
|
In the DTIM Interval field, enter the DTIM interval in milliseconds. The minimum number of frames is 1, the maximum is 255, and the default is 1.
|
|
8
|
In the Fragmentation Threshold (bytes) field, enter the number of bytes of fragmented data you want the network to allow. Fragment wireless frames to increase reliability and throughput in areas with RF interference or poor wireless coverage. Lower threshold numbers produce more fragments. The minimum threshold is 256 bytes, the maximum is 2346 bytes, and the default is 2346 bytes.
|
|
9
|
In the RTS Threshold (bytes) field, enter the threshold for a packet size, in bytes, at which a request to send (RTS) is sent before packet transmission. Sending an RTS ensures that wireless collisions do not take place in situations where clients are in range of the same access point, but might not be in range of each other. The minimum threshold is 256 bytes, the maximum is 2346 bytes, and the default is 2346 byes.
|
|
10
|
In the Maximum Client Associations field, enter the maximum number of clients you want each SonicPoint using this profile to support on this radio at one time. The minimum number of clients is 1, the maximum number is 128, and the default number is 32.
|
|
11
|
In the Station Inactivity Timeout (seconds) field, enter the maximum length of wireless client inactivity before Access Points age out the wireless client, in seconds. The minimum period is 60 seconds, the maximum is 36000 seconds, and the default is 300 seconds.
|
|
12
|
From the WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) drop-down menu, select whether a WMM profile is to be associated with this profile:
|
|
•
|
Disabled (default)
|
|
•
|
Create new WMM profile. If you select Create new WMM profile, the Add Wlan WMM Profile window displays.
|
|
13
|
Select Enable Short Slot Time to allow clients to disassociate and reassociate more quickly. Specifying this option increases throughput on the 802.11n/g wireless band by shortening the time an access point waits before relaying packets to the LAN. By default, this option is not selected.
|
|
14
|
Select Does not allow Only 802.11b Clients to Connect if you are using Turbo G mode and, therefore, are not allowing 802.11b clients to connect. Specifying this option limits wireless connections to 802.11g clients only. By default, this option is not selected.
|
|
15
|
Select Enable Green AP to allow the SonicPoint ACe/ACi/N2 radio to go into sleep mode. This saves power when no clients are actively connected to the SonicPoint. The SonicPoint immediately goes into full power mode when any client attempts to connect to it. Green AP can be set on each radio independently, Radio 0 (5GHz) and Radio 1 (2.4GHz).
|
|
16
|
In the Green AP Timeout(s) field, enter the timeout value in seconds that the access point waits while it has no active connections before it goes into sleep mode. The timeout values can range from 10 seconds to 600 seconds. The default value is 20 seconds.
|
In the Sensor tab, enable or disable Wireless Intrusion Detection and Prevention (WIDP) mode.
|
1
|
Navigate to the SonicPoint > SonicPoints page.
|
|
2
|
To add a new SonicPoint NDR profile, click Add a new SonicPoint NDR Profile in the SonicPoint N Provisioning Profiles table.
or To edit an existing NDR profile, select the profile and click Configure in the same line as the profile you want to edit. |
The Add/Edit SonicPoint NDR Profile window displays.
In the General tab, configure the desired settings:
|
1
|
Check Enable SonicPoint this to automatically enable each SonicPoint NDR when it is provisioned with this profile. This option is selected by default.
|
|
2
|
Optionally, check Retain Settings to have the SonicPoint NDRs provisioned by this profile retain customized settings until system restart or reboot. This option is not selected by default.
|
If you select this option, Edit becomes active and the Retain Settings window displays. To specify the settings to retain:
|
a
|
If you are editing an existing SonicPoint NDR profile, click Edit. The Retain Settings window displays:
|
|
•
|
Click Retain All Settings; all the other options become dimmed.
|
|
c
|
Click OK.
|
|
3
|
Optionally, check Enable RF Monitoring to enable wireless RF Threat Real Time Monitoring and Management. This option is not selected by default.
|
|
•
|
Enter a prefix for the names of all SonicPoint NDRs connected to this zone in the Name Prefix field. This prefix assists in identifying a SonicPoint NDR on a zone. When each SonicPoint NDR is provisioned, it is given a name that consists of the name prefix and a unique number, for example: SonicPoint NDR 126008.
|
|
•
|
Select the country where you are operating the SonicPoint NDRs from the Country Code drop-down menu. The country code determines which regulatory domain the radio operation falls under.
|
|
4
|
From the EAPOL Version drop-down menu, select the version of EAPoL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) to use: v1 or v2. The default is v1, but v2 provides better security.
|
|
1
|
Optionally, select an 802.11n Virtual Access Point (VAP) group to assign these SonicPoint NDRs to a VAP from the 802.11n Radio 0 Virtual AP Group and 802.11n Radio 1 Virtual AP Group drop-down menus. The drop-down menus allow you to create a new VAP group. For more information on VAPs, see Using and Configuring Virtual Access Points .
|
|
•
|
In the SSL VPN Server field, enter the IP address of the SSL VPN server.
|
|
•
|
In the User Name field, enter the User Name of the SSL VPN server.
|
|
•
|
In the Password field, enter the Password for the SSL VPN server.
|
|
•
|
In the Domain field, enter the domain that the SSL VPN server is located in.
|
|
•
|
Click Auto-Reconnect for the SonicPoint to auto-reconnect to the SSL VPN server.
|
|
NOTE: The sections and options displayed on the 802.11n Radio 0/1 tabs change depending on whether you selected a VAP group in the 802.11n Radio 0/1 Virtual AP Group drop-down menus on the General tab and the mode you select in the Mode drop-down menu. These choices apply only to the radio for which they were selected.
|
|
1
|
Click the Radio 0/1 Basic tab
|
|
1
|
Check Enable Radio to automatically enable the 802.11n radio bands on all SonicPoint NDRs provisioned with this profile.
|
|
•
|
From the Enable Radio drop-down menu, select a schedule for when the 802.11n radio is on or create a new schedule; default is Always on. You can create a new schedule by selecting Create new schedule.
|
|
2
|
Select your preferred radio mode from the Mode drop-down menu. The wireless security appliance supports the following modes:
|
|
3
|
Optionally, select Enable DFS Channels to enable the use of Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) that allows wireless devices to share the same spectrum with existing radar systems within the 5GHz band.
|
|
•
|
In the SSID field, enter a recognizable string for the SSID of each SonicPoint NDR using this profile. This is the name that appears in clients’ lists of available wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
Auto - Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. This is the default setting. Use Auto unless you have a specific reason to use or avoid specific channels.
|
|
•
|
Specific channel – You can select a single channel within the range of your regulatory domain. Selecting a specific channel also can help with avoiding interference with other wireless networks in the area.
|
|
•
|
For (802.11n only): from the Radio Band drop-down menu, select the band for the 802.11n radio:
|
|
•
|
Auto—Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. Both the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel are set to Auto also. This is the default setting.
|
|
•
|
Standard - 20MHz Channel—Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the standard 20MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Standard Channel drop-down menu is displayed instead of the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel options.
|
|
•
|
Standard Channel—This drop-down menu only displays when the 20MHz channel is selected. By default, this is set to Auto, which allows the appliance to set the optimal channel based on signal strength and integrity.
|
|
•
|
Wide - 40MHz Channel—Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the wide 40MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel drop-down menus are active:
|
|
•
|
Primary Channel—By default this is set to Auto. Optionally, you can specify a specific primary channel. The available channels are the same as for 802.11a in <Blue XRef>4.
|
|
•
|
Secondary Channel—Is set to Auto regardless of the setting of Primary Channel.:
|
|
6
|
Enable Short Guard Interval—Specifies the short guard interval of 400ns (as opposed to the standard guard interval of 800ns).
|
|
•
|
Select Enable Aggregation to enable 802.11n frame aggregation that combines multiple data frames in a single transmission to reduce overhead and increase throughput.
|
|
7
|
The Enable MIMO option enables/disables MIMO (multiple-input multiple output). Enabling this option increases 802.11n throughput by using multiple-input/multiple-output antennas. This option is enabled by default for all 802.11n modes and is dimmed to ensure it is not disabled. The option is activated and selected by default if 5GHz 802.11a Only or 2.4GHz 802.11g Only mode is selected.
|
The Wireless Security sections of both 802.11n Radio 0 and 802.11n Radio 1 tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the Wireless Security settings, see Wireless Security .
The Enable Remote MAC Access Control option has also been added to the Add/Edit Virtual Access Point dialog and the Add/Edit Virtual Access Point Profile dialog, under the Remote MAC Address Access Control Settings panel, accessed from the SonicPoint > Virtual Access Point page.
This section displays only if a VAP was selected from the Radio 0 Basic/1 Virtual AP Group drop-down menus in the Virtual Access Point Settings section of the General tab.
The Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings section of both Radio 0 Basic and Radio 1 Basic tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings settings, see Virtual Access Point Encryption Settings .
The ACL Enforcement section of both Radio 0 Basic and Radio 1 Basic tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab. For how to configure the ACL Enforcement settings, see ACL Enforcement .
Enable Remote MAC Access Control has been added to the Add SonicPoint N Profile window and the Add SonicPoint NDR Profile window, accessed from the SonicPoint > SonicPoints page. For information about selecting this option, see 802.11n Radio 0 and 802.11n Radio 1 Tabs .
If a VAP was selected in the 802.11n Radio Virtual AP Group drop-down menu on the Settings tab, this section is not available. Go to Radio 0 Advanced and Radio 1 Advanced Tabs
The Remote MAC Address Access Control Settings section of both 802.11n Radio 0 and 802.11n Radio 1 tabs are the same as for the SonicPoint N 802.11n Radio tab.
In the 802.11n Advanced tab, configure the performance settings for the 802.11n radio. For most 802.11n advanced options, the default settings give optimum performance.
|
•
|
Hide SSID in Beacon: Check this option to have the SSID broadcast as part of the wireless beacon, rather than as a separate broadcast.
|
|
•
|
Schedule IDS Scan: Select a time when there are fewer demands on the wireless network to schedule an Intrusion Detection Service (IDS) scan to minimize the inconvenience of dropped wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
Data Rate: Select the speed at which the data is transmitted and received. Best automatically selects the best rate available in your area given interference and other factors. Or you can manually select a data rate.
|
|
•
|
Transmit Power: Select the transmission power. Transmission power effects the range of the SonicPoint. You can select: Full Power, Half (-3 dB), Quarter (-6 dB), Eighth (-9 dB), or Minimum.
|
|
•
|
Antenna Diversity: The Antenna Diversity setting determines which antenna the SonicPoint uses to send and receive data. You can select:
|
|
•
|
Best: This is the default setting. When Best is selected, the SonicPoint automatically selects the antenna with the strongest, clearest signal. In most cases, Best is the optimal setting.
|
|
•
|
1: Select 1 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 1 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 1 is on the left, closest to the power supply.
|
|
•
|
2: Select 2 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 2 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 2 is on the right, closest to the console port.
|
|
•
|
Beacon Interval (milliseconds): Enter the number of milliseconds between sending out wireless beacons. The minimum interval is 100 milliseconds, the maximum is 1000 milliseconds, and the default is 100 milliseconds.
|
|
•
|
DTIM Interval: Enter to alert 802.11 power-save-mode clients of incoming multicast packets. The Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) interval specifies the number of beacon frames to wait before sending a DTIM. The minimum is 1 frame, the maximum is 255 frames, and the default is 1 frame.
|
|
•
|
Fragmentation Threshold (bytes): Enter the number of bytes of fragmented data, in bytes, you want the network to allow. Fragmented wireless frames increase the reliability and throughput in areas with RF interference or poor wireless coverage. Lower threshold numbers produce more fragments. The minimum number is 256 bytes, the maximum is 2346 bytes, and the default is 2346 bytes.
|
|
•
|
RTS Threshold (bytes): Enter the threshold, in bytes, for a packet size at which a request to send (RTS) is sent before packet transmission. Sending an RTS ensures that wireless collisions do not take place in situations where clients are in range of the same access point, but might not be in range of each other. The minimum is 256 bytes, the maximum is 2346 bytes, and the default is 2346 bytes.
|
|
•
|
Maximum Client Associations: Enter the maximum number of clients you want the SonicPoint to support on this radio at one time. The minimum number is 1, the maximum number is 128, and the default number is 32.
|
|
•
|
Station Inactivity Timeout (seconds)—The number of seconds the station can be inactive before it times out. The minimum time is 60 seconds, the maximum time is 36000 seconds, and the default time is 300 seconds.
|
|
•
|
Preamble Length: Select the length of the preamble--the initial wireless communication send when associating with a wireless host. You can select Long or Short.
|
|
•
|
WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)—Select whether a WMM profile is to be associated with this profile: Disabled (default) or Create new WMM profile. If you select Create new WMM profile, the Add Wlan WMM Profile window displays.
|
These settings affect the operation of the Radio 1 Basic radio bands. The SonicPoint has two separate radios built in. Therefore, it can send and receive on both bands at the same time. The Radio 0 Advanced and Radio 1 Advanced tabs are quite similar; the difference is that the Radio 1 Advanced tab has more options.
In the Sensor tab, you enable or disable Wireless Intrusion Detection and Prevention (WIDP) mode.
|
1
|
Select Enable WIDF sensor to have the SonicPoint NDR operate as a dedicated WIDP sensor.
|
|
1
|
To add a new profile click Add SonicPointN below the list of SonicPoint 802.11n provisioning profiles. To edit an existing profile, select the profile and click the Configure icon in the same line as the profile you are editing.
|
|
2
|
In the General tab of the Add Profile window, specify:
|
|
•
|
Enable SonicPoint: Check this to automatically enable each SonicPoint when it is provisioned with this profile.
|
|
•
|
Retain Settings: Check this to have the SonicPointNs provisioned by this profile retain these settings after they are deleted and re-synchronized. Click Edit to specify the categories of settings that will be retained.
|
|
•
|
Name Prefix: Enter a prefix for the names of all SonicPointNs connected to this zone. When each SonicPointN is provisioned it is given a name that consists of the name prefix and a unique number, for example: “SonicPoint 126008.”
|
|
•
|
Country Code: Select the country where you are operating the SonicPointNs. The country code determines which regulatory domain the radio operation falls under.
|
|
•
|
802.11n Virtual AP Group: (optional; on SonicWALL NSA only) Select a Virtual Access Point (VAP) group to assign these SonicPointNs to a VAP. This pull-down menu allows you to create a new VAP group. For more information on VAPs, refer to Using and Configuring Virtual Access Points .
|
|
3
|
In the 802.11n tab, configure the radio settings for the 802.11n radio:
|
|
•
|
Enable Radio: Check this to automatically enable the 802.11n radio bands on all SonicPoints provisioned with this profile.
|
|
•
|
Radio Mode: Select your preferred radio mode from the Radio Mode menu. The wireless security appliance supports the following modes:
|
|
•
|
2.4GHz 802.11n Only - Allows only 802.11n clients access to your wireless network. 802.11a/b/g clients are unable to connect under this restricted radio mode.
|
|
•
|
2.4GHz 802.11n/g/b Mixed - Supports 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n clients simultaneously. If your wireless network comprises multiple types of clients, select this mode.
|
|
•
|
2.4GHz 802.11g Only - If your wireless network consists only of 802.11g clients, you might select this mode for increased 802.11g performance. You might also select this mode if you wish to prevent 802.11b clients from associating.
|
|
•
|
5GHz 802.11n Only - Allows only 802.11n clients access to your wireless network. 802.11a/b/g clients are unable to connect under this restricted radio mode.
|
|
•
|
5GHz 802.11n/a Mixed - Supports 802.11n and 802.11a clients simultaneously. If your wireless network comprises both types of clients, select this mode.
|
|
•
|
5GHz 802.11a Only - Select this mode if only 802.11a clients access your wireless network.
|
|
•
|
SSID: Enter a recognizable string for the SSID of each SonicPoint using this profile. This is the name that appears in clients’ lists of available wireless connections.
|
Radio Band (802.11n only): Sets the band for the 802.11n radio:
|
•
|
Auto - Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. This is the default setting.
|
|
•
|
Standard - 20MHz Channel - Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the standard 20MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Standard Channel pull-down menu is displayed.
|
|
•
|
Standard Channel - This pull-down menu only displays when the 20MHz channel is selected. By default, this is set to Auto, which allows the appliance to set the optimal channel based on signal strength and integrity. Optionally, you can select a single channel within the range of your regulatory domain. Selecting a specific a channel can also help with avoiding interference with other wireless networks in the area.
|
|
•
|
Wide - 40MHz Channel - Specifies that the 802.11n radio uses only the wide 40MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Primary Channel and Secondary Channel pull-down menus are displayed:
|
|
•
|
Primary Channel - By default this is set to Auto. Optionally, you can specify a specific primary channel.
|
|
•
|
Secondary Channel - The configuration of this pull-down menu is controlled by your selection for the primary channel:
|
Enable Short Guard Interval: Specifies the short guard interval of 400ns (as opposed to the standard guard interval of 800ns). The guard interval is a pause in transmission intended to avoid data loss from interference or multipath delays.
Enable Aggregation: Enables 802.11n frame aggregation, which combines multiple frames to reduce overhead and increase throughput.
|
TIP: The Enable Short Guard Interval and Enable aggregation options can slightly improve throughput. They both function best in optimum network conditions where users have strong signals with little interference. In networks that experience less than optimum conditions (interference, weak signals, and so on), these options might introduce transmission errors that eliminate any efficiency gains in throughput.
|
ACL Enforcement: Select this to enforce Access Control by allowing or denying traffic from specific devices. Select a MAC address group from the Allow List to automatically allow traffic from all devices with MAC address in the group. Select a MAC address group from the Deny List to automatically deny traffic from all devices with MAC address in the group. The deny list is enforced before the Allow list.
|
4
|
|
•
|
Authentication Type: Select the method of authentication for your wireless network. You can select WEP - Both (Open System & Shared Key), WEP - Open System, WEP - Shared Key, WPA - PSK, WPA - EAP, WPA2-PSK, WPA2-EAP, WPA2-AUTO-PSK, and WPA2-AUTO-EAP.
|
|
•
|
WEP Key Mode: Select the size of the encryption key.
|
|
•
|
Default Key: Select which key in the list below is the default key that is tried first when trying to authenticate a user.
|
|
•
|
Key Entry: Select whether the key is alphanumeric or hexadecimal.
|
|
•
|
Key 1 - Key 4: Enter the encryptions keys for WEP encryption. Enter the most likely to be used in the field you selected as the default key.
|
|
•
|
Cipher Type: The cipher that encrypts your wireless data. Choose either TKIP (older, more compatible), AES (newer, more secure), or Both (backward compatible).
|
|
•
|
Group Key Interval: The time period for which a Group Key is valid. The default value is 86400 seconds. Setting to low of a value can cause connection issues.
|
|
•
|
Passphrase (PSK only): This is the passphrase your network users must enter to gain network access.
|
|
•
|
RADIUS Server Settings (EAP Only): Configure settings for your RADIUS authentication server.
|
|
5
|
In the Advanced tab, configure the performance settings for the 802.11n radio. For most 802.11n advanced options, the default settings give optimum performance.
|
|
•
|
Hide SSID in Beacon: Check this option to have the SSID broadcast as part of the wireless beacon, rather than as a separate broadcast.
|
|
•
|
Schedule IDS Scan: Select a time when there are fewer demands on the wireless network to schedule an Intrusion Detection Service (IDS) scan to minimize the inconvenience of dropped wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
Data Rate: Select the speed at which the data is transmitted and received. Best automatically selects the best rate available in your area given interference and other factors. Or you can manually select a data rate.
|
|
•
|
Transmit Power: Select the transmission power. Transmission power effects the range of the SonicPoint. You can select: Full Power, Half (-3 dB), Quarter (-6 dB), Eighth (-9 dB), or Minimum.
|
|
•
|
Antenna Diversity: The Antenna Diversity setting determines which antenna the SonicPoint uses to send and receive data. When Best is selected, the SonicPoint automatically selects the antenna with the strongest, clearest signal.
|
|
•
|
Beacon Interval (milliseconds): Enter the number of milliseconds between sending out a wireless beacon.
|
|
•
|
DTIM Interval: Enter the interval in milliseconds.
|
|
•
|
Fragmentation Threshold (bytes): Enter the number of bytes of fragmented data you want the network to allow.
|
|
•
|
RTS Threshold (bytes): Enter the number of bytes.
|
|
•
|
Maximum Client Associations: Enter the maximum number of clients you want the SonicPoint to support on this radio at one time.
|
|
•
|
Preamble Length: Select the length of the preamble--the initial wireless communication send when associating with a wireless host. You can select Long or Short.
|
|
•
|
Protection Mode: Select the CTS or RTS protection. Select None, Always, or Auto. None is the default.
|
|
•
|
Protection Rate: Select the speed for the CTS or RTS protection, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5 Mbps, or 11 Mbps.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
Enable Short Slot Time: Allow clients to disassociate and reassociate more quickly.
|
|
•
|
Allow Only 802.11g Clients to Connect: Use this if you are using Turbo G mode and therefore are not allowing 802.11b clients to connect.
|
|
1
|
To add a new profile click Add below the list of SonicPoint provisioning profiles. To edit an existing profile, select the profile and click the edit icon
|
|
•
|
In the General tab of the Add Profile window, specify:Enable SonicPoint: Check this to automatically enable each SonicPoint when it is provisioned with this profile.
|
|
•
|
Retain Settings: Check this to have the SonicPointNs provisioned by this profile retain these settings after they are deleted and re-synchronized. Click Edit to specify the categories of settings that are retained.
|
|
•
|
Name Prefix: Enter a prefix for the names of all SonicPoints connected to this zone. When each SonicPoint is provisioned it is given a name that consists of the name prefix and a unique number, for example: “SonicPoint 126008.”
|
|
•
|
Country Code: Select the country where you are operating the SonicPoints. The country code determines which regulatory domain the radio operation falls under.
|
|
•
|
802.11g Virtual AP Group and 802.11a Virtual AP Group: (optional; on SonicWALL NSA only) Select a Virtual Access Point (VAP) group to assign these SonicPoints to a VAP. This pull-down menu allows you to create a new VAP group. For more information on VAPs, see Using and Configuring Virtual Access Points .
|
|
•
|
In the 802.11g tab, Configure the radio settings for the 802.11g (2.4GHz band) radio:Enable 802.11g Radio: Check this to automatically enable the 802.11g radio bands on all SonicPoints provisioned with this profile.
|
|
•
|
SSID: Enter a recognizable string for the SSID of each SonicPoint using this profile. This is the name that appears in clients’ lists of available wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
Radio Mode: Select the speed of the wireless connection. You can choose 11Mbps - 802.11b, 54Mbps - 802.11g, or 108Mbps - Turbo G mode. If you choose Turbo mode, all users in your company must use wireless access cards that support turbo mode.
|
|
•
|
Channel: Select the channel the radio operates on. The default is AutoChannel, which automatically selects the channel with the least interference. Use AutoChannel unless you have a specific reason to use or avoid specific channels.
|
|
•
|
ACL Enforcement: Select this to enforce Access Control by allowing or denying traffic from specific devices. Select a MAC address group from the Allow List to automatically allow traffic from all devices with MAC address in the group. Select a MAC address group from the Deny List to automatically deny traffic from all devices with MAC address in the group. The deny list is enforced before the Allow list.
|
|
•
|
Authentication Type: Select the method of authentication for your wireless network. You can select WEP - Both (Open System & Shared Key), WEP - Open System, WEP - Shared Key, WPA - PSK, WPA - EAP, WPA2-PSK, WPA2-EAP, WPA2-AUTO-PSK, and WPA2-AUTO-EAP.
|
|
•
|
WEP Key Mode: Select the size of the encryption key.
|
|
•
|
Default Key: Select which key in the list that follows is the default key that is tried first when trying to authenticate a user.
|
|
•
|
Key Entry: Select whether the key is alphanumeric or hexadecimal.
|
|
•
|
Key 1 - Key 4: Enter the encryptions keys for WEP encryption. Enter the most likely to be used in the field you selected as the default key.
|
|
2
|
In the 802.11g Advanced tab, configure the performance settings for the 802.11g radio. For most 802.11g advanced options, the default settings give optimum performance.
|
|
•
|
Hide SSID in Beacon: Check this option to have the SSID broadcast as part of the wireless beacon, rather than as a separate broadcast.
|
|
•
|
Schedule IDS Scan: Select a time when there are fewer demands on the wireless network to schedule an Intrusion Detection Service (IDS) scan to minimize the inconvenience of dropped wireless connections.
|
|
•
|
Data Rate: Select the speed at which the data is transmitted and received. Best automatically selects the best rate available in your area given interference and other factors. Or you can manually select a data rate.
|
|
•
|
Transmit Power: Select the transmission power. Transmission power effects the range of the SonicPoint. You can select: Full Power, Half (-3 dB), Quarter (-6 dB), Eighth (-9 dB), or Minimum.
|
|
•
|
Antenna Diversity: The Antenna Diversity setting determines which antenna the SonicPoint uses to send and receive data. You can select:
|
|
•
|
Best: This is the default setting. When Best is selected, the SonicPoint automatically selects the antenna with the strongest, clearest signal. In most cases, Best is the optimal setting.
|
|
•
|
1: Select 1 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 1 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 1 is on the left, closest to the power supply.
|
|
•
|
2: Select 2 to restrict the SonicPoint to use antenna 2 only. Facing the rear of the SonicPoint, antenna 2 is on the right, closest to the console port.
|
|
•
|
Beacon Interval (milliseconds): Enter the number of milliseconds between sending out a wireless beacon.
|
|
•
|
DTIM Interval: Enter the interval in milliseconds.
|
|
•
|
Fragmentation Threshold (bytes): Enter the number of bytes of fragmented data you want the network to allow.
|
|
•
|
RTS Threshold (bytes): Enter the number of bytes.
|
|
•
|
Maximum Client Associations: Enter the maximum number of clients you want the SonicPoint to support on this radio at one time.
|
|
•
|
Preamble Length: Select the length of the preamble--the initial wireless communication send when associating with a wireless host. You can select Long or Short.
|
|
•
|
Protection Mode: Select the CTS or RTS protection. Select None, Always, or Auto. None is the default.
|
|
•
|
Protection Rate: Select the speed for the CTS or RTS protection, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5 Mbps, or 11 Mbps.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
CCK OFDM Power Delta: Select the difference in radio transmit power you will allow between the 802.11b and 802.11g modes: 0 dBm, 1 dBm, or 2 dBm.
|
|
•
|
Enable Short Slot Time: Allow clients to disassociate and reassociate more quickly.
|
|
•
|
Allow Only 802.11g Clients to Connect: Use this if you are using Turbo G mode and therefore are not allowing 802.11b clients to connect.
|
|
3
|
Configure the settings in the 802.11a Radio and 802.11a Advanced tabs. These settings affect the operation of the 802.11a radio bands. The SonicPoint has two separate radios built in. Therefore, it can send and receive on both the 802.11a and 802.11g bands at the same time.
The settings in the 802.11a Radio and 802.11a Advanced tabs are similar to the settings in the 802.11g Radio and 802.11g Advanced tabs. Follow the instructions in step 3 and step 4 in this procedure to configure the 802.11a radio. When a SonicPoint unit is first connected and powered up, it has a factory default configuration (IP address 192.168.1.20, username: admin, password: password). Upon initializing, it attempts to find a SonicOS device with which to peer. If it is unable to find a peer SonicOS device, it enters into a stand-alone mode of operation with a separate stand-alone configuration allowing it to operate as a standard Access Point. If the SonicPoint does locate, or is located by a peer SonicOS device, through the SonicWALL Discovery Protocol, an encrypted exchange between the two units ensues wherein the profile assigned to the relevant Wireless zone is used to automatically configure (provision) the newly added SonicPoint unit. As part of the provisioning process, SonicOS assigns the discovered SonicPoint device a unique name, and it records its MAC address and the interface and zone on which it was discovered. It can also automatically assign the SonicPoint an IP address, if so configured, so that the SonicPoint can communicate with an authentication server for WPA-EAP support. SonicOS then uses the profile associated with the relevant zone to configure the 2.4GHz and 5GHz radio settings. Modifications to profiles do not affect units that have already been provisioned and are in an operational state. Configuration changes to operational SonicPoint devices can occur in two ways: |