How Do Multiple DHCP Scopes per Interface Work?
Normally, a DHCP client initiates an address allocating procedure by sending a Broadcast DHCP Discovery message. Since most routes do not forward broadcast packets, this method requires DHCP clients and server(s) to reside on the same IP network or subnet.
When DHCP clients and their associated DHCP server are not on the same subnet, some type of third-party agent (BOOTP relay agent, IP Helper, etc.) is required to transfer DHCP messages between clients and server. The DHCP relay agent populates the giaddr field with its ingress interface IP address and then forwards it to the configured DHCP server. When the DHCP server receives the message, it examines the giaddr field to determine if it has a DHCP scope that could be used to supply an IP address lease to the client.
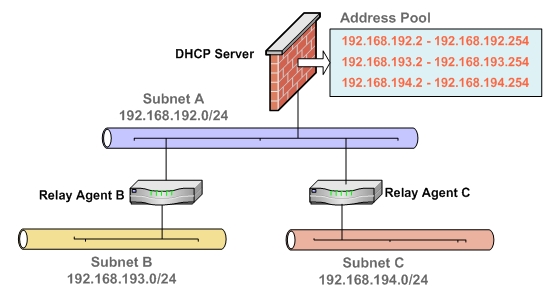
Multiple Subnets Sharing One DHCP Server
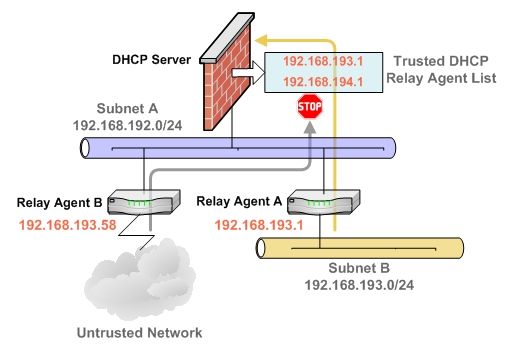
The Multiple DHCP Scopes per Interface feature provides security enhancements to protect against potential vulnerabilities inherent in allowing wider access to the DHCP server. The DHCP Advanced Setting page provides security with a new tab for Trusted Agents where trusted DHCP relay agents can be specified. The DHCP server discards any messages relayed by agents which are not in the list.
Trusted DHCP Relay Agents