firewall_bwm
Bandwidth management (BWM) is a means of allocating bandwidth resources to critical applications on a network.
SonicOS offers an integrated traffic shaping mechanism through its outbound (Egress) and inbound (Ingress) BWM interfaces. Egress BWM can be applied to traffic sourced from Trusted and Public zones travelling to Untrusted and Encrypted zones. Ingress BWM can be applied to traffic sourced from Untrusted and Encrypted zones travelling to Trusted and Public zones.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Understanding Bandwidth Management
• Configuring the Firewall Settings > BWM Page
• Methods of Configuring Bandwidth Management
– Configuring Application Rules
• Glossary
Note Although BWM is a fully integrated Quality of Service (QoS) system, wherein classification and shaping is performed on the single appliance, effectively eliminating the dependency on external systems and thus obviating the need for marking, it is possible to concurrently configure BWM and QoS (layer 2 and/or layer 3 marking) settings on a single Access Rule. This allows those external systems to benefit from the classification performed on the SonicWALL even after it has already shaped the traffic. Refer to Firewall Settings > QoS Mapping for BWM QoS details.
Understanding Bandwidth Management
BWM is controlled by the SuperMassive on ingress and egress traffic. It allows network administrators to guarantee minimum bandwidth and prioritize traffic based on access rules created in the Firewall > Access Rules page on the SonicWALL management interface. By controlling the amount of bandwidth to an application or user, the network administrator can prevent a small number of applications or users to consume all available bandwidth. Balancing the bandwidth allocated to different network traffic and then assigning priorities to traffic can improve network performance. Anti-Spam for UTM provides eight priority queues (0 – 7 or Realtime – Lowest).
Bandwidth Management can be enabled or disabled by selecting Global or None on the Firewall Settings > BWM page.
|
When global BWM is enabled on an interface, all of the traffic to and from that interface is bandwidth managed.
For example, with bandwidth management type none, if there are three traffic types (1, 2, and 3) that are using an interface with the link capability of 100 Mbps, the cumulative capacity for all three types is 100 Mbps.
Then when bandwidth management type Global is enabled on that interface and the available ingress and egress traffic are configured to 10 Mbps, the following occurs:
By default, the traffic types are sent to the Medium (4) Priority queue. This queue has, by default, a Guaranteed percentage of 50 and a Maximum percentage of 100. These values mean that the cumulative link capability is 10 Mbps with no global BWM enabled policies configured.
Packet Queuing
BWM rules each consume memory for packet queuing, so the number of allowed queued packets and rules on SonicOS is limited by platform (values are subject to change):
|
Configuring the Firewall Settings > BWM Page
BWM works by first enabling bandwidth management in the Firewall Settings > BWM page, enabling BWM on an interface/firewall/app rule, and then allocating the available bandwidth for that interface on the ingress and egress traffic. It then assigns individual limits for each class of network traffic. By assigning priorities to network traffic, applications requiring a quick response time, such as Telnet, can take precedence over traffic requiring less response time, such as FTP.
To view the BWM configuration, navigate to the Firewall Settings > BWM page.
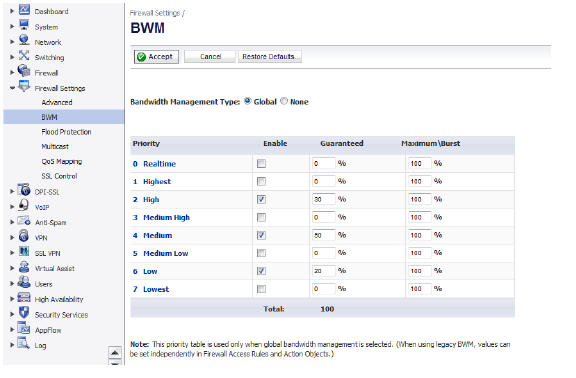
This page consists of the following entities:
Note The defaults are set by SonicWALL to provide BWM ease-of-use. It is recommended that you review the specific bandwidth needs and enter the values on this page accordingly.
• Bandwidth Management Type Option:
– Global — All zones can have assigned guaranteed and maximum bandwidth to services and have prioritized traffic.
– None — (Default) Disables BWM.
• Priority Column — Displays the priority number and name.
• Enable Checkbox — When checked, the priority queue is enabled.
• Guaranteed and Maximum\Burst Text Field — Enables the guaranteed and maximum/burst rates. The corresponding Enable checkbox must be checked in order for the rate to take effect. These rates are identified as a percentage. The configured bandwidth on an interface is used in calculating the absolute value. The sum of all guaranteed bandwidth must not exceed 100%, and the guaranteed bandwidth must not be greater than the maximum bandwidth per queue.
Note The default settings for this page consists of three priorities with preconfigured guaranteed and maximum bandwidth. The medium priority has the highest guaranteed value since this priority queue is used by default for all traffic not governed by a BWM enabled policy.
Methods of Configuring Bandwidth Management
BWM can be configured using the following methods:
Note This section uses Global BWM as the Bandwidth Management Type (Firewall Settings > BWM).
• Configuring Application Rules
To configure BWM per interface, perform the following steps:
1. Navigate to the Firewall Settings > BWM page.
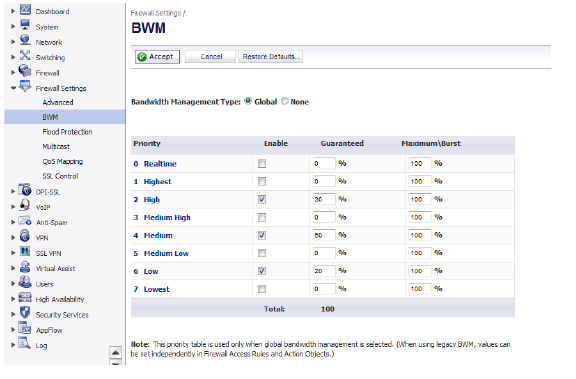
2. For the Bandwidth Management Type, select Global.
3. Click Accept.
4. Navigate to the Network > Interfaces page.
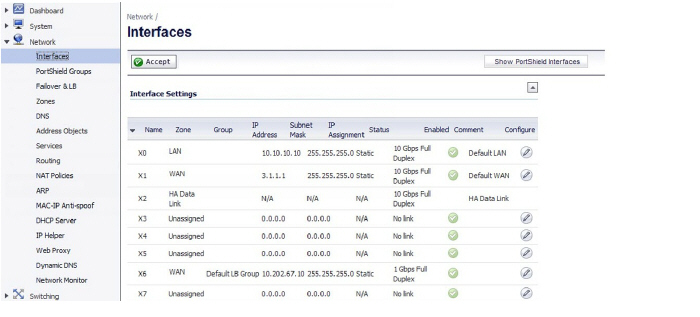
5. Click the Configure icon in the Configure column for the interface for which you want to set BWM. The Edit Interface dialog is displayed.
6. Click the Advanced tab.
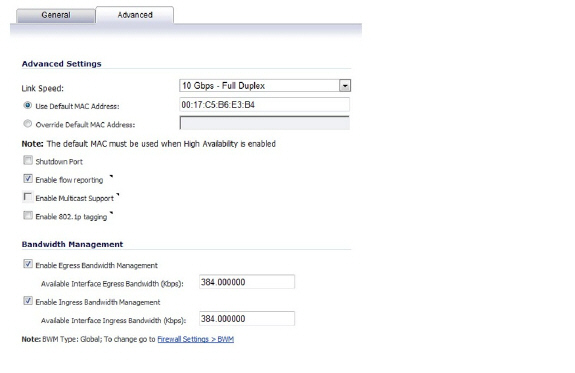
7. Under Bandwidth Management, select the Enable Egress option or the Enable Ingress option, or select both options, and then enter the available bandwidth in kilobits per second (Kbps).
8. Click OK.
Application layer BWM allows you to create policies that regulate bandwidth consumption by specific file types within a protocol, while allowing other file types to use unlimited bandwidth. This enables you to distinguish between desirable and undesirable traffic within the same protocol. Application layer bandwidth management is supported for all Application matches, as well as custom App Rules policies using HTTP client, HTTP Server, Custom, and FTP file transfer types. For more information on Application Rules, see Configuring Application Rules.
Note It is a best practice to configure BWM settings before configuring App Control policies that use BWM.
After bandwidth management is enabled on the interface, you can configure BWM for a specific application rule on the Firewall > App Rules page.
To configure BWM for a specific application, perform the following steps:
1. Navigate to the Firewall > App Rules page.
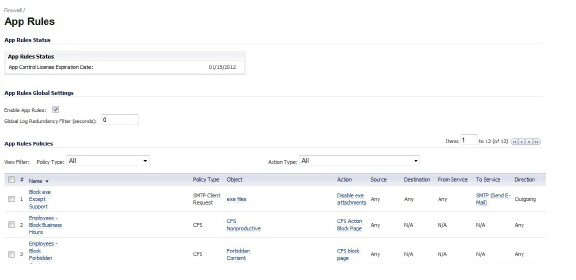
2. Under App Rules Policies, select the Action Type: Bandwidth Management.
The page will sort by Action Type Bandwidth Management.
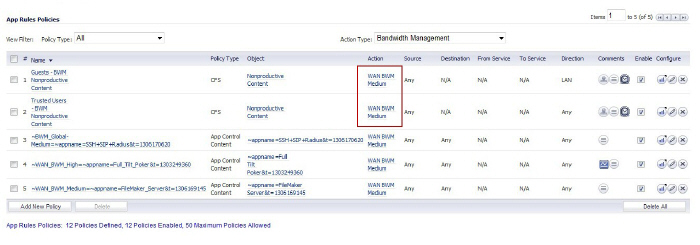
3. Click the Configure icon in the Configure column for the policy you want to change.
The Edit App Control Policy window is displayed.
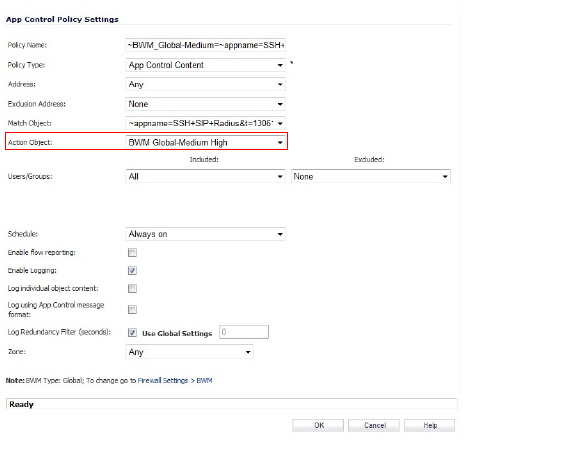
4. Change the Action Object to the desired BWM setting, and then click OK.
Note All priorities will be displayed (Realtime – Lowest) regardless if all have been configured. Refer to the Firewall Settings > BWM page to determine which priorities are enabled. If you select a Bandwidth Priority that is not enabled, the traffic is automatically mapped to the Medium Priority (default).
The change will take effect when you return to the App Rules page.
BWM Action Objects
Action Objects define how the App Rules policy reacts to matching events. You can customize an action or select one of the predefined default actions. The predefined actions are displayed in the App Control Policy Settings page when you add or edit a policy from the App Rules page.
Custom BWM actions behave differently than the default BWM actions. Custom BWM actions are configured by adding a new action object from the Firewall > Action Objects page and selecting the Bandwidth Management action type.
A number of BWM action options are also available in the predefined, default action list. The BWM action options change depending on the Bandwidth Management Type setting on the Firewall Settings > BWM page. If the Bandwidth Management Type is set to Global, all eight levels of BWM are available. For more information about BWM actions, see the Actions Using Bandwidth Management.
Creating a BWM Action Object
When Global BWM is enabled on the Firewall Settings > BWM page, you can create a BWM action object on the Firewall > Action Objects page.
The following predefined default actions are available when you create a BWM action object:
• BWM Global-Realtime
• BWM Global-Highest
• BWM Global-High
• BWM Global-Medium High
• BWM Global-Medium
• BWM Global-Medium Low
• BWM Global-Low
• BWM Global-Lowest
To create a new BWM action object:
1. Navigate to the Firewall > Action Objects page.
2. Click Add New Action Object.
The Add/Edit Action Object dialog appears.
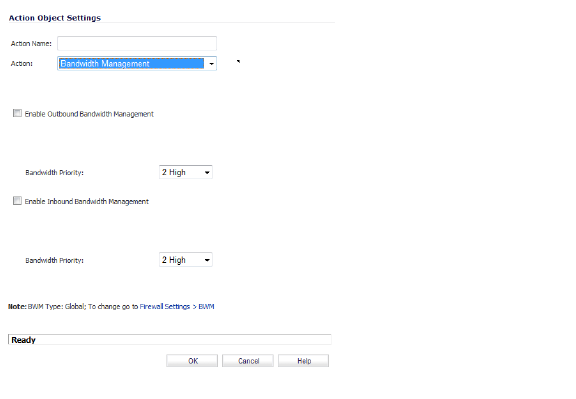
3. In the Action Name box, enter a name for the policy.
4. In the Action box, select Bandwidth Management.
5. Check Enable Outbound Bandwidth Management checkbox and select the Bandwidth Priority.
6. Check Enable Inbound Bandwidth Management checkbox and select the Bandwidth Priority.
Note All priorities will be displayed (0 –7) regardless if all have been configured. Refer to the Firewall Settings > BWM page to determine which priorities are enabled. If you select a Bandwidth Priority that is not enabled, the traffic is automatically mapped to the Medium Priority (default).
7. Click OK.
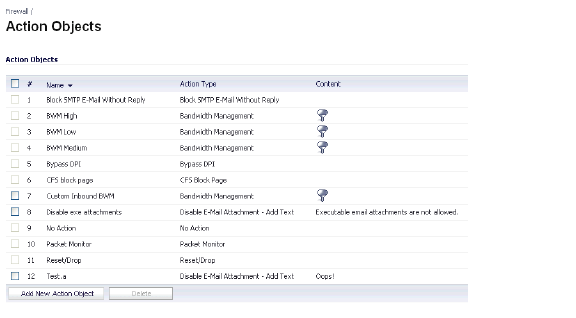
You can see the resulting action on the Firewall > Action Objects page.
BWM can also be configured from the AppFlow Monitor page by selecting a service type application or a signature type application and then clicking the Create Rule button. The Bandwidth Management options available there depend on the enabled priority levels in the Global Priority Queue table on the Firewall Settings > BWM page. The priority levels enabled by default are High, Medium, and Low.
Note You must have the SonicWALL Application Visualization application enabled before proceeding.
To configure BWM using the AppFlow Monitor, perform the following steps:
1. Navigate to the Dashboard > AppFlow Monitor page.
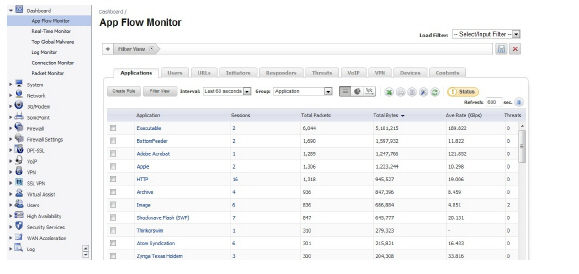
2. Check the service-based applications or signature-based applications to which you want to apply global BWM.
Note General applications cannot be selected. Service-based applications and signature-based applications cannot be mixed in a single rule.
Note Create rule for service-based applications will result in creating a firewall access rule and create rule for signature-based applications will create an application control policy.
3. Click Create Rule. The Create Rule pop-up is displayed.
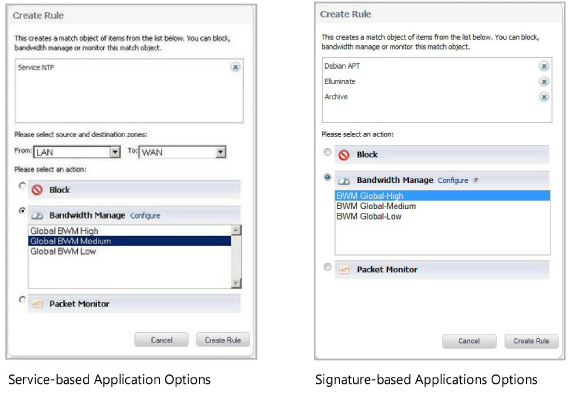
4. Select the Bandwidth Manage radio button, and then select a global BWM priority.
5. Click Create Rule. A confirmation pop-up is displayed.
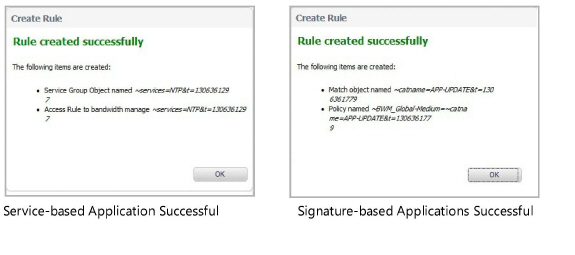
6. Click OK.
7. Navigate to Firewall > Access Rules page (for service-based applications) and Firewall > App Rules (for signature-based applications) to verify that the rule was created.
Note For service-based applications, the new rule is identified with a tack in the Comments column and a prefix in Service column of ~services=<service name>. For example, ~services=NTP&t=1306361297.
Note For signature-based applications, the new rule is identified with a prefix, ~BWM_Global-<priority>=~catname=<app_name> in the Name column and in the Object column prefix ~catname=<app_name>.
Bandwidth Management (BWM): Refers to any of a variety of algorithms or methods used to shape traffic or police traffic. Shaping often refers to the management of outbound traffic, while policing often refers to the management of inbound traffic (also known as admission control). There are many different methods of bandwidth management, including various queuing and discarding techniques, each with their own design strengths. SonicWALL employs a Token Based Class Based Queuing method for inbound and outbound BWM, as well as a discard mechanism for certain types of inbound traffic.
Guaranteed Bandwidth: A declared percentage of the total available bandwidth on an interface which will always be granted to a certain class of traffic. Applicable to both inbound and outbound BWM. The total Guaranteed Bandwidth across all BWM rules cannot exceed 100% of the total available bandwidth. SonicOS 6.0 enhances the Bandwidth Management feature to provide rate limiting functionality. You can now create traffic policies that specify maximum rates for Layer 2, 3, or 4 network traffic. This enables bandwidth management in cases where the primary WAN link fails over to a secondary connection that cannot handle as much traffic. The Guaranteed Bandwidth can also be set to 0%.
Inbound (Ingress) BWM: The ability to shape the rate at which traffic enters a particular interface. For TCP traffic, actual shaping can occur where the rate of the ingress flow can be adjusted by delaying egress acknowledgements (ACKs) causing the sender to slow its rate. For UDP traffic, a discard mechanism is used since UDP has no native feedback controls.
Maximum Bandwidth: A declared percentage of the total available bandwidth on an interface defining the maximum bandwidth to be allowed to a certain class of traffic. Applicable to both inbound and outbound BWM. Used as a throttling mechanism to specify a bandwidth rate limit. The Bandwidth Management feature is enhanced to provide rate limiting functionality. You can now create traffic policies that specify maximum rates for Layer 2, 3, or 4 network traffic. This enables bandwidth management in cases where the primary WAN link fails over to a secondary connection that cannot handle as much traffic.The Maximum Bandwidth can be set to 0%, which will prevent all traffic.
Outbound (Egress) BWM: Conditioning the rate at which traffic is sent out an interface. Outbound BWM uses a credit (or token) based queuing system with 8 priority rings to service different types of traffic, as classified by Access Rules.
Priority: An additional dimension used in the classification of traffic. SonicOS uses eight priority values (0 = highest, 7 = lowest) to comprise the queue structure used for BWM. Queues are serviced in the order of their priority.
Queuing: To effectively make use of the available bandwidth on a link. Queues are commonly employed to sort and separately manage traffic after it has been classified.