RFC 1771, which defines BGP, describes the operation of BGP in terms of the following state machine. The table following BGP Finite State Machine provides additional information on the various states.
BGP communication includes the following types of messages
|
•
|
Open – The first message between BGP peers after TCP session establishment. Contains the necessary information to establish a peering session, for example, ASN, hold time, and capabilities such as multi-product extensions and route-refresh.
|
|
•
|
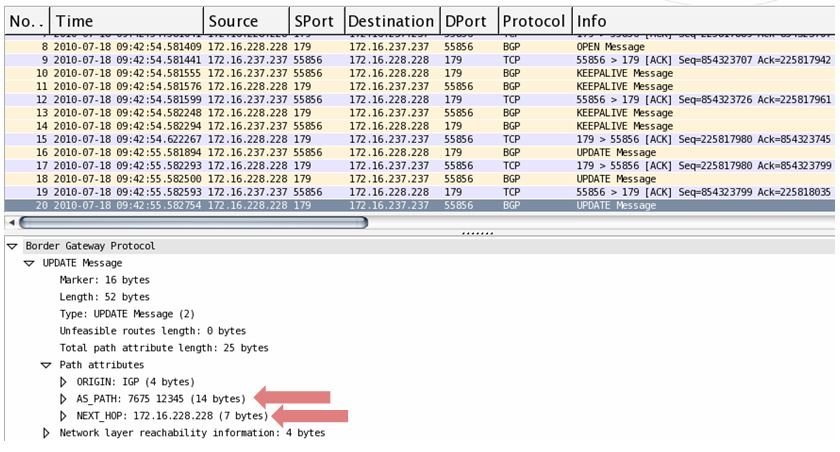
Update – These messages contain path information, such as route announcements or withdrawals.
|
|
•
|
Keepalive – Periodic messages to keep TCP layer up, and to advertise liveliness.
|
|
•
|
Notification – A request to terminate the BGP session. Non-fatal notifications contain the error code “cease”. Subcodes provide further detail:
|
|
•
|
Route-refresh – A request for the peer to resend its routes.
|
BGP update messages can include the following attributes:
For more information on BGP attributes, see: http://www.iana.org/assignments/bgp-parameters/bgp-parameters.xml.