By default, all iBGP routers in an AS must be in a full mesh configuration. Each router must be configured as a peer to every other router.
With route reflection, all iBGP routers do not need to be fully meshed. Route reflection eliminates the need for each iBGP router to communicate with every other iBGP router in the AS. An iBGP router can be designated as a route reflector and can pass iBGP learned routes to multiple iBGP clients.
When a router is configured as a route reflector, it acts as a single point where all the other iBGP routers can get the iBGP learned routes. The route reflector acts like a server, rather than a peer, for every other router in the AS. All the other IBGP routers become route reflector clients. A router is a route reflector as long as it has at least one route reflector client.
BGP Route Reflection Configuration
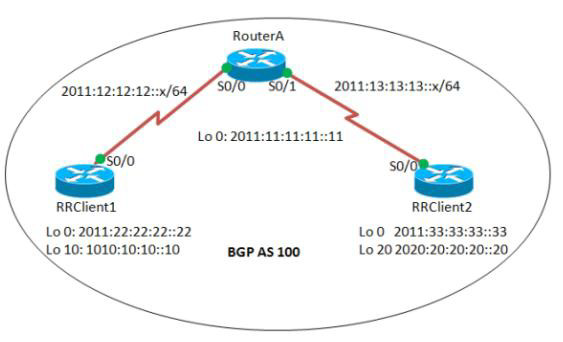
To configure route reflection in an AS:
To check the routes, use the show bgp ipv6 unicast command:
You should see route 2020:20:20:20::20/128.
You should see route 1010:10:10:10::10/128.
