When enabled, the Anti-Spam service creates NAT policies and Access Rules to control and redirect email traffic. The policies and rules are visible in the Network > NAT Policies and Firewall > Access Rules pages, but are not editable. These automatically-created policies are only available when the Anti-Spam service is enabled.
When the Anti-Spam service is licensed and activated, the Anti-Spam > Settings page shows a single check box to enable Anti-Spam. Selecting the check box invokes the Destination Mail Server Policy Wizard if there is no existing custom access rule and NAT policy for an already-deployed scenario. When you set up generated policies, the Anti-Spam service must know where the emails are routed behind the firewall. Specifically it needs the destination mail server IP address and its zone assignment. The Destination Mail Server Policy Wizard is launched if this data cannot be found.
You need the following information for the wizard:
|
•
|
Destination Mail Server Public IP Address – The IP address to which external MTAs (message transfer agents) connect by SMTP.
|
|
•
|
Destination Mail Server Private IP Address – The internal IP address of the Exchange or SMTP server (behind the firewall).
|
|
•
|
Zone Assignment – The zone to which the Exchange server is assigned.
|
|
•
|
Inbound Email Port – The TCP service port number to which emails will be sent, also known as the inbound SMTP port.
|
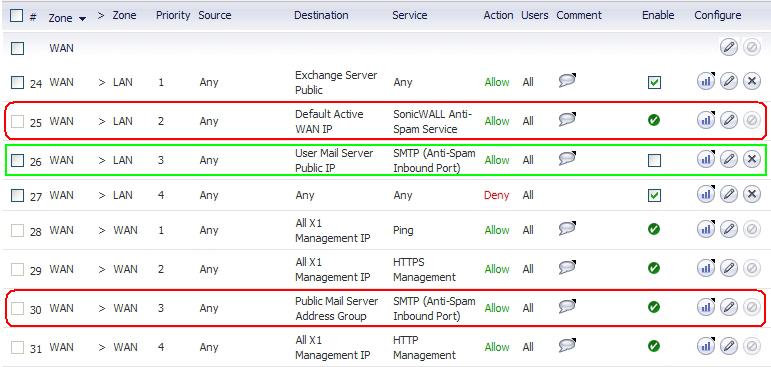
The Firewall > Access Rules page shows the generated rules used for Anti-Spam.
You could also create the following access rules:
The Anti-Spam Service Object is created in the Network > Services page.
This Service Object is referenced by the generated NAT policies.
The following considerations apply to the auto-generation of policies:
|
•
|
A system Address Group Object called the Public Mail Server Address Group is created as a default for the original destination for generated policies. This group contains the Address Object, Destination Mail Server Public IP, which takes the IP address value provided during the wizard.
|
|
•
|
If the existing policy’s original destination is a host-type Address Object, then the generated policies use the Public Mail Server Address Group object as their original destination.
|
|
•
|
If there is more than one public IP address for SMTP, you can manually add Address Objects to the Public Mail Server Address Group.
|