WiFiMultimedia
SonicPoint access points support Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) to provide a better Quality of Service experience on bandwidth-intensive applications such as VoIP and multimedia traffic on wireless networks. WMM is a Wi-Fi Alliance interoperability certification based on the IEEE 802.11e standard. It prioritizes traffic according to four Access Categories:
• Voice – highest priority
• Video – second priority
• Best effort – third priority (intended for applications like email and Internet surfing)
• Background – fourth priority (intended for applications that are not latency sensitive, such as printing)
Note WMM does not provide guaranteed throughput.
Each Access Category has its own transmit queue. Traffic is assigned to the appropriate Access Category based on type of service (ToS) information that is provided by either the application or the firewall. SonicWALL security appliances assign ToS either through access rules or VLAN tagging.
The following table shows how the WMM Access Categories map to 802.1D user priorities.
|
WMM prioritizes traffic through a process known as Enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA). EDCA is a contention-based mechanism for governing access to the transmission channel among the four WMM Access Categories. EDCA requires uses a listen-then-talk method where clients must wait for a random “backoff” period of time to observe if any other devices are transmitting before they transmit. The backoff times are randomized to reduce the likelihood of collisions and to give all devices a fair chance. WMM prioritizes traffic by defining different a range of “backoff” periods for each Access Category. The WMM backoff periods are defined by two parameters:
• Arbitration Inter-Frame Space (AIFS) – The time interval between the wireless channel becomes idle and when the AC can begin negotiating access to the channel.
• Contention Window (CW) – The range of possible values for the random backoff periods. A range of time that specifies the random backoff period. The CW is defined by a minimum and maximum value:
– Minimum contention window size (CWMin) – The initial upper limit of the length of the CW. The AC will wait for a random time between 0 and CWMin before attempting to transmit. Higher priority AC with higher priority is assigned a shorter CWMin.
– Maximum contention window size (CWMax) – The upper limit of the CW. If a collision occurs, the AC doubles the size of the CW, up to the CWMax, and attempts to transmit again. The CWMax must be larger than the CWMin.
Higher priority ACs are generally given lower values for AIFS, CWMin, CWMax.
Note The unit of measure for AIFS, CWMin, and CWMax is multiples of the slot time for the 802.11 standard that is being used. For 802.11b, one slot is 20 microseconds. For 802.11a and 802.11g, one slot is 9 microseconds.
Separate WMM parameters are configured for Access Points (SonicPoints) and for the Station (the SonicWALL security appliance). The following table show the default WMM parameters for the SonicPoints and SonicWALL security appliances.
|
|
Assigning Traffic to Access Categories
SonicWALL security appliances assign traffic to WMM Access Categories through two methods:
• Specifying DSCP through access rules
• Specifying a VLAN tag
Configuring Wi-Fi Multimedia Parameters
By default, a single WMM profile is configured on the SonicWALL security appliance with the parameters set to the values on the 802.11e standard. To customize the WMM configuration, perform the following tasks:
1. Navigate to the SonicPoint > Wi-Fi Multimedia page.
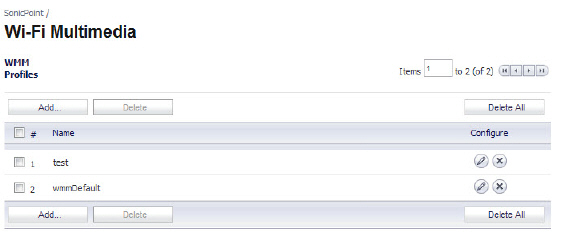
2. To modify the default WMM profile, click the configure icon for the wmmDefault profile. Or to create a new WMM profile, click the Add button. The Add WMM Profile window displays.
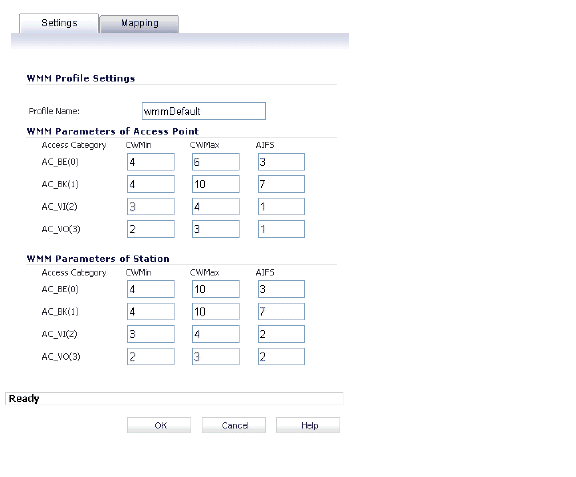
3. For a new WMM profile, enter a Profile Name.
4. The default WMM parameter values are auto-populated in the window. Modify the parameters to customize the WMM profile.
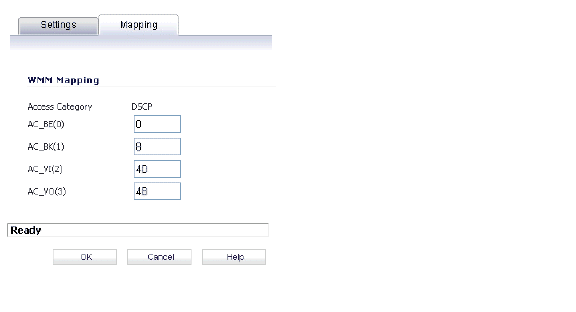
5. Click the Mapping tab to customize how the Access Categories are mapped to DSCP values.