Deep Packet Inspection of Secure Socket Layer (DPI-SSL) extends SonicWALL’s Deep Packet
Inspection technology to allow for the inspection of encrypted HTTPS traffic and other SSL-based traffic. The SSL traffic is decrypted transparently, scanned for threats and then re-encrypted and sent along to its destination if no threats or vulnerabilities are found. DPI-SSL provides additional security, application control, and data leakage prevention for analyzing encrypted HTTPS and other SSL-based traffic.
The following security services and features are capable of utilizing DPI-SSL:
DPI-SSL has two main deployment scenarios:
The DPI-SSL feature is available in SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 and higher. The following table
shows which platforms support DPI-SSL and the maximum number of concurrent connections on which the appliance can perform DPI-SSL inspection.
TThe Client DPI-SSL deployment scenario typically is used to inspect HTTPS traffic when
clients on the LAN browse content located on the WAN. In the Client DPI-SSL scenario, the SonicWALL UTM appliance typically does not own the certificates and private keys for the content it is inspecting. After the appliance performs DPI-SSL inspection, it re-writes the certificate sent by the remote server and signs this newly generated certificate with the certificate specified in the Client DPI-SSL configuration. By default, this is the SonicWALL certificate authority (CA) certificate, or a different certificate can be specified. Users should be instructed to add the certificate to their browser’s trusted list to avoid certificate trust errors.
The following sections describe how to configure Client DPI-SSL:
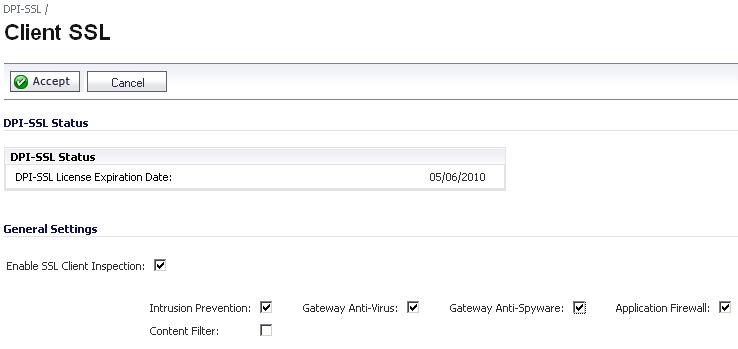
To enable Client DPI-SSL inspection, perform the following steps:
By default, the DPI-SSL applies to all traffic on the appliance when it is enabled. You can
configure an Inclusion/Exclusion list to customize which traffic DPI-SSL inspection will apply to. The Inclusion/Exclusion list provides the ability to specify certain objects, groups, or hostnames. In deployments that are processing a large amount of traffic, it can be useful to exclude trusted sources in order to reduce the CPU impact of DPI-SSL and to prevent the appliance from reaching the maximum number of concurrent DPI-SSL inspected connections.
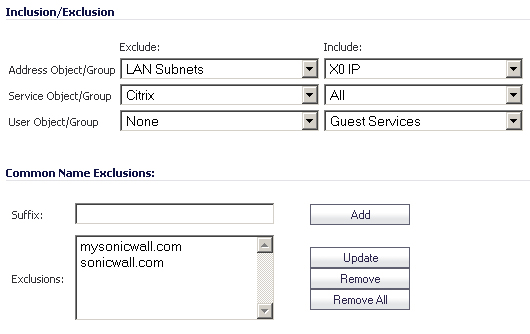
The
Inclusion/Exclusion
section of the Client SSL
page contains three options for specifying the inclusion list:
|
|
•
|
On the
Address Object/Group
line, select an address object or group from the Exclude
pulldown menu to exempt it from DPI-SSL inspection.
|
|
|
•
|
On the
Service Object/Group
line, select a service object or group from the Exclude
pulldown menu to exempt it from DPI-SSL inspection.
|
|
|
•
|
On the
User Object/Group
line, select a user object or group from the Exclude
pulldown menu to exempt it from DPI-SSL inspection.
|
|
|
Tip
|
The
Include
pulldown menu can be used to fine tune the specified exclusion list. For example, by selecting the Remote-office-California
address object in the Exclude
pulldown and the Remote-office-Oakland
address object in the Include
pulldown.
|
The
Common Name Exclusions
section is used to add domain names to the exclusion list. To add a domain name, type it in the text box and click Add
. Click Apply
at the top of the page to confirm the configuration.
By default, DPI-SSL uses the
Default SonicWALL DPI-SSL CA Certificate
to re-sign traffic that has been inspected. Optionally, users can specify that another certificate will be used. To use a custom certificate, you must first import the certificate to the SonicWALL UTM appliance:
|
2.
|
Click
Import Certificate
.
|
|
3.
|
Select the
Import a local end-user certificate with private key from a PKCS#12 (.p12
or .pfx) encoded file
option.
|
|
4.
|
Choose
password
and click Import
.
|
After the certificate has been imported, you must configure it on the Client DPI-SSL page:
|
2.
|
Scroll down to the
Certificate Re-Signing Authority
section and select the certificate from the pulldown menu.
|
For help with creating PKCS-12 formatted files, see
“Creating PKCS-12 Formatted Certificate File”
.
Adding Trust to the Browser
In the previous section we described how to configure a re-signing certificate authority. In order
for re-signing certificate authority to successfully re-sign certificates browsers would have to trust this certificate authority. Such trust can be established by having re-signing certificate imported into the browser's trusted CA list.
|
|
•
|
Internet Explorer: Go to
Tools > Internet Options
, click the Content
tab and click Certificates
. Click the Trusted Root Certification Authorities
tab and click Import
. The Certificate Import Wizard
will guide you through importing the certificate.
|
|
|
•
|
Firefox: Go to
Tools > Options
, click the Advanced
tab and then the Encryption
tab. Click View Certificates
, select the Authorities
tab, and click Import
. Select the certificate file, make sure the Trust this CA to identify websites
check box is selected, and click OK
.
|
PKCS12 formatted certificate file can be created using Linux system with OpenSSL. In order to
create a PKCS-12 formatted certificate file, one needs to have two main components of the certificate:
For example, Apache HTTP server on Linux has its private key and certificate in the following
locations:
With these two files available, run the following command:
In this example
out.p12
will become the PKCS-12 formatted certificate file and server.key
and server.crt
are the PEM formatted private key and the certificate file respectively.
After the above command, one would be prompted for the password to protect/encrypted the
file. After the password is chosen, the creation of PKCS-12 formatted certificate file is complete and it can be imported into the UTM appliance.
The following sections
To perform SonicWALL Content Filtering on HTTPS and SSL-based traffic using DPI-SSL,
perform the following steps:
|
2.
|
Select the
Enable SSL Inspection
checkbox and the Content Filter
checkbox.
|
|
4.
|
Navigate to the
Security Services > Content Filter
page and click the Configure
button.
|
|
5.
|
Uncheck the
Enable IP based HTTPS Content Filtering
checkbox.
|
Enable Application Firewall checkbox on the Client DPI-SSL screen and enable Application
Firewall on the Application Firewall >Policies screen.
|
2.
|
Select the
Enable SSL Inspection
checkbox and the Application Firewall
checkbox.
|
|
5.
|
Enable
Application Firewall
.
|
|
6.
|
Configure an
HTTP Client policy
to block Microsoft Internet Explorer browser.
|
|
7.
|
Select
block page
as an action for the policy. Click Apply
.
|
DPI-SSL also supports Application Level Bandwidth Management over SSL tunnels.
Application Firewall HTTP bandwidth management policies also applies to content that is accessed over HTTPS when DPI-SSL is enabled for Application Firewall.