The
Wireless > Settings
page allows you to configure settings for the 802.11 wireless antenna.
The Radio Role allows you to configure the SonicWALL TZ wireless for one of two modes:
Access Point
- Configures the SonicWALL as an Internet/network gateway for wireless clients.

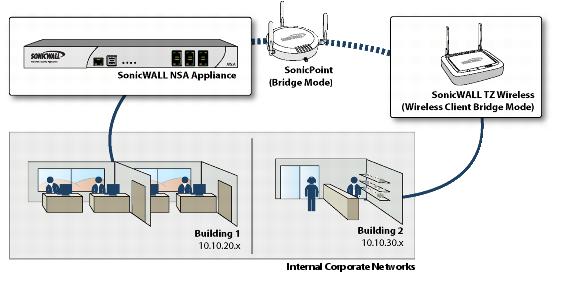
Wireless Client Bridge
- The SonicWALL TZ wireless provides Internet/network access by bridging wirelessly to another SonicWALL wireless device or SonicPoint access point, selected on the Wireless > Status
screen. This mode allows for the possibility of secure network communications between physically seperate locations, without the need for long and costly ethernet cabling runs.
Enable WLAN Radio
: Check this checkbox to turn the radio on, and enable wireless networking. Click Apply
in the top right corner of the management interface to have this setting take effect.
Schedule
: The schedule determines when the radio is on to send and receive data. The default value is Always on
. The Schedule list displays the schedule objects you create and manage in the System
>
Schedule
page. The default choices are:
|
|
•
|
Work Hours
or M-T-W-TH-F 08:00-17:00
(these two options are the same schedules)
|
|
|
•
|
After Hours
or M-T-W-TH-F 17:00-24:00
(these two options are the same schedules)
|
|
|
•
|
Weekend Hours
or SA-SU 00:00-24:00
(these two options are the same schedules)
|
SSID
: The default value, sonicwall
, for the SSID can be changed to any alphanumeric value with a maximum of 32 characters.
Country Code
: The country code determines which regulatory domain the radio operation falls under.
Radio Mode
: Select your preferred radio mode from the Radio Mode
menu. The wireless security appliance supports the following modes:
|
|
•
|
2.4GHz 802.11n Mixed
- Supports 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n clients simultaneously. If your wireless network comprises multiple types of clients, select this mode.
|
|
|
•
|
802.11n Only
- Allows only 802.11n clients access to your wireless network. 802.11a/b/g clients are unable to connect under this restricted radio mode.
|
|
|
•
|
2.4GHz 802.11b/g Mixed
- Supports 802.11b and 802.11g clients simultaneously. If your wireless network comprises both types of clients, select this mode.
|
|
|
•
|
802.11g
Only
- If your wireless network consists only of 802.11g clients, you may select this mode for increased 802.11g performance. You may also select this mode if you wish to prevent 802.11b clients from associating.
|
|
|
•
|
802.11b Only
- Select this mode if only 802.11b clients access your wireless network.
|
When the wireless radio is configured for a mode that supports 802.11n, the following options
are displayed:
Radio Band
(802.11n only): Sets the band for the 802.11n radio:
|
|
•
|
Auto
- Allows the appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based on signal strength and integrity. This is the default setting.
|
|
|
•
|
Standard - 20 MHz Channel
- Specifies that the 802.11n radio will use only the standard 20 MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Standard Channel
pulldown menu is displayed.
|
|
|
–
|
Standard Channel
- This pulldown menu only displays when the 20 MHz channel is selected. By default, this is set to Auto
, which allows the appliance to set the optimal channel based on signal strength and integrity. Optionally, you can select a single channel within the range of your regulatory domain. Selecting a specific a channel can also help with avoiding interference with other wireless networks in the area.
|
|
|
•
|
Wide - 40 MHz Channel
- Specifies that the 802.11n radio will use only the wide 40 MHz channel. When this option is selected, the Primary Channel
and Secondary Channel
pulldown menus are displayed:
|
|
|
–
|
Primary Channel
- By default this is set to Auto
. Optionally, you can specify a specific primary channel.
|
|
|
–
|
Secondary Channel
- The configuration of this pulldown menu is controlled by your selection for the primary channel:
|
Enable Short Guard Interval
: Specifies the short guard interval of 400ns (as opposed to the standard guard interval of 800ns). The guard interval is a pause in transmission intended to avoid data loss from interference or multipath delays.
Enable Aggregation
: Enables 802.11n frame aggregation, which combines multiple frames to reduce overhead and increase throughput.
|
|
Tip
|
The
Enable Short Guard Interval
and Enable aggregation
options can slightly improve throughput. They both function best in optimum network conditions where users have strong signals with little interference. In networks that experience less than optimum conditions (interference, weak signals, etc.), these options may introduce transmission errors that eliminate any efficiency gains in throughput.
|
When the wireless radio is configured for 802.11b or 802.11g, the
Channel
pulldown menu is displayed. An Auto
setting allows the wireless security appliance to automatically detect and set the optimal channel for wireless operation based upon signal strength and integrity. Auto is the default channel setting, and it displays the selected channel of operation to the right. Alternatively, an operating channel within the range of your regulatory domain can be explicitly defined.

