WiFiMultimedia
SonicPoint access points support Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) to provide a better Quality of Service experience on bandwidth-intensive applications such as VoIP and multimedia traffic on IEEE 802.11 networks. WMM is a Wi-Fi Alliance interoperability certification based on the IEEE 802.11e standard. It prioritizes traffic according to four access categories:
• Voice – highest priority
• Video – second priority
• Best effort – third priority (intended for applications like email and Internet surfing)
• Background – fourth priority (intended for applications that are not latency sensitive, such as printing)
Note that WMM does not provide guaranteed throughput. Supported on SonicPoint-N/Ni/Ne/NDR.
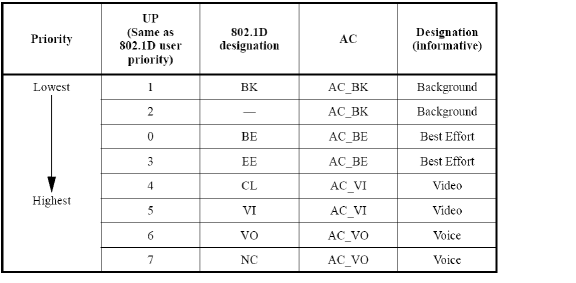
The following table shows the User Priority to Access Category mapping for the four access categories:

Each Access Category has its own transmit queue. WMM requires the SonicPoint-N to implement multiple queues for multiple priority access categories. The SonicPoint-N relies on either the application or the firewall to provide type of service (ToS) information in the IP data in order to differentiate traffic types. One way to provide ToS is through firewall services and access rules; another way is through VLAN tagging.
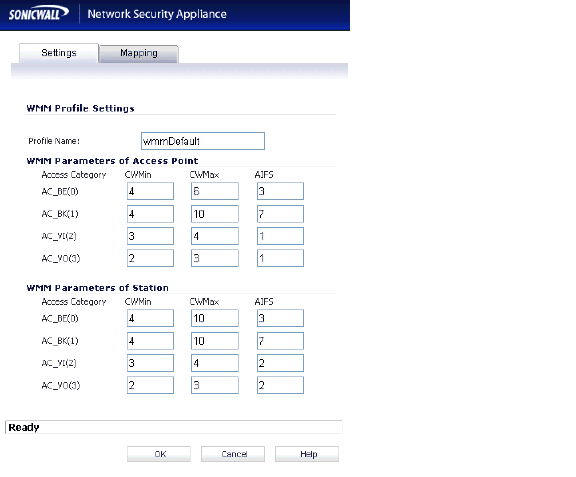
When configuring the WMM profile, on the Settings tab, the administrator can configure the size of the contention window (CWMin/CWMax) and the arbitration interframe space (AIFS) number when creating a WMM profile. These values can be configured individually for each priority, AC_BK, AC_BE, AC_VI, and AC_VO on the Access Point (SonicPoint-N) and for the Station (firewall).
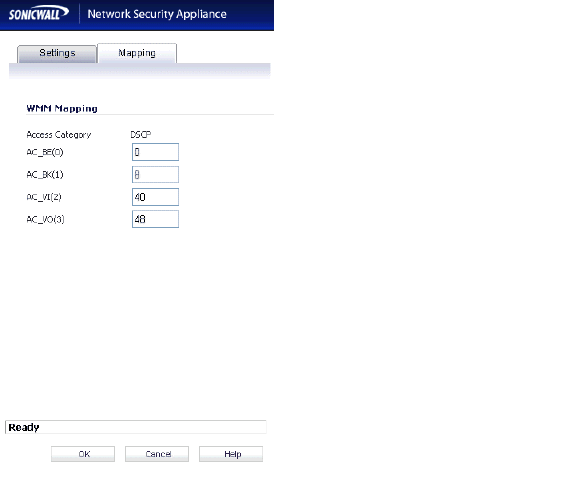
The Mapping tab allows you to map priority levels to DSCP values. The default DSCP values are as same as the ones in Firewall > Access Rules, QoS mapping.
The following four key parameters are used for differentiation:
• Minimum contention window size (CWMin). AC with higher priority is assigned a shorter CWMin.
• Maximum contention window size (CWMax).
• TXOP limit. specifies the maximum duration a QSTA can transmit and is specified per AC. The TXOP limit can be used to ensure that high-bandwidth traffic gets greater access to the medium. TXOP limit also makes the channel access protocol significantly more efficient.
• Arbitration Inter-Frame Space (AIFS). Specifies the time interval between the wireless medium becoming idle and the start of channel-access negotiation. Each AC is assigned a different AIFS[AC] based on the AC to further provide QoS differentiation.