CLIguide
The SonicOS Enterprise Command Line Interface (E-CLI) provides a concise and powerful way to configure Dell SonicWALL network security appliances without using the SonicOS Web based management interface. You can use the CLI commands individually on the command line, or in scripts for automating configuration tasks.
This appendix contains a categorized listing of Command Line Interface (CLI) commands for SonicOS 6.2 firmware. Each command is described, and where appropriate, an example of usage is included.
For a listing of Command Line Interface (CLI) commands for SonicOS 6.2 firmware, refer to the SonicOS 6.2 CLI Reference Guide.
This introduction contains the following sections:
• Input Data Format Specification
• Editing and Completion Features
• Logging in to the SonicOS CLI
• Configuring the Dell SonicWALL Network Security Appliance
• Example: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using the CLI
Note The complete SonicWALL CLI Command Reference is included in the SonicOS online help. To access the Command Reference, click the Help button from the SonicOS GUI, and then navigate to Appendices > CLI Guide.
Bold text indicates a command executed by interacting with the user interface.
Courier bold text indicates commands and text entered using the CLI.
Italic text indicates the first occurrence of a new term, as well as a book title, and also emphasized text. In this command summary, items presented in italics represent user-specified information.
Items within angle brackets (“< >”) are required information.
Items within square brackets (“[ ]”) are optional information.
Items separated by a “pipe” (“|”) are options. You can select any of them.
Note Though a command string may be displayed on multiple lines in this guide, it must be entered on a single line with no carriage returns except at the end of the complete command.
Input Data Format Specification
The table below describes the data formats acceptable for most commands. H represents one or more hexadecimal digit (0-9 and A-F). D represents one or more decimal digit.
Table 4
|
Input Data Formats
The firewall name, configurable via the SonicOS Web UI on the System > Administration page, is used in the prompts throughout the CLI, rather than the generic product name like NSA3600 or SM9600.
This allows the administrator to more easily identify which firewall is currently being managed, and to identify which firewalls are being used for which departments in a business structure. For example, the administrator could name several NSA3600s with names like Marketing, Tech Pubs, Engineering, Testing, etc.
If no firewall name is configured, the default is the serial number or MAC address of the device, resulting in a prompt such as:
C0EAE4599008>
In the examples in this document, we use NSA3600 as the configured name of the device and consequently as the prompt in the examples.
Editing and Completion Features
You can use individual keys and control-key combinations to assist you with the CLI. The table below describes the key and control-key combination functions.
Table 5
|
Key Reference
Most configuration commands require completing all fields in the command. For commands with several possible completing commands, the Tab or ? key display all options.
: : : : myDevice> show [TAB]
|
The Tab key can also be used to finish a command if the command is uniquely identified by user input.
myDevice> show al [TAB]
displays
myDevice> show alerts
Additionally, commands can be abbreviated as long as the partial commands are unique. The following text:
myDevice> sho int inf
is an acceptable abbreviation for
myDevice> show interface info
The CLI configuration manager allows you to control hardware and firmware of the appliance through a discreet mode and submode system. The commands for the appliance fit into the logical hierarchy shown below.
To configure items in a submode, activate the submode by entering a command in the mode above it.
For example, to set the default LAN interface speed or duplex, you must first enter configure, then interface x0 lan. To return to the higher Configuration mode, simply enter end or finished.
SonicWALL Internet Security appliances allow easy, flexible configuration without compromising the security of their configuration or your network.
The SonicWALL CLI currently uses the administrator’s password to obtain access. SonicWALL devices are shipped with a default password of password. Setting passwords is important in order to access the SonicWALL and configure it over a network.
If you are unable to connect to your device over the network, you can use the command restore to reset the device to factory defaults during a serial configuration session.
CAUTION The restore command erases all the settings on the appliance, leaving it in a factory default state.
Management Methods for the SonicWALL Network Security Appliance
You can configure the SonicWALL appliance using one of three methods:
• Using a serial connection and the configuration manager
– An IP address assignment is not necessary for appliance management.
– A device must be managed while physically connected via a serial cable.
• Web browser-based User Interface
– An IP address must have been assigned to the appliance for management or use the default of 192.168.168.168.
Initiating a Management Session using the CLI
Serial Management and IP Address Assignment
Follow the steps below to initiate a management session via a serial connection and set an IP address for the device.
Note The default terminal settings on the SonicWALL and modules is 80 columns by 25 lines. To ensure the best display and reduce the chance of graphic anomalies, use the same settings with the serial terminal software. The device terminal settings can be changed, if necessary. Use the standard ANSI setting on the serial terminal software.
1. Attach the included null modem cable to the appliance port marked CONSOLE. Attach the other end of the null modem cable to a serial port on the configuring computer.
2. Launch any terminal emulation application that communicates with the serial port connected to the appliance. Use these settings:
• 115,200 baud
• 8 data bits
• no parity
• 1 stop bit
• no flow control
3. Press Enter/Return. Initial information is displayed followed by a DEVICE NAME> prompt.
Initiating an SSH Management Session via Ethernet
Note This option works for customers administering a device that does not have a cable for console access to the CLI.
Follow the steps below to initiate an SSH management session through an Ethernet connection from a client to the appliance.
1. Attach an Ethernet cable to the interface port marked XO. Attach the other end of the Ethernet cable to an Ethernet port on the configuring computer.
2. Launch any terminal emulation application (such as PuTTY) that communicates via the Ethernet interface connected to the appliance.
3. Within the emulation application, enter the IP destination address for the appliance and enter 22 as the port number.
4. Select SSH as the connection type and open a connection.
When the connection is established, log in to the security appliance:
1. At the User prompt enter the Admin’s username. Only the admin user will be able to login from the CLI. The default Admin username is admin. The default can be changed.
2. At the Password prompt, enter the Admin’s password. If an invalid or mismatched username or password is entered, the CLI prompt will return to User:, and a “CLI administrator login denied due to bad credentials” error message will be logged. There is no lockout facility on the CLI.
Configuring the Dell SonicWALL Network Security Appliance
You can configure the Dell SonicWALL network security appliance using one of three methods:
• Configuring Features using the CLI on a Serial Connection via the Console Port
• Configuring Features using the CLI in an SSH Management Session via Ethernet
• Configuring Features using the Management Interface (Web UI)
Note To use the CLI on a serial connection or in an SSH management session, you need to use a terminal emulation application (such as Tera Term) or an SSH Client application (such as PuTTY). You can find suitable, free terminal emulators on the Internet.
• Configuring Features using the Management Interface (Web UI)
Note To use the CLI on a serial connection or in an SSH management session, you need to use a terminal emulation application (such as Tera Term) or an SSH Client application (such as PuTTY). You can find suitable, free terminal emulators on the Internet.
Configuring Features using the CLI on a Serial Connection via the Console Port
You do not need to assign an IP address to the firewall to use the CLI on a serial connection to the Console port.
Note The default terminal settings on the firewall are 80 columns by 25 lines. To ensure the best display and reduce the chance of graphic anomalies, use the same settings with the serial terminal software. The device terminal settings can be changed, if necessary. Use the standard ANSI setting on the serial terminal software.
To configure features using the CLI on a serial connection via the console port:
1. Attach an RJ-45 to DB-9 serial cable to the appliance port marked CONSOLE. Attach the other end of the cable to a serial port on the configuring computer.
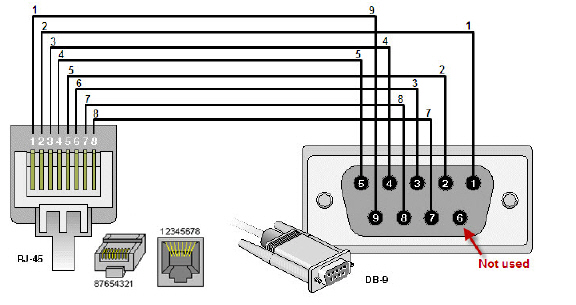
The RJ-45 to DB-9 serial cable pin assignments are as follows:
|
The RJ-45 to DB-9 serial cable pin diagram is shown below:
2. Launch a terminal emulation application that communicates with the serial port connected to the appliance. Use these settings:
• 115,200 baud
• 8 data bits
• no parity
• 1 stop bit
• no flow control
3. Press Enter/Return. Initial information is displayed followed by a DEVICE NAME> prompt.
Configuring Features using the CLI in an SSH Management Session via Ethernet
You can use an SSH client to access the CLI by connecting to the appliance with an Ethernet cable. This option is useful for customers that do not have access to an RJ-45 to DB-9 serial cable for the Console port on the firewall.
To use SSH management, you must assign an IP address to X0 (LAN) or X1 (WAN), or use the default LAN IP address of 192.168.168.168.
To configure features using the CLI in an SSH management session via Ethernet:
1. Attach an Ethernet cable to the interface port marked X0. Attach the other end of the Ethernet cable to an Ethernet port on the configuring computer.
2. Launch a terminal emulation application or SSH client that communicates via Ethernet.
3. In the emulation application, enter the IP destination address for the X0 interface and enter 22 as the port number.
4. Select SSH as the connection type and open a connection.
Configuring Features using the Management Interface (Web UI)
You can manage the appliance securely from your Web browser using HTTPS by connecting to either the LAN or WAN IP address of the appliance, directly or over the network.
There are a number of features in SonicOS that cannot be configured using the CLI. The following features can only be configured in the SonicOS management interface (Web UI):
|
SafeMode
SafeMode is a limited Web management interface that provides a way to upload firmware from your computer and reboot the appliance.
The SafeMode feature allows you to recover quickly from uncertain configuration states with a simplified management interface that includes the same settings available on the System > Settings page.
For instructions on how to restart your firewall in SafeMode, refer to Using SafeMode to Upgrade Firmwareor see the Getting Started Guide for your appliance.
Note You cannot use the CLI commands in SafeMode.
Example: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using the CLI
This section describes how to create a VPN policy using the Command Line Interface. You can configure all of the parameters using the CLI, and enable the VPN without using the Web management interface.
Note In this example, the VPN policy on the other end has already been created.
CLI Access
1. Use a DB9 to RJ45 connector to connect the serial port of your PC to the console port of your firewall.
2. Using a terminal emulator program (such as PuTTY or Tera Term) use the following parameters:
• 115,200 baud
• 8 bits
• No parity
• 1 stop bit
• No flow control
3. You may need to hit return two to three times to get to a command prompt, which will look similar to the following:
• NSA3600>
or
• SM9200>
4. If you have used any other CLI, such as Unix shell or Cisco IOS, this process should be relatively easy and similar. It has auto-complete so you do not have to type in the entire command.
5. When you need to make a configuration change, you must be in configure mode. To enter configure mode, type configure.
• NSA3600> configure
• (config[NSA3600])>
6. The command prompt changes and adds the word config to distinguish it from the normal mode. Now you can configure all the settings, enable and disable the VPNs, and configure the firewall.
Configuration
In this example, a site-to-site VPN is configured between two NSA 3600 appliances, with the following settings:
Local NSA 3600 (home):
WAN IP: 10.50.31.150
LAN subnet: 192.168.61.0
Mask 255.255.255.0
Remote NSA 3600 (office):
WAN IP: 10.50.31.104
LAN subnet: 192.168.15.0
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Authentication Method: IKE using a Pre-Shared Key
Phase 1 Exchange: Main Mode
Phase 1 Encryption: 3DES
Phase 1 Authentication SHA1
Phase 1 DH group: 2
Phase 1 Lifetime: 28800
Phase 2 Protocol: ESP
Phase 2 Encryption: 3DES
Phase 2 Authentication: SHA1
Phase 2 Lifetime: 28800
No PFS
1. In configure mode, create an address object for the remote network, specifying the name, zone assignment, type, and address. In this example, we use the name OfficeLAN:
(config[NSA3600]> address-object Office LAN
(config-address-object[OfficeLAN])>
Note The prompt has changed to indicate the configuration mode for the address object.
(config-address-object[OfficeLAN])> zone VPN
(config-address-object[OfficeLAN])> network 192.168.15.0 255.255.255.0
(config-address-object[OfficeLAN])> finished
2. To display the address object, type the command show address-object [name]:
NSA3600 > show address-object OfficeLAN
The output will be similar to the following:
address-object OfficeLAN
network 192.168.15.0 255.255.255.0
zone VPN
3. To create the VPN policy, type the command:
vpn policy [name] [authentication method]
(config[NSA3600])> vpn policy OfficeVPN pre-shared
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])>
Note The prompt changes to indicate the configuration mode for the VPN policy. All the settings regarding this VPN will be entered here.
4. Configure the Pre-Shared Key. In this example, the Pre-Shared Key is sonicwall:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> pre-shared-secret sonicwall
5. Configure the IPSec gateway:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> gw ip-address 10.50.31.104
6. Define the local and the remote networks:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> network local address-object "LAN Primary Subnet"
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> network remote address-object "OfficeLAN"
7. Configure the IKE and IPSec proposals:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> proposal ike main encr triple-des auth sha1 dh 2
: lifetime 28800
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> proposal ipsec esp encr triple-des auth sha1 dh no
: lifetime 28800
8. In the Advanced tab in the UI configuration, enable keepalive on the VPN policy:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> advanced keepalive
9. To enable the VPN policy, use the command vpn enable [name]:
(config[NSA3600])> vpn enable "OfficeVPN"
10. Use the finished command to save the VPN policy and exit from the VPN configure mode:
(config-vpn[OfficeVPN])> finished
(config[NSA3600])>
The configuration is complete.
Note The command prompt goes back to the configure mode prompt.
Viewing a VPN Configuration
To view a list of all the configured VPN policies:
1. Type the command show vpn policy. The output will be similar to the following:
(config[NSA3600])> show vpn policy
Policy: WAN GroupVPN (Disabled)
Key Mode: Pre-shared
Pre Shared Secret: DE65AD2228EED75A
Proposals:
IKE: Aggressive Mode, 3DES SHA, DH Group 2, 28800 seconds
IPSEC: ESP, 3DES SHA, No PFS, 28800 seconds
Advanced:
Allow NetBIOS OFF, Allow Multicast OFF
Management: HTTP OFF, HTTPS OFF
Lan Default GW: 0.0.0.0
Require XAUTH: ON, User Group: Trusted Users
Client:
Cache XAUTH Settings: Never
Virtual Adapter Settings: None
Allow Connections To: Split Tunnels
Set Default Route OFF, Apply VPN Access Control List OFF
Require GSC OFF
Use Default Key OFF
Policy: OfficeVPN (Enabled)
Key Mode: Pre-shared
Primary GW: 10.50.31.104
Secondary GW: 0.0.0.0
Pre Shared Secret: sonicwall
IKE ID:
Local: IP Address
Peer: IP Address
Network:
Local: LAN Primary Subnet
Remote: OfficeLAN
Proposals:
IKE: Main Mode, 3DES SHA, DH Group 2, 28800 seconds
IPSEC: ESP, 3DES SHA, No PFS, 28800 seconds
Advanced:
Keepalive ON, Add Auto-Rule ON, Allow NetBIOS OFF
Allow Multicast OFF
Management: HTTP ON, HTTPS ON
User Login: HTTP ON, HTTPS ON
Lan Default GW: 0.0.0.0
Require XAUTH: OFF
Bound To: Zone WAN
2. To view the configuration for a specific policy, specify the policy name in double quotes.
For example:
(config[NSA3600])> show vpn policy "OfficeVPN"
The output will be similar to the following:
Policy: OfficeVPN (Enabled)
Key Mode: Pre-shared
Primary GW: 10.50.31.104
Secondary GW: 0.0.0.0
Pre Shared Secret: sonicwall
IKE ID:
Local: IP Address
Peer: IP Address
Network:
Local: LAN Primary Subnet
Remote: OfficeLAN
Proposals:
IKE: Main Mode, 3DES SHA, DH Group 2, 28800 seconds
IPSEC: ESP, 3DES SHA, No PFS, 28800 seconds
Advanced:
Keepalive ON, Add Auto-Rule ON, Allow NetBIOS OFF
Allow Multicast OFF
Management: HTTP ON, HTTPS ON
User Login: HTTP ON, HTTPS ON
Lan Default GW: 0.0.0.0
Require XAUTH: OFF
Bound To: Zone WAN
3. Type the command show vpn sa [name] to see the active SA:
(config[NSA3600])> show vpn sa "OfficeVPN"
Policy: OfficeVPN
IKE SAs
GW: 10.50.31.150:500 --> 10.50.31.104:500
Main Mode, 3DES SHA, DH Group 2, Responder
Cookie: 0x0ac298b6328a670b (I), 0x28d5eec544c63690 (R)
Lifetime: 28800 seconds (28783 seconds remaining)
IPsec SAs
GW: 10.50.31.150:500 --> 10.50.31.104:500
(192.168.61.0 - 192.168.61.255) --> (192.168.15.0 - 192.168.15.255)
ESP, 3DES SHA, In SPI 0xed63174f, Out SPI 0x5092a0b2
Lifetime: 28800 seconds (28783 seconds remaining)
| best-effort | Commits only valid configuration (best effort). |
| terminal | Terminal. |
| size | Command history buffer size. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| json | Render all CLI output as JSON. |
| plain-text | Render all CLI output as plain-text. |
| xml | Render all CLI output as XML. |
| <CLI_IDLE_TIMEOUT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Max: 60 Example: 5 |
| <CLI_IDLE_TIMEOUT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Max: 60 Example: 5 |
| <CLI_SCREEN_WIDTH> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Min: 80 Max: 2560 Example: 80 |
| <CLI_SCREEN_WIDTH> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Min: 80 Max: 2560 Example: 80 |
| <CLI_SCREEN_LENGTH> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Min: 24 Max: 1600 Example: 24 |
| <CLI_SCREEN_LENGTH> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Min: 24 Max: 1600 Example: 24 |
| default | Default setting (changes take effect upon next login). |
| session | Apply to the current session. |
| default | Default setting (changes take effect upon next login). |
| session | Apply to the current session. |
| default | Default setting (changes take effect upon next login). |
| session | Apply changes to the current session. |
| default | Default setting (changes take effect upon next login). |
| session | Apply changes to the current session. |
| load | Page load. |
| update | Page update. |
| popup | Popup. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| connection | Configure connection banner |
| login | Configure login banner |
| logout | Configure logout banner |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| connection | Clear connection banner |
| login | Clear login banner |
| logout | Clear logout banner |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| banner | Show CLI Banner. |
| data-model | Display data model debug information. |
| group | Group ID. |
| <INT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| tag | CGI tag name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| data-store | Display data store debug information. |
| group | Group ID. |
| <INT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| debug | Display CLI debug information. |
| ftp | Display CLI FTP configuration. |
| history | Show a list of recent keywords issued. |
| top | Show the specified number of recent keywords issued. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| idle-timeout | Show idle timeout. |
| interactive-prompts | show cli interactive prompts. |
| mode | Show CLI mode command table. |
| all | Show all CLI mode command tables. |
| current | Show current CLI mode command table. |
| name | Show CLI mode command table by name. |
| <CDL_MODE_NAME> |
CDL Mode name. Example: config_mode |
| exclude | Exclude options. |
| global | Exclude globally available commands. |
| include | Include options. |
| cgi-nvp | Include CGI tag name and configuration value. |
| submodes | Include sub-modes. |
| pager | Show tty pager. |
| rest-api | Show CLI REST-API configuration or status. |
| screen-length | Show screen length. |
| screen-width | Show screen width. |
| show-api | Display Show command API debug information. |
| show-unmodified | Show unmodified settings. |
| staging-area | Display staging area debug information. |
| command-hash | Display only the command hash. |
| current-mode | Display only the current mode. |
| token-types | Display token type debug information. |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| interface | Route ping request through the specified interface. |
| <WAN_MGMT_INTERFACE> |
WAN interface name. Example: X1 |
| ipv6-preferred | Prefer to use IPv6 network. |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| interface | Route traceroute request through the specified interface. |
| <WAN_MGMT_INTERFACE> |
WAN interface name. Example: X1 |
| ipv6-preferred | Prefer to use IPv6 network. |
| <IP_V4V6_HOST> |
IPV4: address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652 |
| <IP_V4V6_HOST> |
IPV4: address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652 |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| ipv6 | DNS lookup IPv6 host. |
| ipv4-dns | IPv4 DNS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ipv6-dns | IPv6 DNS server. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| ipv6 | DNS lookup IPv6 host. |
| ipv4-dns | IPv4 DNS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ipv6-dns | IPv6 DNS server. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| ipv6 | DNS lookup IPv6 host. |
| ipv4-dns | IPv4 DNS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ipv6-dns | IPv6 DNS server. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| ip | RBL IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| domain | RBL domain name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| dns-server | RBL DNS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ip | RBL IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| domain | RBL domain name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| dns-server | RBL DNS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| port | Specified the SMTP port. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| port | Specified the SMTP port. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| interface | Path MTU discovery request through the specified interface. |
| <WAN_MGMT_INTERFACE> |
WAN interface name. Example: X1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| verbose | Verbose. |
| current | Current tracelog. |
| last | Last tracelog. |
| <INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| top | Maximum alerts to display. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| top | Maximum entries to display. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ip | Start ping test at specified host IP. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| log | Log ping test. |
| stop | Stop ping test. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| all | All. |
| current | Current. |
| last | Last. |
| amount | Set limit of gratuitous ARPs in any 60 second period. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| interval | Set the interval for periodically broadcast system ARPs in minutes. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| maximum | Set the maximum allowed advertised TCP window with any DPI-based service enabled. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| val | Set the optimal value. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| primary | Primary local CFS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary local CFS server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| info | Reset client CF enforcement info. |
| cache | Reset client CF enforcement cache. |
| host | Private cloud AV server IP or name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ssl-v23 | ssl version23. |
| ssl-v3 | ssl version3.0. |
| tls-v1 | tls version1.0. |
| aes128-sha1 | AES128_SHA1 cipermethod. |
| aes256-sha1 | AES256-SHA1 ciper method. |
| default | Default cipher method. |
| rc4-md5 | RC4-MD5 cipermethod. |
| tripldes-sha1 | 3DES-SHA1 cipermethod. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| default | Use the default global help system URL. |
| override | Override the default using the configured value. |
| url | Set URL. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| sso-auth-log | Log in in memory to download as ssoAuthLog.wri. |
| buffer-full | When buffer is full. |
| stop | When buffer is full, stop logging. |
| wrap | Enable including SSO polling, wrap logging. |
| max-buffer | Max buffer size. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| event-log | Log in the event log. |
| all | All. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| error | Error. |
| fatal | Fatal. |
| info | Info. |
| verbose | Verbose. |
| warning | Warning. |
| every | Set number of minutes to auto-restart system. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| all | All types. |
| sonicpoint-only | Only support sonicpoint. |
| sonicpointn-only | Only support sonicpointn. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| extremely-high | Extremely high. |
| extremely-low | Extremely low. |
| high | High. |
| low | Low. |
| medium | Medium. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| auto-resolve | Resolve automatically. |
| static-ip | Use this static IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| any | Any interface. |
| interface | Set interface. |
| <ASSIGNED_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| failed-proxied-connection | Set temporarily bypass TCP acceleration for failed proxied connections (minutes). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| short-lived-proxied-connection | Set temporarily bypass TCP acceleration for short-lived proxied connections (minutes). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| failed-proxied-connection | Set temporarily bypass TCP acceleration for failed proxied connections (minutes). |
| short-lived-proxied-connection | Set temporarily bypass TCP acceleration for short-lived proxied connections (minutes). |
| always | Always use this IP for geoipdata.global.sonicwall.com. |
| failed-resolution | Use if geoipdata.global.sonicwall.com does not resolve. |
| default | Set the IP address to the default setting. |
| ip | Specify the IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| node | Per node GMSFlow server. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| ip-addr | GMSFlow server address for each node. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| node | Per node GMSFlow server. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| ip-addr | GMSFlow server address for each node. |
| ip | Use this IP address for App reports upload. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| sonicwall | Connect to appreports.global.sonicwall.com. |
| interval | Main log process reschedule interval. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| app-data | App data. |
| html | HTML. |
| libpcap | LibPcap. |
| text | Text. |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| http | HTTP/HTTPS. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| http | HTTP/HTTPS. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| gms-server | GMS server. |
| syslog-servers | Sylog servers. |
| gms-server | GMS server. |
| syslog-servers | Sylog servers. |
| ha | High availability. |
| sonicpoint | SonicPoint. |
| ha | High availability. |
| sonicpoint | SonicPoint. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| consumed | Consumed. |
| dropped | Dropped. |
| forwarded | Forwarded. |
| consumed | Consumed. |
| dropped | Dropped. |
| forwarded | Forwarded. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| consumed | Consumed. |
| dropped | Dropped. |
| forwarded | Forwarded. |
| generated | Generated. |
| consumed | Consumed. |
| dropped | Dropped. |
| forwarded | Forwarded. |
| generated | Generated. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| fragmented | Enable monitoring of intermediate fragmented traffic. |
| iphelper | Enable monitoring of intermediate IP helper traffic. |
| ipsec | Enable monitoring of intermediate IPSEC traffic. |
| ldap-over-tls | Enable monitoring of intermediate decrypted LDAP over TLS traffic. |
| multicast | Enable monitoring of intermediate multicast traffic. |
| reassembled | Enable monitoring of intermediate reassembled traffic. |
| remote-mirrored | Enable monitoring of intermediate remote mirrored traffic. |
| ssl | Enable monitoring of intermediate SSL decrypted traffic. |
| sso-agent | Enable monitoring of intermediate decrypted Single Sign On agent messages. |
| fragmented | Disable monitoring of intermediate fragmented traffic. |
| iphelper | Disable monitoring of intermediate IP helper traffic. |
| ipsec | Disable monitoring of intermediate IPSEC traffic. |
| ldap-over-tls | Disable monitoring of intermediate decrypted LDAP over TLS traffic. |
| multicast | Disable monitoring of intermediate multicast traffic. |
| reassembled | Disable monitoring of intermediate reassembled traffic. |
| remote-mirrored | Disable monitoring of intermediate remote mirrored traffic. |
| ssl | Disable monitoring of intermediate SSL decrypted traffic. |
| sso-agent | Disable monitoring of intermediate decrypted Single Sign On agent messages. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <CONFIGURABLE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <CONFIGURABLE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| current | Current users. |
| detail | Detail of users. |
| inactive | Include inactive of users. |
| current | Current users. |
| detail | Detail of users. |
| inactive | Include inactive of users. |
| interval | Specify backup interval. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ipv6 | IPv6 |
| from | Source zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| ipv6 | IPv6 |
| from | Source zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| anti-spam | Anti-Spam settings. |
| arp | ARP settings. |
| backend | Backend Server settings. |
| control-plane | Control Plane Master/Slaves Monitoring and Diagnostics settings. |
| dhcp | DHCP settings. |
| diagnostics | Diagnostics settings. |
| dial-up | Dial-up settings. |
| dpi-ssl | DPI-SSL settings. |
| encryption | Encryption settings |
| firewall | Firewall settings. |
| flow-reporting | Flow Reporting settings. |
| geoip-location-service | GeoIP/Location Service settings. |
| high-availability | High Availability settings. |
| management | Management settings. |
| network | Network settings. |
| pppoe | PPPoE settings. |
| preference | Preference Conversion settings. |
| security-service | Security Services settings. |
| ssl-vpn | SSL-VPN settings. |
| user-authentication | User Authentication settings. |
| voip | VoIP settings. |
| vpn | VPN settings. |
| watchdog | Watchdog settings. |
| wireless | Wireless settings. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| packet | Show one captured packet with detail. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| packets | Show all captured packets in list. |
| statistics | Show packet monitor statistics. |
| access-rules | Access rules technical support report. |
| active-utm | Active-active UTM technical support report. |
| address-objects | Address object table technical support report. |
| anti-spam | Anti-spam technical support report. |
| anti-virus | AV technical support report. |
| arp-cache | ARP cache technical support report. |
| cache-check | Cache check technical support report. |
| content-filtering | CFL technical support report. |
| data-plane-task-jobs | Data plane task jobs technical support report. |
| db-trace | DB trace dump technical support report. |
| dhcp-client | DHCP client technical support report. |
| dhcp-network-disc | DHCP network discovery technical support report. |
| dhcp-persistence | DHCP persistence technical support report. |
| dhcp-relay | DHCP relay technical support report. |
| dhcp-server | DHCP server technical support report. |
| dhcp-serverstat | DHCP server stats technical support report. |
| diag | Diagnostics technical support report. |
| dpi-ssl | DPI SSL technical support report. |
| client | DPI SSL client technical support report. |
| server | DPI SSL server technical support report. |
| dynamic-dns | Dynamic dns technical support report. |
| ethernet | Ethernet technical support report. |
| flight-data-recorder | Flight data recorder technical support report. |
| gateway-anti-virus | Global anti-virus technical support report. |
| guest-profile-objects | Guest profile objects technical support report. |
| h323 | H.323 technical support report. |
| high-availability | HA technical support report. |
| hypervisor | Hypervisor technical support report. |
| interfaces | Interfaces technical support report. |
| intrusion-detection-prevention | IDP technical support report. |
| ip-helper | IP helper technical support report. |
| ip-reassembly | IP fragment reassembly technical support report. |
| ipsec | IPSec technical support report. |
| l2tp-client | L2tp client technical support report. |
| l2tp-server | L2tp server technical support report. |
| ldap | LDAP technical support report. |
| license | License technical support report. |
| management | Management technical support report. |
| mirror-state | Flash prefs mirror state technical support report. |
| msn | MSN technical support report. |
| multicast | Mcast igmp config technical support report. |
| nat-policies | NAT policies technical support report. |
| network | Network technical support report. |
| objects | Network objects technical support report. |
| options | Options of technical support report. |
| pki | PKI technical support report. |
| pppoe-client | PPPoE client technical support report. |
| pptp-client | PPTP client technical support report. |
| pref-stats | Flash prefs load/save technical support report. |
| product | Product technical support report. |
| qos | QOS technical support report. |
| radius | Radius technical support report. |
| route-policies | Detailed route policy table technical support report. |
| routes | Routing table. |
| rtsp | RTSP technical support report. |
| schedule-objects | Service object table technical support report. |
| service-objects | Service object table technical support report. |
| single-sign-on | Single sign on technical support report. |
| sip | SIP technical support report. |
| snmp | Snmp technical support report. |
| sonicpoint | Sonicpoint technical support report. |
| ssl-control | SSL control technical support report. |
| stateful-stats | Stateful stats technical support report. |
| stateful-sync | Stateful sync technical support report. |
| status | Status technical support report. |
| svrrp | SVRRP technical support report. |
| time | Time technical support report. |
| timers | Timers technical support report. |
| update | Update technical support report. |
| user-objects | User object table technical support report. |
| users | Users technical support report. |
| vx-net-stats | Vxworks network status technical support report. |
| wan-load-balancing | WLB technical support report. |
| wire-mode | Wire mode technical support report. |
| wlan-zone | Wlan zone technical support report. |
| zone-objects | Zone object table technical support report. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| fqdn | Delete all custom FQDN address objects. |
| host | Delete all custom host address objects. |
| mac | Delete all custom MAC address objects. |
| network | Delete all custom network address objects. |
| range | Delete all custom range address objects. |
| fqdn | Purge a FQDN address object. |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| mac | Purge a MAC address object. |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| zone | Address object zone. |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| zone | Address object zone. |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| address | MAC address. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| zone | Address object zone. |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| domain | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| zone | Address object zone. |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| ipv4 | Delete all IPV4 address groups. |
| ipv6 | Delete all IPV6 address groups. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_PREFIX_LEN> |
Network prefix length in decimal or CIDR form: D OR /D. Max: 128 Example: 128 |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| mixed | Set for both recurring schedule and single occurrence. |
| once | Set for single occurrence. |
| recurring | Set for recurring schedule. |
| <TIME_YYYYMMDDHHMMSS> |
Timestamp in the form: YYYY:MM:DD:HH:MM:SS. Example: 2010:06:30:23:30:59 |
| <TIME_YYYYMMDDHHMMSS> |
Timestamp in the form: YYYY:MM:DD:HH:MM:SS. Example: 2010:06:30:23:30:59 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| sun | Day of the week. |
| mon | Day of the week. |
| tue | Day of the week. |
| wed | Day of the week. |
| thu | Day of the week. |
| fri | Day of the week. |
| sat | Day of the week. |
| all | Everyday. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| sun | Day of the week. |
| mon | Day of the week. |
| tue | Day of the week. |
| wed | Day of the week. |
| thu | Day of the week. |
| fri | Day of the week. |
| sat | Day of the week. |
| all | Everyday. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| 6over4 | Service object 6over4. |
| ah | Service object AH. |
| custom | Custom service object. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| eigrp | Service object EIGRP. |
| esp | Service object ESP. |
| gre | Service object GRE. |
| icmp | Service object ICMP. |
| address-mask-reply | ICMP with sub-type of address mask reply. |
| address-mask-request | ICMP with sub-type of address mask request. |
| datagram-error | ICMP with sub-type of datagram error. |
| destination-unreachable | ICMP with sub-type of destination unreachable. |
| domain-name | ICMP with sub-type of domain name. |
| domain-name-reply | ICMP with sub-type of domain name reply. |
| echo-reply | ICMP with sub-type of echo reply. |
| echo-request | ICMP with sub-type of echo request. |
| info-reply | ICMP with sub-type of info reply. |
| info-request | ICMP with sub-type of info request. |
| none | ICMP with sub-type of none. |
| parameter-problem | ICMP with sub-type of parameter problem. |
| redirect | ICMP with sub-type of redirect. |
| router-advertise | ICMP with sub-type of router advertise. |
| router-solicit | ICMP with sub-type of router solicit. |
| source-quench | ICMP with sub-type of source quench. |
| time-exceeded | ICMP with sub-type of time exceeded. |
| timestamp | ICMP with sub-type of timestamp. |
| timestamp-reply | ICMP with sub-type of timestamp reply. |
| traceroute | ICMP with sub-type of traceroute. |
| icmpv6 | Service object ICMPV6/ND. |
| destination-unreachable | ICMPV6 with sub-type of destination unreachable. |
| echo-reply | ICMPV6 with sub-type of echo reply. |
| echo-request | ICMPV6 with sub-type of echo request. |
| neighbour-advertisement | ICMPV6 with sub-type of neighbour advertisement. |
| neighbour-solicitation | ND with sub-type of neighbour solicitation. |
| none | ICMPV6 with sub-type of none. |
| packet-too-big | ICMPV6 with sub-type of packet too big. |
| parameter-problem | ICMPV6 with sub-type of parameter problem. |
| redirect | ND with sub-type of redirect. |
| router-advertisement | ND with sub-type of router advertisement. |
| router-solicitation | ND with sub-type of router solicitation. |
| time-exceeded | ICMPV6 with sub-type of time exceeded. |
| igmp | Service object IGMP. |
| leave-group | IGMP with sub-type of leave group. |
| member-query | IGMP with sub-type of member query. |
| none | IGMP with sub-type of none. |
| v1-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v1 member report. |
| v2-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v2 member report. |
| v3-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v3 member report. |
| ipcomp | Service object IPCOMP. |
| l2tp | Service object l2tp. |
| ospf | Service object OSPF. |
| database-description | OSPF with sub-type of database description. |
| hello | OSPF with sub-type of hello. |
| link-state-acknowledge | OSPF with sub-type of link state acknowledge. |
| link-state-request | OSPF with sub-type of link state request. |
| link-state-update | OSPF with sub-type of link state update. |
| none | OSPF with sub-type of none. |
| pim | Service object PIM. |
| assert | PIM with sub-type of assert. |
| bootstrap | PIM with sub-type of bootstrap. |
| candidate-rp | PIM with sub-type of candidate rp. |
| graft | PIM with sub-type of graft. |
| graft-acknowledge | PIM with sub-type of graft acknowledge. |
| hello | PIM with sub-type of hello. |
| join-prune | PIM with sub-type of join/prune. |
| none | PIM with sub-type of none. |
| register | PIM with sub-type of register. |
| register-stop | PIM with sub-type of register stop. |
| state-refresh | PIM with sub-type of state refresh. |
| tcp | Service object TCP. |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| udp | Service object UDP. |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| address-mask-reply | ICMP with sub-type of address mask reply. |
| address-mask-request | ICMP with sub-type of address mask request. |
| datagram-error | ICMP with sub-type of datagram error. |
| destination-unreachable | ICMP with sub-type of destination unreachable. |
| domain-name | ICMP with sub-type of domain name. |
| domain-name-reply | ICMP with sub-type of domain name reply. |
| echo-reply | ICMP with sub-type of echo reply. |
| echo-request | ICMP with sub-type of echo request. |
| info-reply | ICMP with sub-type of info reply. |
| info-request | ICMP with sub-type of info request. |
| none | ICMP with sub-type of none. |
| parameter-problem | ICMP with sub-type of parameter problem. |
| redirect | ICMP with sub-type of redirect. |
| router-advertise | ICMP with sub-type of router advertise. |
| router-solicit | ICMP with sub-type of router solicit. |
| source-quench | ICMP with sub-type of source quench. |
| time-exceeded | ICMP with sub-type of time exceeded. |
| timestamp | ICMP with sub-type of timestamp. |
| timestamp-reply | ICMP with sub-type of timestamp reply. |
| traceroute | ICMP with sub-type of traceroute. |
| leave-group | IGMP with sub-type of leave group. |
| member-query | IGMP with sub-type of member query. |
| none | IGMP with sub-type of none. |
| v1-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v1 member report. |
| v2-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v2 member report. |
| v3-member-report | IGMP with sub-type of v3 member report. |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination-unreachable | ICMPV6 with sub-type of destination unreachable. |
| echo-reply | ICMPV6 with sub-type of echo reply. |
| echo-request | ICMPV6 with sub-type of echo request. |
| neighbour-advertisement | ICMPV6 with sub-type of neighbour advertisement. |
| neighbour-solicitation | ND with sub-type of neighbour solicitation. |
| none | ICMPV6 with sub-type of none. |
| packet-too-big | ICMPV6 with sub-type of packet too big. |
| parameter-problem | ICMPV6 with sub-type of parameter problem. |
| redirect | ND with sub-type of redirect. |
| router-advertisement | ND with sub-type of router advertisement. |
| router-solicitation | ND with sub-type of router solicitation. |
| time-exceeded | ICMPV6 with sub-type of time exceeded. |
| database-description | OSPF with sub-type of database description. |
| hello | OSPF with sub-type of hello. |
| link-state-acknowledge | OSPF with sub-type of link state acknowledge. |
| link-state-request | OSPF with sub-type of link state request. |
| link-state-update | OSPF with sub-type of link state update. |
| none | OSPF with sub-type of none. |
| assert | PIM with sub-type of assert. |
| bootstrap | PIM with sub-type of bootstrap. |
| candidate-rp | PIM with sub-type of candidate rp. |
| graft | PIM with sub-type of graft. |
| graft-acknowledge | PIM with sub-type of graft acknowledge. |
| hello | PIM with sub-type of hello. |
| join-prune | PIM with sub-type of join/prune. |
| none | PIM with sub-type of none. |
| register | PIM with sub-type of register. |
| register-stop | PIM with sub-type of register stop. |
| state-refresh | PIM with sub-type of state refresh. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| encrypted | VPN zone. |
| management | Management zone. |
| public | Public zone. |
| sslvpn | SSLVPN zone. |
| trusted | Trusted zone. |
| untrusted | WAN/MULTICAST zone. |
| wireless | Wireless zone. |
| allow-from-higher | Allow traffic from zones with higher trust level. |
| allow-from-to-equal | Allow traffic between zones with the same trust level. |
| allow-to-lower | Allow traffic to zones with lower trust level. |
| deny-from-lower | Deny traffic from zones with lower trust level. |
| allow-from-higher | Allow traffic from zones with higher trust level. |
| allow-from-to-equal | Allow traffic between zones with the same trust level. |
| allow-to-lower | Allow traffic to zones with lower trust level. |
| deny-from-lower | Deny traffic from zones with lower trust level. |
| policy | Specify a content filtering services policy. |
| <CFS_POLICY_NAME> | CFS policy name. |
| anti-virus | Enable client anti-virus enforcement service. |
| content-filtering | Enable client content filtering services enforcement service. |
| anti-virus | Disable client anti-virus enforcement service. |
| content-filtering | Disable client content filtering services enforcement service. |
| anti-virus | Enable bypass anti-virus check for guests. |
| content-filtering | Enable bypass client content filtering check for guests. |
| anti-virus | Disable bypass anti-virus check for guests. |
| content-filtering | Disable bypass client content filtering check for guests. |
| http | Set protocol HTTP. |
| https | Set protocol HTTPS. |
| http | Set protocol HTTP. |
| https | Set protocol HTTPS. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | Configure the external web server IP addresses or hostname. |
| <ADDR_FQDNHOST_ADDR> |
FQDN/host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| name | Configure webserver to named address object. |
| <ADDR_FQDNHOST_ADDR> |
FQDN/host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| port | Configure the external web server port. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| method | Set external message authentication method. |
| md5 | Use HMAC - MD5 authentication. |
| sha1 | Use HMAC - SHA1 authentication. |
| shared-secret | Set external message authentication shared secret. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| confirm-secret | Confirm external message authentication shared secret. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| custom | Set a custom Web content redirect message. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| use-default | Use the default Web content redirect message. |
| custom | Set a custom Web content server down message. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| use-default | Use the default Web content server down message. |
| every | Set auto-logout expired session every (minutes). |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| cgi | Set logout CGI. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| every | Set check server status every (minutes). |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| cgi | Set server status CGI. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| every | Set synchronize every (minutes). |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| cgi | Set session sync CGI. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| all | All MAC addresses. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_MAC_GROUP> |
MAC group address object name. Example: Sales & Marketing Network Access Points |
| mac | MAC address. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | MAC address object name. |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| host | Set the SMTP server to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the SMTP server as named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Set the denied networks as named address group. |
| <ADDR_FHNR_GROUP> |
FQDN/host/network/range group address object name. Example: Web Server Group |
| host | Set the denied networks to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the denied networks as named address object. |
| <ADDR_FHNR_NAME> |
FQDN/host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set the denied networks to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set the denied networks to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Set the pass networks as named address group. |
| <ADDR_FHNR_GROUP> |
FQDN/host/network/range group address object name. Example: Web Server Group |
| host | Set the pass networks to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the pass networks as named address object. |
| <ADDR_FHNR_NAME> |
FQDN/host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set the pass networks to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set the pass networks to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| text | Use configured text for custom login page footer. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| url | Use configured url location for custom page footer. |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| text | Use configured text for custom login page header. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| url | Use configured url location for custom login page header. |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| server | Set the SSLVPN server as a named address object. |
| host | Set the SSLVPN server to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the SSLVPN server as named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| service | Set the SSLVPN service as a named service object. |
| name | Set the SSLVPN service as named service object. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Set the SSLVPN service as a protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| exception-service | Specify services that are allowed to bypass wifisec enforcement. |
| name | Name of service object for the exception service. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Set the WiFiSec exception service as a protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| exception-service | Disable WiFiSec enforcement exception service. |
| fqdn | Show FQDN address objects. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPV4 address objects. |
| host | Show host address objects. |
| network | Show network address objects. |
| range | Show range address objects. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPV6 address objects. |
| host | Show host address objects. |
| network | Show network address objects. |
| range | Show range address objects. |
| mac | Show MAC address objects. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_MAC_NAME> |
MAC address object name. Example: Sales Network Access Point |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPV4 address groups. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPV6 address groups. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| all | Show all Schedule Objects. |
| mixed | Show all Schedule Objects set for both recurring schedule and single occurrence. |
| once | Show all Schedule Objects set for single occurrence. |
| recurring | Show all Schedule Objects set for recurring. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| 6over4 | Show 6over4 service objects. |
| ah | Show AH service objects. |
| eigrp | Show EIGRP service objects. |
| esp | Show ESP service objects. |
| gre | Show GRE service objects. |
| icmp | Show ICMP service objects. |
| icmpv6 | Show ICMPV6 service objects. |
| igmp | Show IGMP service objects. |
| l2tp | Show l2tp service objects. |
| ospf | Show OSPF service objects. |
| pim | Show PIM service objects. |
| tcp | Show TCP service objects. |
| udp | Show UDP service objects. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show zones status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| status | Show a zone status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| ipv4 | Reset interface IPv4 statistics. |
| ipv6 | Reset interface IPv6 statistics. |
| statistics | Reset interface statistics. |
| ipv6 | Configure interface IPv6 parameters. |
| <CONFIGURABLE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| vlan | Configure VLAN sub-interface. |
| <VLAN_TAG> |
VLAN tag. Example: 23 |
| <CONFIGURABLE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| vlan | Configure VLAN sub-interface. |
| <VLAN_TAG> |
VLAN tag. Example: 23 |
| ipv6 | Renew interface DHCPv6 lease. |
| <DHCP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| ipv6 | Release interface DHCPv6 lease. |
| <DHCP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <CONNECT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <CONNECT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| auto-negotiate | Set interface link speed to auto-negotiate. |
| full | Full duplex. |
| 10 | Set interface link speed to 10 Mbps-full duplex. |
| 100 | Set interface link speed to 100 Mbps-full duplex. |
| 1000 | Set interface link speed to 1000 Mbps-full duplex. |
| 10000 | Set interface link speed to 10 Gbps(10000 Mbps)-full duplex. |
| half | Half duplex. |
| 10 | Set interface link speed to 10 Mbps-half duplex. |
| 100 | Set interface link speed to 100 Mbps-half duplex. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <DECIMAL> |
Decimal in the form: n+.n+. Example: 0.999 |
| <DECIMAL> |
Decimal in the form: n+.n+. Example: 0.999 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| default | Factory configured MAC. |
| override | Override factory configured MAC. |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| background | 1-Background. |
| best-effort | 0-Best effort. |
| controlled-load | 4-Controlled load. |
| excellent-effort | 3-Excellent effort. |
| network-control | 7-Network control. |
| spare | 2-Spare. |
| video | 5-Video(<100ms latency). |
| voice | 6-Voice(<10ms latency). |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <PORT_GROUP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <PORT_GROUP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <PORT_GROUP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| any | Use any interface. |
| interface | Specify interface. |
| <PHYS_WAN_INTERFACE> |
WAN interface name. Example: X1 |
| <SONICPOINT_LIMIT> |
SonicPoint limit per interface. Example: 8 |
| dynamic | Dynamically reserve SonicPoint address. |
| manual | Manually reserve SonicPoint address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| <INTERFACE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| dhcp | IP address obtained by DHCP. |
| l2bridge | Interface uses layer two bridging (IP route option). |
| l2tp | Interface uses layer2 tunneling protocol. |
| portshield | Interface is portshielded. |
| <PORTSHIELD_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| pppoe | Interface uses point to point protocol over ethernet. |
| pptp | Interface uses point to point tunneling protocol. |
| static | Static IP address assignment. |
| tap-mode | Interface in tap mode. |
| transparent | Interface uses transparent bridging (splice L3 subnet). |
| wire-mode | Interfaces paired in wire mode. |
| bypass | Bypass (via internal switch / relay). |
| inspect | Inspect (passive deep packet inspection of mirrored traffic). |
| secure | Secure (active deep packet inspection of inline traffic). |
| <PORT_GROUP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <WIRE_INTERFACE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| netmask | Set interface netmask. |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| backup-ip | Secondary IP address. |
| ip | IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| backup-ip | Secondary IP address. |
| ip | IP address. |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| netmask | Set interface netmask. |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| netmask | Set interface netmask. |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <L2BRIDGE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| allow | Allow. |
| block | Block. |
| <VLAN_FILTER_TAG> |
Filtered VLAN ID list. Example: 23 |
| <VLAN_FILTER_TAG> |
Filtered VLAN ID list. Example: 23 |
| group | Set transparent addresses to named address group. |
| <WAN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
WAN group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Set transparent address as host address. |
| <WAN_ADDR_HOST> |
WAN address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set transparent addresses to named address object. |
| <WAN_ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
WAN address object name. Example: X1 IP |
| network | Set transparent addresses to network address. |
| <WAN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
WAN address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set transparent addresses to range of addresses. |
| <WAN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
WAN address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| auto-detect | Auto-detect. |
| modem | Analog Modem. |
| wwan | WWAN/Mobile. |
| data-usage | Data usage. |
| all | Specify period to clear. |
| billing-cycle | Specify period to clear. |
| month | Specify period to clear. |
| week | Specify period to clear. |
| year | Specify period to clear. |
| session-history | WWAN Session history. |
| at-commands | Initialize modem connection using AT commands. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| use-in | Initialize mode connections for use in specified country. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ntp-packets | NTP packets. |
| gms-heartbeats | GMS heartbeats. |
| system-log-emails | System log emails. |
| av-profile-updates | AV profile updates. |
| snmp-traps | SNMP traps. |
| licensed-updates | Licensed updates. |
| firmware-update-requests | Firmware update requests. |
| syslog-traffic | Syslog traffic. |
| ntp-packets | NTP packets. |
| gms-heartbeats | GMS heartbeats. |
| system-log-emails | System log emails. |
| av-profile-updates | AV profile updates. |
| snmp-traps | SNMP traps. |
| licensed-updates | Licensed updates. |
| firmware-update-requests | Firmware update requests. |
| syslog-traffic | Syslog traffic. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| ssh | SSH. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| authentication | Authentication required. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| no-authentication | No authentication required. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| 1_0x | Specify multiple. |
| 1_5x | Specify multiple. |
| 2_0x | Specify multiple. |
| 2_5x | Specify multiple. |
| 3_0x | Specify multiple. |
| 3_5x | Specify multiple. |
| 4_0x | Specify multiple. |
| primary | Primary connection profile. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| secondary | Alternate 1 connection profile. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| tertiary | Alternate 2 connection profile. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| primary | Primary connection profile. |
| secondary | Alternate 1 connection profile. |
| tertiary | Alternate 2 connection profile. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| cdma-edvo | CDMA/EDVO. |
| gprs-edge-hspa | GPRS/EDGE/HSPA. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| connect-on-data | Connect on data. |
| manual | Manual connection. |
| persistent | Persistent connection. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| 14400 | Baud rate. |
| 19200 | Baud rate. |
| 2400 | Baud rate. |
| 38400 | Baud rate. |
| 4800 | Baud rate. |
| 57600 | Baud rate. |
| 9600 | Baud rate. |
| auto | Baud rate. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| *70 | Call wait string. |
| 1170 | Call wait string. |
| 70 | Call wait string. |
| other | Custom call waiting string. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| automatic | Obtain an IP address automatically. |
| static | Specify IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| automatic | Obtain an IP address of DNS servers automatically. |
| sun | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| mon | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| tue | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| wed | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| thu | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| fri | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| sat | Day of the week. |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| billing-start | Set billing start date. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| limit | Set data usage limit. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| units | Set units for data usage limit. |
| gb | Gigabytes. |
| kb | Kilobytes. |
| mb | Megabytes. |
| minutes | Minutes. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ARP_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ARP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <ARP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <ARP_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ARP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <ARP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <ARP_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ARP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <ARP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| dynamic | Enable automatic update of IP address. |
| dynamic | Disable automatic update of IP address. |
| <ARP_FLUSH_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ARP_FLUSH_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ipv6 | Set IPv6 DNS server |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| ipv6 | Clear IPv6 DNS server |
| primary | Clear the primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear the secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear the tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| action | Set action when experiencing attack. |
| drop-dns-reply | Log the attack and drop the DNS reply. |
| log-attack-only | Log the attack only. |
| return-query-refused | Log the attack and return a query refused reply. |
| allowed-domains | Specify the domains for which checking is not done. |
| fqdn | Create FQDN address object with same name as defined. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Specify FQDN group name. |
| <ADDR_CUSTOM_FQDN_GROUP> |
Custom FQDN group address object name. Example: Forbidden Domains |
| name | Specify FQDN address object name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN_NAME> |
FQDN address object name. Example: www.example.com |
| allowed-domains | Clear DNS rebinding allowed domains. |
| interface-reverse | Clear interface names reverse DNS cache. |
| <DDNS_PROFILE_NAME> |
Dynamic DNS profile name. Example: mydns |
| <DDNS_PROFILE_NAME> |
Dynamic DNS profile name. Example: mydns |
| <DDNS_PROFILE_NAME> |
Dynamic DNS profile name. Example: mydns |
| changeip | changeip.com. |
| dyndns | DynDNS.org. |
| noip | No-IP.com. |
| yi | yi.org. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| any | Any interface. |
| interface | Specify interface. |
| <WAN_INTERFACE> |
WAN interface name. Example: X1 |
| detect | Let the dynamic DNS provider detect the IP address. |
| manual | Specify the IP address manually. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| set-to-wan | Automatically set the IP address to the primary WAN IP address. |
| do-nothing | Allows the previously registered IP address to remain current with the Provider. |
| make-host-unknown | Let the dynamic DNS provider detect the IP address. |
| manual | Specify the IP address manually. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| use-previous | Use the off-line IP address previously configured at the provider's site. |
| custom | Custom. |
| dynamic | Dynamic. |
| static | Static. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| ipv6 | Enter IPv6 DHCP server configuration mode. |
| monitoring-interval | Set DHCP server persistence monitoring interval in minutes. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <SCOPE_START_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SCOPE_END_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SCOPE_START_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SCOPE_END_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <DHCP_LEASE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <ADDR_DHCP_TRUSTED_RELAY_AGENT_GROUP> |
Group address object name. Example: Default Trusted Relay Agent List |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| primary | Specify primary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| secondary | Specify secondary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary VOIP call manager address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| primary | Clear primary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary VOIP call manager address. |
| boot-file | Specify boot file. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| next-server | Specify next server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| server-name | Specify server name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| boot-file | Clear boot file. |
| next-server | Clear next server. |
| server-name | Clear server name. |
| group | Specify generic option group. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| object | Specify generic option object. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| primary | Specify primary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| secondary | Specify secondary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary VOIP call manager address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| primary | Clear primary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary VOIP call manager IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary VOIP call manager address. |
| boot-file | Specify boot file. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| next-server | Specify next server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| server-name | Specify server name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| boot-file | Clear boot file. |
| next-server | Clear next server. |
| server-name | Clear server name. |
| group | Specify generic option group. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| object | Specify generic option object. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| boolean | Option object type: boolean. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| domain-name | Option object type: domain name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| four-byte | Option object type: four byte. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ip | Option object type: IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| one-byte | Option object type: one byte. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| string | Option object type: string. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| two-byte | Option object type: two byte. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name in specify option group. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name in specify option group. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| any-tcp-syn | Enable responding to any TCP SYN. |
| port | TCP port. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| disable-any-tcp-syn | Disable responding to any TCP SYN. |
| <FLB_GROUP_NAME> |
Failover & LB group name. Example: myFLBGroup |
| basic | Connection use primary member unless failover occurs. |
| ratio | Connections use members according to the set percentages. |
| round-robin | Connections cycle through members in round robin fashion. |
| spillover | Connections use primary member until bandwidth is exceeded. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <FLB_GROUP_MEMBER> |
WAN interface name. Example: X0 |
| <FLB_CURRENT_GROUP_MEMBER> |
Group member name. Example: X0 |
| <FLB_FINAL_BACKUP> |
WAN interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <FLB_CURRENT_GROUP_MEMBER> |
Group member name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| logical | Use logical/probe monitoring. |
| physical | Use only physical checking of member status, no probing. |
| always | Always succeeds (no probing). |
| both | Probes succeed when both main target and alternate target respond. |
| either | Probes succeed when either main target or alternate target responds. |
| main | Probes succeed when main target responds. |
| protocol | Set the probe protocol. |
| ping | Ping probes. |
| tcp | TCP SYN probes. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| host | Target name or IP address. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| protocol | Set the probe protocol. |
| ping | Ping probes. |
| tcp | TCP SYN probes. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| host | Target Name or IP address. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| protocol | Specify the IP helper relay protocol. |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| source | Specify source. |
| group | IP helper policy source address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| interface | IP helper policy source interface. |
| <INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| name | IP helper policy source address object name. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK_NAME> |
Network address object name. Example: Sales Network |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| zone | IP helper policy source zone. |
| <ZONE_NO_MULTICAST_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| destination | Specify destination. |
| group | Destination address object group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Destination address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Destination address object name. |
| <ADDR_IPH_POLICY_DST_NAME> |
Host or network address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| protocol | Specify the IP helper relay protocol. |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| source | Specify source. |
| group | IP helper policy source address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| interface | IP helper policy source interface. |
| <INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| name | IP helper policy source address object name. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK_NAME> |
Network address object name. Example: Sales Network |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| zone | IP helper policy source zone. |
| <ZONE_NO_MULTICAST_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| destination | Specify destination. |
| group | Destination address object group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Destination address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Destination address object name. |
| <ADDR_IPH_POLICY_DST_NAME> |
Host or network address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| enable | Enable specified IP helper relay protocol. |
| name | IP helper relay protocol name. |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| enable | Enable IP Helper settings or objects. |
| name | IP helper relay protocol name. |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| group | IP helper policy source address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| interface | IP helper policy source interface. |
| <INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| name | IP helper policy source address object name. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK_NAME> |
Network address object name. Example: Sales Network |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| zone | IP helper policy source zone. |
| <ZONE_NO_MULTICAST_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| group | Destination address object group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Destination address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Destination address object name. |
| <ADDR_IPH_POLICY_DST_NAME> |
Host or network address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | IP helper policy source network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| 10 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| 20 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| 30 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| 40 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| 50 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| 60 | Timeout value (in seconds). |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof interface. Example: X0 |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_IP> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static ip. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_MAC> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static mac. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof enabled static interface. Example: X0 |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_IP> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static ip. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_MAC> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static mac. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof enabled static interface. Example: X0 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof enabled static interface. Example: X0 |
| spoof-detected-list | Spoof detected list. |
| spoof-detected-list | Spoof detected list. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| ipv4 | Delete all IPv4 NAT policies. |
| ipv6 | Delete all IPv6 NAT policies. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| any | Any virtual group. |
| id | Virtual group id. |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| block-remap | Block remap. |
| random-distribution | Random distribution. |
| round-robin | Round robin. |
| sticky-ip | Sticky IP. |
| symmetrical-remap | Symmetrical remap. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| icmp-ping | ICMP ping probe. |
| tcp | TCP probe. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <NETMON_NAME> |
Atom Object name. Example: Web Services Monitor |
| <NETMON_NAME> |
Atom Object name. Example: Web Services Monitor |
| <NETMON_NAME> |
Atom Object name. Example: Web Services Monitor |
| fqdn | Set the probe target to FQDN address. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Set the probe target to group address object. |
| <ADDR_FHR_GROUP> |
FQDN/host/range group address object name. Example: Web Server Group |
| host | Set the probe target to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the probe target to named address object. |
| <ADDR_FQDN_HOST_RANGE_NAME> |
FQDN/host/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| range | Set the probe target to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| host | Set the next hop to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the next hop to named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| host | Set the local IP to host address. |
| <NETMON_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the local IP to named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <NETMON_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| ping | Ping probe. |
| ping-explicit | Ping probe using explicit route. |
| tcp | TCP probe. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| tcp-explicit | TCP probe using explicit route. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| advanced | Advanced routing. |
| simple | Simple RIP advertisement. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| ipv4 | Delete all IPv4 route policies. |
| ipv6 | Delete all IPv6 route policies. |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <NETMON_NAME> |
Atom Object name. Example: Web Services Monitor |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| port | Set web proxy TCP port. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| any | Set client inclusion to any address object. |
| fqdn | Set client inclusion as full qualified domain name (FQDN) address. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Set client inclusion to named address group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Set client inclusion as host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Set client inclusion as MAC address. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Set client inclusion to named address object. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set client inclusion to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set client inclusion to range of address. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| fqdn | Set server exclusion as full qualified domain name (FQDN) address. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Set server exclusion to named address group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Set server exclusion as host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Set server exclusion as MAC address. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Set server exclusion to named address object. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set server exclusion to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set server exclusion to range of address. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <USER_NETPROXY_SERVER> |
User net proxy server. Example: example.com |
| <NDP_IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <NDP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <NDP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <NDP_IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <NDP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <NDP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <NDP_IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <NDP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <NDP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <NDP_FLUSH_IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <NDP_FLUSH_IF_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| ipv6 | Add/edit IPv6 tunnel interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_INTERFACE> |
IPv6 Interface name. Example: myTunnelInterface |
| ipv6 | Delete IPv6 tunnel interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_INTERFACE> |
IPv6 Interface name. Example: myTunnelInterface |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_INTERFACE> |
IPv6 Interface name. Example: myTunnelInterface |
| <INTERFACE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| 6rd | 6rd tunnel. |
| 6to4 | IPv6 6to4 tunnel. |
| gre | GRE tunnel. |
| isatap | ISATAP tunnel. |
| manual | Manual tunnel. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| ping | Ping. |
| snmp | SNMP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| host | Configure the remote IPv4 address to host address. |
| <TUNNEL_IPV4_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the remote IPv4 address to named address object. |
| <TUNNEL_IPV4_ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| group | Configure the remote IPv6 network to named address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Configure the remote network to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the remote IPv6 network to named address object. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Configure the remote network to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Configure the remote network to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Bound to any interface. |
| interface | Bound to interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_BOUND_TO_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| host | Configure the remote IPv4 address to host address. |
| <TUNNEL_IPV4_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the remote IPv4 address to named address object. |
| <TUNNEL_IPV4_ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| group | Configure the remote IPv6 network to named address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Configure the remote network to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the remote IPv6 network to named address object. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Configure the remote network to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Configure the remote network to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Bound to any interface. |
| interface | Bound to interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_BOUND_TO_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| interface | Bound to interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_BOUND_TO_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| interface | Bound to interface. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_BOUND_TO_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| name | Set tunnel interface IPv6 subnet prefix to named address object. |
| <ISATAP_ADDR_NETWORK_NAME> |
Network address object name. Example: Sales Network |
| network | Set tunnel interface IPv6 subnet prefix to network address. |
| <ISATAP_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ISATAP_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| auto | Interface IPv6 configuration set to auto. |
| dhcpv6 | Interface IPv6 configuration obtained by dhcpv6. |
| l2bridge | Interface uses layer two bridging. |
| static | Static IPv6 configuration assignment. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| 6rd | Add downstream IPv6 address delegated from 6rd |
| prefix-delegation | Add downstream IPv6 address delegated from DHCP-PD |
| static | Add statioc IPv6 address |
| <IPV6_EXTRA_ADDR> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| 6rd | Delete downstream IPv6 address delegated from 6rd |
| prefix-delegation | Delete downstream IPv6 address delegated from DHCP-PD |
| static | Delete statioc IPv6 address |
| <IPV6_EXTRA_ADDR> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| 6rd | Add downstream IPv6 address delegated from 6rd |
| prefix-delegation | Add downstream IPv6 address delegated from DHCP-PD |
| static | Add statioc IPv6 address |
| <IPV6_EXTRA_ADDR> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| name | Set delegated prefix to named address object. |
| <DELEGATED_PREFIX_ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| max | Router advertisement interval range maximum. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| min | Router advertisement interval range minimum. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV6_ADVERTISING_PREFIX> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2001:: |
| <IPV6_ADVERTISING_PREFIX> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2001:: |
| <IPV6_ADVERTISING_PREFIX> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2001:: |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| auto | Automatic. |
| manual | Manual. |
| delegated-prefix | Release delegated prefixes acquired via DHCPv6. |
| delegated-prefix | Renew delegated prefixes acquired via DHCPv6. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_IPV6_OPTION_OBJECT_NUMBER> |
IPv6 DHCP server option object number. Example: 12 |
| boolean | Option object type: boolean. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| domain-name | Option object type: domain name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| four-byte | Option object type: four byte data. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ip | Option object type: IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| one-byte | Option object type: one byte. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| string | Option object type: string. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| two-byte | Option object type: two byte. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name in specify option group. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name in specify option group. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| <DHCP_IPV6_DYNAMIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server dynamic scope name. Example: abc |
| <DHCP_IPV6_DYNAMIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server dynamic scope name. Example: abc |
| <DHCP_IPV6_DYNAMIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server dynamic scope name. Example: abc |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| group | Set IPv6 DHCP server option group for dynamic scope. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| object | Set IPv6 DHCP server option object for dynamic scope. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_IPV6_STATIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server static scope name. Example: abc |
| <DHCP_IPV6_STATIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server static scope name. Example: abc |
| <DHCP_IPV6_STATIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server static scope name. Example: abc |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| preferred | Set IPv6 DHCP server static scope preferred lifetime (minutes). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| valid | Set IPv6 DHCP server static scope valid lifetime (minutes). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| preferred | Clear IPv6 DHCP server static scope preferred lifetime. |
| valid | Clear IPv6 DHCP server static scope valid lifetime. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| group | Set IPv6 DHCP server option group for static scope. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| object | Set IPv6 DHCP server option object for static scope. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| <DHCP_IPV6_LEASE_HOST> |
IPv6 DHCP server lease IP. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| ip | Show interfaces IP. |
| ipv4 | Show all IPv4 interfaces. |
| ipv6 | Show all IPv6 interfaces. |
| physical | Show physical interfaces. |
| vlan | Show VLAN interfaces. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| statistics | Show interfaces statistics. |
| display-all-traffic | Show interface statistics option. |
| mac | Show interfaces MAC. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| ipv6 | Show IPv6 interface configuration. |
| <CONFIGURABLE_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| vlan | Sub-interface VLAN. |
| <VLAN_TAG> |
VLAN tag. Example: 23 |
| dialup | Show 3G/Modem status, sessions, or usage. |
| data-usage | Show 3G data usage. |
| session-details | Show 3G session details for specified session. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| sessions | Show 3G sessions. |
| status | Show 3G/Modem status. |
| ip | Show interface IP. |
| mac | Show interface MAC. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| statistics | Show interface statistics. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| cache | Show ARP cache. |
| entries | Show all static ARP entries. |
| entry | Show a specified static ARP entry. |
| <ARP_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ARP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <ARP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| statistics | Show ARP statistics. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| fqdn-binding | Show DNS binging for FQDN configuration. |
| rebinding | Show DNS rebinding attack prevention configuration. |
| servers | Show DNS server configuration. |
| ipv4 | Show IPv4 DNS server configuration. |
| ipv6 | Show IPv6 DNS server configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| cache | Show DNS cache. |
| interface-reverse | Show interface names reverse DNS cache. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show all dynamic DNS profiles status. |
| <DDNS_PROFILE_NAME> |
Dynamic DNS profile name. Example: mydns |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show a dynamic DNS profile status. |
| ipv6 | Show IPv6 DHCP server configuration. |
| leases | Show IPv6 DHCP server leases. |
| statistic | Show IPv6 DHCP server leases status. |
| option | IPv6 DHCP server option configuration. |
| group | Specify option group. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| groups | IPv6 DHCP server all option groups. |
| object | Specify option object. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| objects | IPv6 DHCP server all option objects. |
| scope | IPv6 DHCP server static or dynamic scope. |
| dynamic | IPv6 DHCP server dynamic configuration. |
| <DHCP_IPV6_DYNAMIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server dynamic scope name. Example: abc |
| static | IPv6 DHCP server static configuration. |
| <DHCP_IPV6_STATIC_SCOPE_NAME> |
IPv6 DHCP server static scope name. Example: abc |
| scopes | IPv6 DHCP server all static or dynamic scopes. |
| dynamic | IPv6 DHCP server dynamic configuration. |
| static | IPv6 DHCP server static configuration. |
| ipv4 | Show IPv4 DHCP server configuration. |
| leases | Show DHCP server leases. |
| statistic | Show DHCP server leases status. |
| option | DHCP server option configuration. |
| group | Specify option group. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_GROUP> |
DHCP server option group name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Group |
| groups | All option groups. |
| object | Specify option object. |
| <DHCP_OPTION_OBJECT> |
DHCP server option object name. Example: Corp Network DHCP Options |
| objects | All option objects. |
| scope | DHCP server static or dynamic scope. |
| dynamic | DHCP server dynamic configuration. |
| <SCOPE_START_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SCOPE_END_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| static | DHCP server static configuration. |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <STATIC_SCOPE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| scopes | DHCP server all static or dynamic scopes. |
| dynamic | DHCP server dynamic configuration. |
| static | DHCP server static configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| group | Show Failover and Load Balancing Group configuration. |
| <FLB_GROUP_NAME> |
Failover & LB group name. Example: myFLBGroup |
| responder | Show status for Respond To Probes. |
| statistics | Show Failover and Load Balancing statistics. |
| status | Show status of all Failover and Load Balancing groups. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| policies | Show all IP helper policies. |
| protocol | Show an IP helper relay protocol. |
| <IPH_PROTOCOL> |
IP Helper relay protocol name. Example: mydns |
| protocols | Show all IP helper relay protocols. |
| statistics | Show statistics for policies or specified protocol. |
| dhcp-relay-leases | Show all IP helper DHCP relay leases. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| cache | Show MAC-IP anti-spoof cache. |
| entries | Show all MAC anti-spoof cache entries. |
| status | Show all MAC-IP anti-spoof cache entries status. |
| entry | Show an MAC anti-spoof cache entry. |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_IP> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static ip. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_MAC> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof static mac. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_STATIC_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof enabled static interface. Example: X0 |
| detected-list | Show MAC-IP anti-spoof spoof detected list. |
| interface | Show MAC-IP anti-spoof interface configuration. |
| <MAC_IP_ANTI_SPOOF_INTERFACE> |
MAC-IP anti-spoof interface. Example: X0 |
| interfaces | Show MAC-IP anti-spoof configuration for all interfaces. |
| lookup-statistics | Show MAC-IP anti-spoof lookup statistics. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPv4 NAT policies. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPv6 NAT policies. |
| statistics | Show statistics for all nat policies. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| statistics | Show statistics for specified nat policy. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| outbound | Outbound interface. |
| <NAT_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source | Original source (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-source | Translated source (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original source IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Original destination (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-destination | Translated destination (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Address object group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original destination IP. |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Original service (\"Any\" if not specified). |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| translated-service | Translated service (\"Original\" if not specified). |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| original | Original service. |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| statistics | Show statistics for specified nat policy. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| status | Show all network monitor policies status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <NETMON_NAME> |
Atom Object name. Example: Web Services Monitor |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show a specific network monitor policy status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPv4 route policies. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPv6 route policies. |
| dynamic | Show all dynamic route policies. |
| system | Show all ephemeral system route policies. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <ROUTING_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Route interface name. Example: X0 |
| metric | Route policy metric. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| source | Route policy source. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| destination | Route policy destination. |
| any | Any host. |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| service | Route policy service. |
| any | Any service. |
| group | Service group. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| gateway | Route policy gateway. |
| default | Default gateway 0.0.0.0/:: |
| host | Gateway IP. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NAME> |
Host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| database | Database summary. |
| interface | Interface status and configuration. |
| database | Database summary. |
| database | Database summary. |
| neighbor | Neighbor list. |
| routes | OSPF routing table. |
| neighbor | Neighbor list. |
| summary | Summary of BGP neighbor status. |
| unicast | |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| cache | Show NDP caches. |
| entries | Show all static NDP entries. |
| entry | Show a static NDP entry. |
| <NDP_IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| <NDP_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <NDP_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| ipv6 | Show IPv6 tunnel interface configuration. |
| <IPV6_TUNNEL_INTERFACE> |
IPv6 Interface name. Example: myTunnelInterface |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| ipv6 | Show all IPv6 tunnel interface configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| highest | UTM services (application firewall, anti-spyware, gateway AV, and IPS engine) disabled for highest number of SPI connections. |
| optimized | Optimized for deployments requiring more UTM connections but less performance critical. |
| recommended | Recommended for normal deployments with UTM services enabled. |
| reserved-address-packets | Enable drop and log network packets whose source or destination address is reserved by RFC. |
| routing-header-0 | Enable drop IPv6 routing header type 0 packets. |
| reserved-address-packets | Disable drop and log network packets whose source or destination address is reserved by RFC. |
| routing-header-0 | Disable drop IPv6 routing header type 0 packets. |
| destination-unreachable | Generate IPv6 ICMP destination unreachable packets |
| parameter-problem | Generate IPv6 ICMP parameter problem packets |
| redirect | Generate IPv6 ICMP redirect packets |
| time-exceeded | Generate IPv6 ICMP time-exceeded packets |
| destination-unreachable | Never generate IPv6 ICMP destination unreachable packets |
| parameter-problem | Never generate IPv6 ICMP parameter problem packets |
| redirect | Never generate IPv6 ICMP redirect packets |
| time-exceeded | Never generate IPv6 ICMP time-exceeded packets |
| life-time | Resolved name ISATAP is valid for (seconds). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| advanced | Advanced. |
| global | Global. |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 7. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| guaranteed | Guaranteed percent. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| maximum | Maximum/burst percent. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 7. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| timeout | Set the multicast state table entry timeout in minutes. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| all | All multicast host. |
| group | Multicast address object group. |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Multicast address group name. Example: Multicast Group |
| host | Multicast address object host. |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Multicast address object name. |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_NAME> |
Multicast address object name. Example: Multicast Address |
| network | Multicast address object network. |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Multicast address object range. |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <MULTICAST_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| address | Specified multicast group address. |
| <MULTICAST_GROUP_IPV4_HOST> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| interface | Specified interface/ vpn tunnel. |
| <MULTICAST_INTERFACE> |
Multicast interface name. Example: X0 |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| from | From zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | To zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination Zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| from | From zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | To zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| threshold | Set the destination IP address connection limit threshold. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| threshold | Set the source IP address connection limit threshold. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| explicit | Set explicit marking. |
| background | Background. |
| best-effort | Best effort. |
| controlled-load | Controlled load. |
| excellent-effort | Excellent effort. |
| network-control | Network control. |
| spare | Spare. |
| video | Video (<100ms latency). |
| voice | Voice (<100ms latency). |
| map | Map marking. |
| none | No marking. |
| preserve | Preserve marking. |
| explicit | Set explicit marking. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| map | Map marking. |
| cos-override | Allow 802.1p marking to override DSCP values. |
| disable-cos-override | Disable allowing of 802.1p marking to override DSCP values.. |
| none | No marking. |
| preserve | Preserve marking. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| administrator | Administrator. |
| all | All users. |
| group | Group object name. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guest users. |
| name | User object name. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Administrator. |
| group | Group object name. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guest users. |
| name | User object name. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| none | No users. |
| bandwidth-object | Bandwidth object name. |
| <BANDWIDTH_RULE_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| priority | Egress traffic priority. |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 7. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| bandwidth-object | Bandwidth object name. |
| <BANDWIDTH_RULE_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| priority | Ingress traffic priority. |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 7. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| block | Block the connection and log the event. |
| log | Log the event. |
| <BLACKLIST_CERTIFICATE> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: certificateName |
| <BLACKLIST_CERTIFICATE> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: certificateName |
| <WHITELIST_CERTIFICATE> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: certificateName |
| <WHITELIST_CERTIFICATE> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: certificateName |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| always-proxy | Always proxy WAN client connections. |
| proxy-suspect-attack | Proxy WAN client connections when attack is suspected. |
| watch-and-report | Watch and report possible SYN floods. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| max | Set maximum TCP MSS sent to WAN clients. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <BANDWIDTH_RULE_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| <BANDWIDTH_OBJ_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| <BANDWIDTH_OBJ_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| kbps | Kilobits per second. |
| mbps | Megabits per second. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| kbps | Kilobits per second. |
| mbps | Megabits per second. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 7. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| delay | Delay. |
| drop | Drop. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| kbps | Kilobits per second. |
| mbps | Megabits per second. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| any | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list to any. |
| group | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list to named address group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list as host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list to named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set UDP flood attack protected destination list to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| any | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list to any. |
| group | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list to named address group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list as host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list to named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_RANGE_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list to network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Set ICMP flood attack protected destination list to range of addresses. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| to-dscp | Set the DSCP value to map to. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| from-dscp | Set the from DSCP range. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| connection-status | Show firewall connections status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| state | Show multicast state. |
| entries | Show multicast state entries. |
| entry | Show a specified multicast state entry. |
| address | Multicast group address. |
| <MULTICAST_GROUP_IPV4_HOST> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| interface | Interface or vpn tunnel. |
| <MULTICAST_INTERFACE> |
Multicast interface name. Example: X0 |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Destination service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| ipv4 | Show IPv4 access rules. |
| ipv6 | Show IPv6 access rules. |
| from | Source zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| statistics | Show access rule statistics |
| unused | Show access rules assigned to a Zone that has not been assigned to an interface. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| to | Destination Zone. |
| <ACCESS_RULE_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| action | Set the action for this access rule. |
| allow | Allow traffic matching the criteria. |
| deny | Deny traffic matching the criteria. |
| discard | Discard traffic matching the criteria. |
| source | Source. |
| address | Source address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| port | Source port. |
| any | Any source service. |
| group | Source service Group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Source service Object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Source service Object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| service | Destination service. |
| any | Any destination service. |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| protocol | Service object protocol. |
| <SVC_PROTOCOL> |
Service protocol. Example: TCP |
| <SVC_PORT_BEGIN> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SVC_PORT_END> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| destination | Destination. |
| address | Destination address. |
| any | Any address. |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| group | Address group name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| mac | Address object mac. |
| <ADDR_MAC> |
Address object MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH or HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| schedule | Schedule. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <OBJECT_INDEX> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 1 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| statistics | Show TCP statistics. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <BANDWIDTH_OBJ_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| statistics | Show UDP statistics. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| statistics | Show ICMP statistics. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| chinese | Chinese. |
| chinese_traditional | Chinese (Traditional). |
| english | English. |
| french | French. |
| german | German. |
| italian | Italian. |
| japanese | Japanese. |
| korean | Korean. |
| portuguese | Portuguese. |
| spanish | Spanish. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| old-password | Enter the old password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| new-password | Enter the new password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| confirm-password | Confirm the new password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| duration | Set the number of days before the password must be changed. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| count | Set the number of password changes before repeated password are allowed. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| digital | Set minimum digital character number. |
| lower-case | Set minimum lower case character number. |
| symbolic | Set minimum symbolic character number. |
| upper-case | Set minimum upper case character number. |
| builtin-admin | Built in administrator. |
| full-admins | Other full administrators. |
| limited-admins | Limited administrators. |
| local-users | Other local users. |
| guest-admins | Guest admins. |
| builtin-admin | Built in administrator. |
| full-admins | Other full administrators. |
| limited-admins | Limited administrators. |
| local-users | Other local users. |
| guest-admins | Guest admins. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| failures-per-minute | Set the failed login attempts per minute before lockout. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| lockout-duration | Set number of minutes a user should be locked out. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| goto-non-config | Drop to non-config mode. |
| logout | Logout. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| name | Specify certificate. |
| <CERT_NAME> |
Certificate name. Example: my_cert |
| use-self-signed | Use self signed certificate. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <CERT_ISSUER> |
Certificate Issuer. Example: Thawte Server CA |
| <URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| form-delay | Set form tooltip delay. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| button-delay | Set button tooltip delay. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| text-delay | Set text tooltip delay. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <ENC_PIN_VALUE> |
String contains 4-6 numeric (0-9) characters. Example: 123456 |
| confirm-pin | Confirm pin value. |
| <ENC_PIN_VALUE> |
String contains 4-6 numeric (0-9) characters. Example: 123456 |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| url | Specify URL. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| url | Specify URL. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| url | Specify URL. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| existing-tunnel | Use existing tunnel. |
| https | Use HTTPS. |
| ipsec-tunnel | Use IPSEC tunnel. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| ip | Set IP of NAT device. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| des-md5 | DES-MD5. |
| <HEX_STRING> |
String of hexadecimal digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| <HEX_STRING> |
String of hexadecimal digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| ip | Set distributed GMS reporting server IP address. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| port | Set distributed GMS reporting server port. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| ip | Clear distributed GMS reporting server IP address. |
| port | Clear distributed GMS reporting server port. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <SNMP_VIEW_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: ICMP |
| oid | Add an OID to the SNMP view list. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <SNMP_VIEW_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: ICMP |
| oid | Delete an OID from the SNMP view list. |
| <SNMP_OID_IN_VIEW> |
SNMP view oid name. Example: 1.3.5 |
| <SNMP_GROUP_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <SNMP_GROUP_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <SNMP_USER_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <SNMP_USER_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| authentication-and-privacy | Use authentication and encryption. |
| authentication-only | Use authentication. |
| md5 | MD5. |
| sha1 | SHA-1. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| aes | AES. |
| des | DES. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <SNMP_GROUP_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <SNMP_ACCESS_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <SNMP_ACCESS_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <SNMP_VIEW_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: ICMP |
| <SNMP_GROUP_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: Group1 |
| authentication-and-privacy | Use authentication and encryption. |
| authentication-only | Use authentication. |
| cli | Export configuration using the SonicOS E-CLI command format. |
| exp | Export configuration using the SonicOS WebUI (.exp) format. |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| cli | Export configuration using the SonicOS E-CLI command format. |
| exp | Export configuration using the SonicOS WebUI (.exp) format. |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| current | Current Firmware. |
| system-backup | Download the system backup firmware image. |
| uploaded | Download the latest uploaded firmware image. |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| download | Enable automatic downloading of firmware from SonicWALL software site. |
| update | Enable periodic checking of SonicWALL site for firmware update. |
| download | Disable automatic downloading of firmware from SonicWALL software site. |
| update | Disable periodic checking of SonicWALL site for firmware update. |
| ftp | Import using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| at | Restart at the time specified. |
| <TIME_YYYYMMDDHHMMSS> |
Timestamp in the form: YYYY:MM:DD:HH:MM:SS. Example: 2010:06:30:23:30:59 |
| in | Restart after the specified interval. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set in days. |
| hours | Set in hours. |
| minutes | Set in minutes. |
| now | Restart immediately. |
| time | Restart after the specified number of seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| current | Boot current firmware image. |
| uploaded | Boot the latest uploaded firmware image. |
| backup | Boot firmware with backup settings. |
| factory-default | Boot current firmware with default settings. |
| system-backup | Boot system backup firmware. |
| <TIME_HHMMSS> |
Time in the form: DD:DD:DD. Example: 12:00:00 |
| <DATE_YYYYMMDD> |
Date in the form: YYYY:MM:DD. Example: 2010:06:30 |
| <TIME_ZONE> |
Time Zone. Example: pacific-time |
| <NTP_SERVER> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| md5 | NTP server uses MD5 authentication. |
| trust-key-no | Trust key. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| key-number | Key number. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| password | Password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| no-auth | NTP server doesn't require authentication. |
| <NTP_SERVER> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| key | Upgrade by key. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| key-set | Upgrade by key set. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show license status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| ldap | Use LDAP user authentication. |
| ldap+local | Use both LDAP and local user authentication. |
| local | Use local user authentication. |
| radius | Use RADIUS user authentication. |
| radius+local | Use both RADIUS and local user authentication. |
| characters | Characters format. |
| mixed | Mixed format. |
| numbers | Numbers format. |
| min | Minimum length. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| max | Maximum length. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| html | Html format. |
| plain-text | Plain-text format. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| host-name | Redirect the browser via domain name configured for firewall. |
| interface-ip | Redirect the browser via the interface ip address. |
| name-from-certificate | Redirect the browser via name from the administration certificate. |
| reverse-dns | Redirect the browser via domain name from a reverse DNS lookup of the interface IP address. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| login | Enable make the user initially inactive until they send traffic on being notified of a login. |
| timeout | Enable make all users inactive instead of logging out on inactivity timeout. |
| login | Disable make the user initially inactive until they send traffic on being notified of a login. |
| timeout | Disable make all users inactive instead of logging out on inactivity timeout. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| period | Period in seconds. |
| <TEN_SEC_GRANULARITY_PERIOD> |
A number of seconds that must be a multiple of 10. Example: 20 |
| timeout | Time in minutes. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| public | On login from public zones. |
| trusted | On login from trusted zones. |
| vpn | On login from the VPN zone. |
| wan | On login from the WAN zone. |
| wireless | On login from wireless zones. |
| public | On login from public zones. |
| trusted | On login from trusted zones. |
| vpn | On login from the VPN zone. |
| wan | On login from the WAN zone. |
| wireless | On login from wireless zones. |
| access-barred | Customize policy access barred page. |
| access-down | Customize policy access down page. |
| access-unavailable | Customize policy access unavailable page. |
| authentication | Customize login authentication page. |
| disallowed | Customize login disallowed page. |
| full | Customize login full page. |
| guest-status | Customize guest login status page. |
| lockout | Customize login lockout page. |
| logged-out | Customize logged out page. |
| message | Customize user login message page. |
| password-update | Customize user password update page. |
| preempt | Customize admin preempt page. |
| redirect | Customize policy login redirect page. |
| sso-failure | Customize policy SSO probe failure page. |
| status | Customize login status page. |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| access-barred | Customize policy access barred page. |
| access-down | Customize policy access down page. |
| access-unavailable | Customize policy access unavailable page. |
| authentication | Customize login authentication page. |
| disallowed | Customize login disallowed page. |
| full | Customize login full page. |
| guest-status | Customize guest login status page. |
| lockout | Customize login lockout page. |
| logged-out | Customize logged out page. |
| message | Customize user login message page. |
| password-update | Customize user password update page. |
| preempt | Customize admin preempt page. |
| redirect | Customize policy login redirect page. |
| sso-failure | Customize policy SSO probe failure page. |
| status | Customize login status page. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| password | Set the user password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| member-of | Add membership to a user group for this user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <DATE_YYYYMMDD> |
Date in the form: YYYY:MM:DD. Example: 2010:06:30 |
| <TIME_HHMM> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the lifetime in days. |
| expired | Expired user. |
| hours | Set the lifetime in hours. |
| minutes | Set the lifetime in minutes. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| group | Select an existing address group by name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Give VPN client access to an IP address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Select an existing address object by name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Give VPN client access to a network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Give VPN client access to an IP address range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Group address object name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the idle timeout in days. |
| hours | Set the idle timeout in hours. |
| minutes | Set the idle timeout in minutes. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| at | Set the location at the given LDAP location for users. |
| under-or-at | Set the location under or at the given LDAP location for users. |
| group | Select an existing address group by name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Give VPN client access to an IP address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Select an existing address object by name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Give VPN client access to a network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Give VPN client access to an IP address range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Group address object name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <CFS_POLICY_NAME> | CFS policy name. |
| <LOCAL_USER_OR_GROUP_NAME> |
User or user group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <LOCAL_USER_OR_GROUP_NAME> |
User or user group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <USER_LOGIN_NAME> |
A connected user's login name. Example: jdoe |
| <USER_IPV4_ADDR> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| user | For Terminal Services users only, selects the user at the IP address. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <USER_IPV4_ADDR> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| inactive-users | Enable show inactive users' status. |
| unauthenticated-users | Enable show unauthenticated users' status. |
| inactive-users | Disable show inactive users' status. |
| unauthenticated-users | Disable show unauthenticated users' status. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ldap | Read user groups via LDAP. |
| local-only | Set using local users that duplicate RADIUS users. |
| radius-attribute | Read user groups via a RADIUS attribute. |
| filter-id | Use the standard RADIUS filter-id attribute. |
| vendor-specific | Use the SonicWALL vendor-specific RADIUS attribute. |
| primary | Configure the primary RADIUS server. |
| secondary | Configure the secondary RADIUS server. |
| primary | Delete the primary RADIUS server. |
| secondary | Delete the secondary RADIUS server. |
| <RADIUS_SERVER_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: RADIUS-Server |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| chap | Run the test with RADIUS in CHAP mode. |
| mschap | Run the test with RADIUS in MSCHAP mode. |
| mschapv2 | Run the test with RADIUS in MSCHAPv2 mode. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| all | Mirror all user groups on the LDAP server. |
| have-members | Only mirror groups that have member users or groups. |
| refresh | Refresh mirrored LDAP user groups. |
| now | Refresh now. |
| period | Set refresh period. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| operation | Set the overall timeout on an LDAP operation. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| server | Set the server timeout which is the maximum time to wait for each response from the LDAP server over the network. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <CERT_NAME> |
Certificate name. Example: my_cert |
| auto-configuration | Don't follow references during auto-configuration. |
| domain-search | Don't follow references when searching for domains. |
| other-search | Don't follow references in other searches. |
| user-authentication | Don't follow references during user authentication. |
| auto-configuration | Don't follow references during auto-configuration. |
| domain-search | Don't follow references when searching for domains. |
| other-search | Don't follow references in other searches. |
| user-authentication | Don't follow references during user authentication. |
| custom | Configure the schema manually. |
| inet-org-person | Use the pre-configured RFC-2798 InetOrgPerson schema. |
| microsoft-active-directory | Use the pre-configured Microsoft Active Directory schema. |
| network-information-service | Use the pre-configured RFC-2307 Network Information Service schema. |
| novell-edirectory | Use the pre-configured Novell eDirectory schema. |
| samba-smb | Use the pre-configured Samba SMB schema. |
| <LDAP_SERVER_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: LDAP-Server |
| <LDAP_SERVER_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: LDAP-Server |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| additional-group-id | Set the additional user group ID attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| framed-ip-address | Set the framed IP address attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| group-membership | Set the user group membership attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| logon-name | Set the user logon name attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| qualified-logon-name | Set the qualified logon name attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| use-additional-group-id | Use the additional user group ID attribute. |
| additional-group-id | Remove the additional user group ID attribute. |
| framed-ip-address | Remove the framed IP address attribute. |
| group-membership | Remove the user group membership attribute. |
| logon-name | Remove the user logon name attribute. |
| qualified-logon-name | Remove the qualified logon name attribute. |
| use-additional-group-id | Do not use the additional user group ID attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| additional-group-match | Set the additional user group match attribute. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| member | Set the name/type of the member attribute. |
| distinguished-name | The member attribute holds a distinguished name. |
| user-id | The member attribute holds a user ID (uid). |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| additional-group-match | Remove the additional user group match attribute. |
| member | Remove the name of the member attribute. |
| domain | The domain to search under. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| append | Append to any current directory trees. |
| replace | Replace any current directory trees. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| position | Position in the search order (1 = the first searched). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <LDAP_DIRECTORY_NAME> |
LDAP directory user or group name. Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| position | Position in the search order (1 = the first searched). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <LDAP_DIRECTORY_NAME> |
LDAP directory user or group name. Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| anonymous | Bind anonymously. |
| distinguished-name | Set the full distinguished name to use. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | Set the account name to use. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| location | Set the account location in the directory tree. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| public-zones | Allow incoming RADIUS requests from public zones. |
| trusted-zones | Allow incoming RADIUS requests from trusted zones. |
| vpn-zone | Allow incoming RADIUS requests from vpn zone. |
| wan-zone | Allow incoming RADIUS requests from wan zone. |
| wireless-zones | Allow incoming RADIUS requests from wireless zones. |
| public-zones | Discard incoming RADIUS requests from public zones. |
| trusted-zones | Discard incoming RADIUS requests from trusted zones. |
| vpn-zone | Discard incoming RADIUS requests from vpn zone. |
| wan-zone | Discard incoming RADIUS requests from wan zone. |
| wireless-zones | Discard incoming RADIUS requests from wireless zones. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| internet | Set the user group for users with Internet access. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| l2tp | Set the user group for L2TP users. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| vpn | Set the user group for VPN users. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| vpn-client | Set the user group for VPN client users. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| internet | Clear the user group for users with Internet access. |
| l2tp | Clear the user group for L2TP users. |
| vpn | Clear the user group for VPN users. |
| vpn-client | Clear the user group for VPN client users. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| chap | Test LDAP in a CHAP-compatible way. |
| agent | Reset SSO agent statistics. |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| global | Reset global (non-agent) SSO statistics. |
| radius-accounting-client | Reset SSO RADIUS accounting client statistics. |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_CLIENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| terminal-services-agent | Reset SSO terminal services agent statistics. |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| browser-ntlm | Enable browser NTLM authentication. |
| after-sso-agent-failed | Use NTLM to authenticate HTTP traffic only if SSO via the agent fails. |
| before-sso-agent | Use NTLM to authenticate HTTP traffic before attempting SSO via the agent. |
| radius-accouting | Enable RADIUS accounting authentication. |
| sso-agent | Enable SSO agent authentication. |
| ts-agent | Enable terminal services agent authentication. |
| browser-ntlm | Disable browser NTLM authentication. |
| radius-accouting | Disable RADIUS accounting authentication. |
| sso-agent | Disable SSO agent authentication. |
| ts-agent | Disable terminal services agent authentication. |
| all | Allow through user traffic for all access rules. |
| selected | Allow through user traffic for all access rules. |
| netapi | Probe for NetAPI, default over NetBIOS. |
| over-netbios | Probe for NetAPI over NetBIOS. |
| over-tcp | Probe for NetAPI over TCP. |
| test-mode | Enable probe test-mode. Probe test mode allows testing that SSO probes are functioning correctly during SSO without their interfering with the user authentications |
| timeout | Set timeout for probing IP addresses. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| wmi | Probe for WMI. |
| test-mode | Disable probe test-mode. |
| ldap | Read user groups via LDAP. |
| local-only | Set using local users that duplicate SSO users. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WINDOWS_SERVICE_USER_NAME> |
The login name of a windows service. Example: abc |
| group | Group address object name. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address object name. |
| <SECURITY_SERVICE_BYPASS_IP_NAME> |
Security service bypass ip name. Example: Web Server |
| group | Service group name. |
| <SVC_GROUP_NAME> |
Service object group name. Example: VOIP |
| name | Service object name. |
| <SVC_NAME> |
Service object name. Example: HTTPS |
| <SSO_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <SSO_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| custom | User the custom domain. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| inherit-from-ldap | User the domain from the LDAP configuration. |
| certificate-name | Via the name from the administration certificate |
| domain-name | Via the domain name |
| configured | Via its configured domain name |
| reverse-dns-look-up | Via its domain name from a reverse DNS lookup of the interface IP address |
| ip-address | Via the interface IP address |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| linux | Set polling method for linux users. |
| macintosh | Set polling method for macintosh users. |
| windows | Set polling method for windows users. |
| agent | Poll via the SSO agent. |
| none-reauth | Don't re-authenticate. |
| reauth-ntlm | Re-authenticate via NTLM. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <ENC_HEX_STRING> |
String of hexadecimal digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <ENC_HEX_STRING> |
String of hexadecimal digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_CLIENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_CLIENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| canonical | Set to pre-defined \"Domain/User-name\" format. |
| down-level-logon | Set to pre-defined \"Domain\\User-name\" format. |
| sonicwall-aventail | Set to pre-defined \"SonicWALL Aventail\" format. |
| user-name | Set to pre-defined \"User-name\" format. |
| user-principle | Set to pre-defined \"User-name@Domain\" format. |
| ldap-look-up | Look up the user name via LDAP. |
| local-user | Assume a non-domain user. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_FORWARD_SERVER_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_PROXY_FWD_SERVER_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| port | Set the server's port number. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| shared-secret | Set the shared secret. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_FORWARD_SERVER_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| shared-secret | Clear the shared secret. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| forward-to-all | Proxy forword to all servers. |
| try-next-on-timeout | Try next server when timeout. |
| agent | Specify an agent to test. |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| user-ip | The IP address of a user to test. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| terminal-services-agent | Specify a terminal services agent to test. |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| <GUEST_PROFILE_NAME> |
Guest profile name. Example: profile1 |
| <GUEST_PROFILE_NAME> |
Guest profile name. Example: profile1 |
| name | The name of the guest account. |
| <GUEST_USER_NAME> |
Guest user name. Example: guest1 |
| profile | Apply the settings from a guest profile. |
| <GUEST_PROFILE_NAME> |
Guest profile name. Example: profile1 |
| hide-password | Don't show the auto-generated password. |
| password | Set the guest user password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| generate | Generate multiple guest accounts. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <GUEST_USER_NAME> |
Guest user name. Example: guest1 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| scp | Export using the SCP protocol. |
| <SCP_URL> |
SCP URL in the form: scp://username@host/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: scp://username@host/\nscp://host/ |
| at | Logout a guest user by IP. |
| <GUEST_LOGIN_USER_BY_IP> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | Auto-generate names for created guest accounts. |
| password | Auto generate passwords for created guest accounts. |
| name | Disable auto-generate names for created guest accounts. |
| password | Disable auto generate passwords for created guest accounts. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the lifetime in days. |
| hours | Set the lifetime in hours. |
| minutes | Set the lifetime in minutes. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the session limit in days. |
| hours | Set the session limit in hours. |
| minutes | Set the session limit in minutes. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the idle timeout in days. |
| hours | Set the idle timeout in hours. |
| minutes | Set the idle timeout in minutes. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | Generate a login name for the guest account. |
| password | Generate a password for the guest account. |
| hide | Disable showing the generated password. |
| <GUEST_PROFILE_NAME> |
Guest profile name. Example: profile1 |
| hide-password | Disable showing the auto-generated password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the lifetime in days. |
| hours | Set the lifetime in hours. |
| minutes | Set the lifetime in minutes. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the session limit in days. |
| hours | Set the session limit in hours. |
| minutes | Set the session limit in minutes. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Set the idle timeout in days. |
| hours | Set the idle timeout in hours. |
| minutes | Set the idle timeout in minutes. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| group | Show a local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| groups | Show all local user groups. |
| user | Show a local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| users | Show all local users. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| at | Show detail of a user at a given IP address. |
| <USER_IPV4_ADDR> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| user | For Terminal Services users only, select the user at the IP address. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| inactive | Show information of inactive users. |
| name | Show information of the users with the given name |
| <USER_LOGIN_NAME> |
A connected user's login name. Example: jdoe |
| unauthenticated | Show information of unauthenticated users. |
| pending | Include users currently being authenticated. |
| logged-in | Include logged in users. |
| locked-out | Include locked out users. |
| server | Show RADIUS server settings. |
| primary | Show the primary RADIUS server. |
| secondary | Show the secondary RADIUS server. |
| servers | Show settings for all RADIUS servers. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| directory | Show the LDAP directory configuration. |
| relay | Show LDAP relay configuration. |
| schema | Show the LDAP schema. |
| server | Show LDAP server settings. |
| <LDAP_SERVER_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: LDAP-Server |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| agent | Show SSO agent settings. |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| agents | Show settings for all SSO agents. |
| radius-accounting-client | Show SSO RADIUS accounting client settings. |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_CLIENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| radius-accounting-clients | Show settings for all SSO RADIUS accounting clients. |
| statistics | Show SSO statistics. |
| agent | Show statistics for an SSO agent. |
| <SSO_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Agent |
| all | Show all SSO statistics. |
| radius-accounting-client | Show statistics for an SSO RADIUS accounting client. |
| <SSO_RAD_ACCT_CLIENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| terminal-services-agent | Show statistics for an SSO terminal services agent. |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| status | Show SSO agent status. |
| terminal-services-agent | Show SSO terminal services agent settings. |
| <SSO_TS_AGENT_HOST_NAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: SSO-Terminal-Services-Agent |
| terminal-services-agents | Show settings for all SSO terminal services agents. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| profile | Show a guest user profile. |
| <GUEST_PROFILE_NAME> |
Guest profile name. Example: profile1 |
| profiles | Show all guest user profiles. |
| user | Show a guest user. |
| <GUEST_USER_NAME> |
Guest user name. Example: guest1 |
| users | Show all guest users. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| statistic | Show the logged-in guest users' statistic. |
| user | Show the logged-in guest user's statistic. |
| <GUEST_LOGIN_USER_BY_IP> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| status | Show the logged-in guest users' status. |
| user | Show the logged-in guest user's status. |
| <GUEST_LOGIN_USER_BY_IP> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| users | Show the logged-in guest users' status. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <ASSIGNED_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| status | Show AppFlow Server status. |
| discovered | Show discovered AppFlow servers. |
| detail | Show detail of specified AppFlow server. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| password | Password of the PKCS#12 (.p12 or .pfx) encoded file. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| cert-key-pair | Local end-user certificate with private key from a PKCS#12 (.p12 or .pfx) encoded file. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| password | Password of the PKCS#12 (.p12 or .pfx) encoded file. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| ca-name | CA certificate associated with CRL. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| disable-invalidate-certificates | Disable Invalidate Certificates and Security Associations if CRL import or processing fails. |
| invalidate-certificates | Invalidate Certificates and Security Associations if CRL import or processing fails. |
| directly | Import CRL directly from a PEM (.pem) or DER (.der or .crl) encoded file. |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| periodically | Periodically auto-import CRL via HTTP. |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| country | Country. Adds C=country-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| locality | Locality, City, or County. Adds L=locality-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| organization | Company or organization. Adds O=orgainization-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| state | State. Adds ST=state-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| country | Country. Adds C=country-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| department | Department. Adds OU=department-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| locality | Locality, City, or County. Adds L=locality-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| organization | Company or organization. Adds O=orgainization-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| state | State. Adds ST=state-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| department | Department. Adds OU=department-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| group | Group. Adds OU=group-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| locality | Locality, City, or County. Adds L=locality-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| organization | Company or organization. Adds O=orgainization-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| team | Team. Adds OU=team-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| common-name | Common Name. Adds CN=common-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| department | Department. Adds OU=department-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| E-mail Address. Adds Email=email-address to distinguished name. | |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| group | Group. Adds OU=group-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| organization | Company or organization. Adds O=orgainization-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| serial | Serial Number. Adds SN=serial-number to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| team | Team. Adds OU=team-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| common-name | Common Name. Adds CN=common-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| department | Department. Adds OU=department-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| E-mail Address. Adds Email=email-address to distinguished name. | |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| group | Group. Adds OU=group-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| serial | Serial Number. Adds SN=serial-number to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| team | Team. Adds OU=team-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| common-name | Common Name. Adds CN=common-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| E-mail Address. Adds Email=email-address to distinguished name. | |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| group | Group. Adds OU=group-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| serial | Serial Number. Adds SN=serial-number to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| team | Team. Adds OU=team-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| common-name | Common Name. Adds CN=common-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| E-mail Address. Adds Email=email-address to distinguished name. | |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| serial | Serial Number. Adds SN=serial-number to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| team | Team. Adds OU=team-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| common-name | Common Name. Adds CN=common-name to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| E-mail Address. Adds Email=email-address to distinguished name. | |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| serial | Serial Number. Adds SN=serial-number to distinguished name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| domain-name | Domain Name. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| email-address | E-mail Address. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ipv4-address | IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| active-active-clustering | Active-active clustering mode. |
| active-active-clustering-dpi | Active-active clustering with DPI mode. |
| active-active-dpi | Active-active DPI mode. |
| active-standby | Active-standby mode. |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| virtual-group | Virtual group. |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| none | No assignment. |
| owner | Owner. |
| standby | Standby. |
| standby2 | Standby2. |
| standby3 | Standby3. |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| primary | Primary serial number. |
| secondary | Secondary serial number. |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| primary | Primary serial number. |
| secondary | Secondary serial number. |
| <DPI_INTERFACE_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| <HA_DATA_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <DPI_INTERFACE_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| <HA_LINK_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <HA_DATA_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <SVRRP_LINK> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| <HA_LINK_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <SVRRP_LINK> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| ipv6 | High availability monitoring interface IPv6. |
| interface | High availability monitoring interface. |
| <HA_MONITOR_INTERFACE> |
Physical interface name. Example: X0 |
| node | Specify the node. |
| <VIRTUAL_GROUP_ID> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 1 |
| interface | High availability monitoring interface. |
| <HA_MONITOR_INTERFACE> |
Physical interface name. Example: X0 |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <HOST_IP> |
IPV4: IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| monitoring | Show high availability monitoring interface. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPv4 high availability monitoring interface. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPv6 high availability monitoring interface. |
| interface | Show high availability monitoring interface. |
| <HA_MONITOR_INTERFACE> |
Physical interface name. Example: X0 |
| status | Show high availability status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| csv | CSV format. |
| txt | Text format. |
| ftp | Use ftp. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| zmodem | Use zmodem. |
| all-entries | All entries. |
| last | Last time range. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| days | Days. |
| hours | Hours. |
| minutes | Minutes. |
| <LOG_EVENT_ID_FOR_ATTRIBUTES> |
Event ID for showing the attributes. Example: 123 |
| <LOG_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Log category name. Example: Firewall |
| group | Group configuration. |
| <LOG_GROUP_NAME> |
Group name. Example: Firewall Event |
| event | Event configuration. |
| <LOG_EVENT_NAME> |
Event name. Example: Activate Firewall |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| analyzer-viewpoint-gms | Set event log settings to work well with analyzer / viewpoint / GMS server. |
| custom | Set event log settings to previously saved settings. |
| default | Restore all event log settings to default values. |
| minimal | Set event log settings so that a minimal amount of logs are created. |
| all | All categories. |
| category | Specify category. |
| <LOG_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Log category name. Example: Firewall |
| group | Specify group. |
| <LOG_GROUP_NAME> |
Group name. Example: Firewall Event |
| event | Specify event. |
| <LOG_EVENT_NAME> |
Event name. Example: Activate Firewall |
| event-id | Specify event ID. |
| <LOG_EVENT_ID_FOR_ATTRIBUTES> |
Event ID for showing the attributes. Example: 123 |
| alert | Alert. |
| critical | Critical. |
| debug | Debug. |
| emergency | Emergency. |
| error | Error. |
| inform | Inform. |
| notice | Notice. |
| warning | Warning. |
| alert | Alert. |
| critical | Critical. |
| debug | Debug. |
| emergency | Emergency. |
| error | Error. |
| inform | Inform. |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| notice | Notice. |
| warning | Warning. |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| keep-original-redundancy-interval | Keep original redundancy filter interval. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| keep-original-redundancy-interval | Keep original redundancy filter interval. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| keep-original-redundancy-interval | Keep original redundancy filter interval. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| black | Black. |
| blue | Blue. |
| green | Green. |
| hex | Hex representation. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| keep-original | Keep original color. |
| orange | Orange. |
| purple | Purple. |
| red | Red. |
| rgb | Red, green, blue scale. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| yellow | Yellow. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| keep-original | Keep original log e-mail address. |
| use-default | Use the default log e-mail address. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| keep-original | Keep original alert e-mail address. |
| use-default | Use the default alert e-mail address. |
| alert | Alert. |
| critical | Critical. |
| debug | Debug. |
| emergency | Emergency. |
| error | Error. |
| inform | Inform. |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| notice | Notice. |
| warning | Warning. |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| black | Black. |
| blue | Blue. |
| green | Green. |
| hex | Hex representation. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| keep-original | Keep original. |
| orange | Orange. |
| purple | Purple. |
| red | Red. |
| rgb | Red, green, blue scale. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| yellow | Yellow. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| address | Specify the alert e-mail address. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| keep-original | Keep the original setting for children categories. |
| alert | Alert. |
| critical | Critical. |
| debug | Debug. |
| emergency | Emergency. |
| error | Error. |
| inform | Inform. |
| mixed | Mixed. |
| notice | Notice. |
| warning | Warning. |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| mixed | Categories under this are of mixed settings. |
| black | Black. |
| blue | Blue. |
| green | Green. |
| hex | Hex representation. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| keep-original | Keep original. |
| orange | Orange. |
| purple | Purple. |
| red | Red. |
| rgb | Red, green, blue scale. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| yellow | Yellow. |
| address | Specify the alert e-mail address. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| keep-original | Keep the original setting for children categories. |
| alert | Alert. |
| critical | Critical. |
| debug | Debug. |
| emergency | Emergency. |
| error | Error. |
| inform | Inform. |
| notice | Notice. |
| warning | Warning. |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| redundancy-interval | Set the redundancy interval in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| black | Black. |
| blue | Blue. |
| green | Green. |
| hex | Hex representation. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| orange | Orange. |
| purple | Purple. |
| red | Red. |
| rgb | Red, green, blue scale. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| yellow | Yellow. |
| address | Specify the alert e-mail address. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| authpriv-messages | AUTHPRIV security/authorization messages. |
| clock-daemon-linux-bsd | Clock daemon (BSP,Linux). |
| clock-daemon-solaris | Clock daemon (solaris). |
| ftp-daemon | FTP daemon. |
| generated-internally | Messages generated internally by syslogd. |
| kernel | Kernel. |
| line-printer-subsystem | Line printer subsystem. |
| local-use0 | Local use 0. |
| local-use1 | Local use 1. |
| local-use2 | Local use 2. |
| local-use3 | Local use 3. |
| local-use4 | Local use 4. |
| local-use5 | Local use 5. |
| local-use6 | Local use 6. |
| local-use7 | Local use 7. |
| log-alert | Log alert. |
| log-audit | Log audit. |
| mail-system | Mail system. |
| network-news-subsystem | Network news subsystem. |
| ntp-subsystem | NTP subsystem. |
| security-authorization-messages | Security/authorization messages. |
| system-daemons | System daemons. |
| user-level-messages | User-level messages. |
| uucp-subsystem | UUCP subsystem. |
| arcSight | Arcsight format. |
| default | Default format. |
| enhanced-syslog | Enhanced syslog format. |
| webtrends | Webtrends format. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name (FQDN). |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | Address object host |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name |
| <ADDR_FQDNHOST_ADDR> |
FQDN/host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| port | server port. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| outbound-interface | Outbound interface. |
| <VPN_SITE_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site or tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| local-interface | Local interface. |
| <SYSLOG_SERVER_LOCAL_INTERFACE> |
Syslog server local interface name. Example: X1 |
| <SYSLOG_SERVER> |
Syslog custom server in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| port | server port. |
| <SYSLOG_SERVER_PORT> |
Syslog custom server port. Example: 80 |
| fqdn | Address object full qualified domain name (FQDN). |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | Address object host |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name |
| <ADDR_FQDNHOST_ADDR> |
FQDN/host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <VPN_SITE_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site or tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| <SYSLOG_SERVER_LOCAL_INTERFACE> |
Syslog server local interface name. Example: X1 |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| daily | Daily. |
| hour | Hour. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| minute | Minute. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| weekly | Weekly. |
| fri | Day of the week. |
| mon | Day of the week. |
| sat | Day of the week. |
| sun | Day of the week. |
| thu | Day of the week. |
| tue | Day of the week. |
| wed | Day of the week. |
| hour | Hour. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| minute | Minute. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| when-full | When full. |
| attachment | Attachment. |
| csv | CSV. |
| html | HTML. |
| plain-text | Plain text. |
| address | Set the health check E-mail address. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| body | Set the health check E-mail body. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| schedule | Enable E-mail health check and select a schedule. |
| days | Schedule object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| subject | Set the health check E-mail subject. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| address | Clear the health check E-mail address. |
| body | Clear the health check E-mail body. |
| schedule | Disable E-mail health check. |
| subject | Clear the health check E-mail subject. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| none | No authentication. |
| pop-before-smtp | Pop before SMTP. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| ssl-tls | SSL/TLS. |
| start-tls | STARTTLS. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| fqdn | Set the solera server to fqdn address. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | Set the solera server to host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Set the solera server as named address object. |
| <ADDR_FQDNHOST_ADDR> |
FQDN/host address object name. Example: Web Server |
| http | HTTP. |
| https | HTTPS. |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| confirm-password | Confirm solera password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| <URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| <URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| lan | Default LAN |
| wan | Default WAN |
| dns | DNS. |
| dns-then-netbios | DNS then NetBIOS. |
| netbios | NetBIOS. |
| none | None. |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| bandwidth-usage-by-ip | Bandwidth usage by IP address. |
| bandwidth-usage-by-service | Bandwidth usage by service. |
| web-site-hits | Web site hits. |
| report | Show log report. |
| analyzer | Show analyzer settings. |
| automation | Show log automation settings. |
| categories | Show log categories configuration. |
| attributes | Show log categories event attributes which have been changed. |
| category | Show log attributes with specified category name. |
| <LOG_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Log category name. Example: Firewall |
| group | Show log attributes with specified group name. |
| <LOG_GROUP_NAME> |
Group name. Example: Firewall Event |
| event | Show log attributes with specified event name. |
| <LOG_EVENT_NAME> |
Event name. Example: Activate Firewall |
| event-id | Show log event attributes with specified ID. |
| <LOG_EVENT_ID_FOR_ATTRIBUTES> |
Event ID for showing the attributes. Example: 123 |
| global-category-attributes | Show global category attributes. |
| statistics | Show log categories event statistics. |
| category-level | Show event statistics of specified category level: category, group or event. |
| <LOG_CATEGORY_BRANCH_LEVEL> |
Log category branch level. Example: Category |
| id | Show event statistics by event ID. |
| <INT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| name | Show statistics by the name of a category, group or event. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| events-since | Show events time range for showing log view in CLI based current time. |
| name-resolution | Show name resolution settings. |
| syslog | Show syslog settings. |
| view | Show system log. |
| id | Show log with specified ID. |
| <LOG_EVENT_ID_FOR_ATTRIBUTES> |
Event ID for showing the attributes. Example: 123 |
| category | Show log with specified category. |
| <LOG_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Log category name. Example: Firewall |
| priority | Show log with specified priority. |
| <LOG_EVENT_PRIORITY> |
Event priority. Example: Notice |
| source-interface | Show log with specified source interface. |
| <LOG_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| destination-interface | Show log with specified destination interface. |
| <LOG_INTERFACE_NAME> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| source-ip | Show log with specified source-ip. |
| <IP_V4V6_HOST> |
IPV4: address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652 |
| source-port | Show log with specified source-port. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| destination-ip | Show log with specified destination-ip. |
| <IP_V4V6_HOST> |
IPV4: address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652 |
| destination-port | Show log with specified destination-port. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| ip-protocol | Show log with specified IP protocol. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| user-name | Show log with specified user name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| application | Show log with specified application. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| view-status | Show system log status. |
| viewpoint | Show viewpoint settings. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| call-status | Show VoIP call status. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| maximum | Use maximum security (recommended). |
| performance-optimized | Use performance optimized. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| user-name | Set proxy server username. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| password | Set proxy server password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| password | Clear proxy server authentication password. |
| user-name | Clear proxy server authentication username. |
| user-name | Set proxy server portal username. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| password | Set proxy server portal password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| password | Clear proxy server portal password. |
| user-name | Clear proxy server portal username. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Set Log Redundancy in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Set Log Redundancy in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Set Log Redundancy in seconds. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Clear Log Redundancy. |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Clear Log Redundancy. |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| detect-all | Detect All. |
| log-redundancy | Clear Log Redundancy. |
| prevent-all | Prevent All. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| ipv6 | Excluded IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| entry | IPS exclusion list entry. |
| <IPS_EXCLUSION_BEGIN_IPV4_HOST> |
IPS Exclusion List entry begin IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPS_EXCLUSION_END_IPV4_HOST> |
IPS Exclusion List entry end IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| group | Address object group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| list | Enable IPS exclusion list. |
| name | Address object name |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| entries | Delete all IPS exclusion list entries. |
| entry | Delete one IPS exclusion list entry. |
| <IPS_EXCLUSION_BEGIN_IPV4_HOST> |
IPS Exclusion List entry begin IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPS_EXCLUSION_END_IPV4_HOST> |
IPS Exclusion List entry end IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| list | Disable IPS exclusion list. |
| category | Category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| signature | Signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <IPS_POLICY_ID> |
Policy ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <IPS_POLICY_NAME> |
Policy name. Example: ActivePDF WebGrabber ActiveX Instantiation |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| disable | Disable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| global-setting | Use Global Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| global-setting | Use Global Setting. |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| all | All. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| ipv6 | Included IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address Object Host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address Object Network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Specify IP Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| all | All. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Specify name of Range Address Object. |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| ipv6 | Excluded IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address Object Host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address Object Network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Specify IP Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Specify name of Range Address Object. |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| ip | Don't excluded any IP addresses. |
| users | Don't excluded any users/groups. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule Object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule Object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule Object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| filter | Set log redundancy filter in seconds. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| global-setting | Use Global Setting. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| all | All. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| ipv6 | Included IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| all | All. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| ipv6 | Excluded IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| ip | Don't excluded any IP addresses. |
| users | Don't excluded any users/groups. |
| always-on | Always on. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| days | Schedule Object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule Object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule Object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| filter | Set log redundancy filter in seconds. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| high | High priority. |
| low | Low priority. |
| medium | Medium priority. |
| both | Both. |
| incoming | Incoming. |
| outgoing | Outgoing. |
| to-client | To client. |
| to-server | To server. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <GAV_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <GAV_SIG_NAME> |
Signature name. Example: 007SpySoft.G (Trojan) |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <GAV_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <GAV_SIG_NAME> |
Signature name. Example: 007SpySoft.G (Trojan) |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| tcp-stream | TCP Stream. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| tcp-stream | TCP Stream. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| tcp-stream | TCP Stream. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| tcp-stream | TCP Stream. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| cifs-netbios | CIFS/NetBIOS. |
| ftp | FTP. |
| http | HTTP. |
| imap | IMAP. |
| pop3 | POP3. |
| smtp | SMTP. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <GAV_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <GAV_SIG_NAME> |
Signature name. Example: 007SpySoft.G (Trojan) |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <GAV_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <GAV_SIG_NAME> |
Signature name. Example: 007SpySoft.G (Trojan) |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ipv6 | Excluded IPv6 addresses. |
| host | Address object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| network | Address object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| entry | Gateway AV exclusion list entry. |
| <GAV_EXCLUSION_BEGIN_IPV4_HOST> |
Gateway AV Exclusion List entry begin IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <GAV_EXCLUSION_END_IPV4_HOST> |
Gateway AV Exclusion List entry end IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| group | Address object group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME_MIXED> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| list | Enable gateway AV exclusion list. |
| name | Address object name |
| <ADDR_NAME_MIXED> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| entries | Delete all gateway AV exclusion list entries. |
| entry | Delete gateway AV exclusion list entry. |
| <GAV_EXCLUSION_BEGIN_IPV4_HOST> |
Gateway AV Exclusion List entry begin IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <GAV_EXCLUSION_END_IPV4_HOST> |
Gateway AV Exclusion List entry end IPV4 in the form: D.D.D.D. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| list | Disable gateway AV exclusion list. |
| <MATCH_OBJ_NAME> |
Match object name. Example: Match FTP |
| <MATCH_OBJ_NAME> |
Match object name. Example: Match FTP |
| activex-class-id | Active X class ID. |
| application-category-list | Application category list. |
| application-list | Application list. |
| application-signature-list | Application signature list. |
| cfs-allow-forbidden-list | CFS allow/forbidden list. |
| cfs-category-list | CFS category list. |
| custom | Custom object. |
| email-body | E-mail body. |
| email-cc | E-mail CC. |
| email-from | E-mail from. |
| email-size | E-mail size. |
| email-subject | E-mail subject. |
| email-to | E-mail to. |
| file-content | File content. |
| file-extension | File extension. |
| file-name | File name. |
| ftp-command | FTP command. |
| ftp-command-value | FTP command and value. |
| http-cookie | HTTP cookie. |
| http-host | Http host. |
| http-referer | HTTP referer. |
| http-request-custom-header | HTTP request custom header. |
| http-response-custom-header | HTTP response custom header. |
| http-set-cookie | HTTP set cookie. |
| http-uri-content | HTTP URI content. |
| http-url | HTTP URL. |
| http-user-agent | Http user agent. |
| ips-signature-category-list | IPS signature category list. |
| ips-signature-list | IPS signature list. |
| log-email-user | Log e-mail user. |
| mime-custom-header | MIME custom header. |
| web-browser | Web browser. |
| <MATCH_OBJ_NAME> |
Match object name. Example: Match FTP |
| exact | Exact match. |
| partial | Partial match. |
| prefix | Prefix match. |
| regex | Regular expression match. |
| suffix | Suffix match. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| alphanumeric | Alphanumeric. |
| hexadecimal | Hexadecimal. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <MATCH_OBJ_CONTENT_ENTRY> |
Match object content. Example: mpg |
| chrome | Chrome. |
| firefox | Firefox. |
| msie | Internet explorer. |
| netscape | Netscape. |
| safari | Safari. |
| chrome | Chrome. |
| firefox | Firefox. |
| msie | Internet explorer. |
| netscape | Netscape. |
| safari | Safari. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| abort | ABORT. |
| account | ACCOUNT. |
| allocate | ALLOCATE. |
| append | APPEND. |
| ascii | ASCII. |
| binary | BINARY. |
| cd | CD. |
| cdup | CDUP. |
| delete | DELETE. |
| get | GET. |
| help | HELP. |
| ls | LS. |
| mkdir | MKDIR. |
| mode | MODE. |
| modified-time | MODIFIED_TIME. |
| nlist | NLIST. |
| noop | NOOP. |
| passive | PASSIVE. |
| password | PASSWORD. |
| port | PORT. |
| put | PUT. |
| pwd | PWD. |
| quit | QUIT. |
| reinitialize | REINITIALIZE. |
| rename-from | RENAME_FROM. |
| rename-to | RENAME_TO. |
| restart | RESTART. |
| rmdir | RMDIR. |
| site | SITE. |
| size | SIZE. |
| status | STATUS. |
| structure | STRUCTURE. |
| structure-mount | STRUCTURE_MOUNT. |
| structure-unique | STRUCTURE_UNIQUE. |
| system | SYSTEM. |
| type | TYPE. |
| user | USER. |
| abort | ABORT. |
| account | ACCOUNT. |
| allocate | ALLOCATE. |
| append | APPEND. |
| ascii | ASCII. |
| binary | BINARY. |
| cd | CD. |
| cdup | CDUP. |
| delete | DELETE. |
| get | GET. |
| help | HELP. |
| ls | LS. |
| mkdir | MKDIR. |
| mode | MODE. |
| modified-time | MODIFIED_TIME. |
| nlist | NLIST. |
| noop | NOOP. |
| passive | PASSIVE. |
| password | PASSWORD. |
| port | PORT. |
| put | PUT. |
| pwd | PWD. |
| quit | QUIT. |
| reinitialize | REINITIALIZE. |
| rename-from | RENAME_FROM. |
| rename-to | RENAME_TO. |
| restart | RESTART. |
| rmdir | RMDIR. |
| site | SITE. |
| size | SIZE. |
| status | STATUS. |
| structure | STRUCTURE. |
| structure-mount | STRUCTURE_MOUNT. |
| structure-unique | STRUCTURE_UNIQUE. |
| system | SYSTEM. |
| type | TYPE. |
| user | USER. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <MATCH_OBJ_CONTENT_ENTRY> |
Match object content. Example: mpg |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| category | Category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| signature | Signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <IPS_POLICY_ID> |
Policy ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <IPS_POLICY_NAME> |
Policy name. Example: ActivePDF WebGrabber ActiveX Instantiation |
| category | Category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| signature | Signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <IPS_POLICY_ID> |
Policy ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <IPS_POLICY_NAME> |
Policy name. Example: ActivePDF WebGrabber ActiveX Instantiation |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| category | Application category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| category | Application category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| category | Application category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| sig | Signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <AC_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <AC_SIG_NAME> | Signature name. |
| category | Application category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| sig | Signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <AC_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <AC_SIG_NAME> | Signature name. |
| abortion-advocacy-groups | Rating. |
| adult-mature-content | Rating. |
| advertisement | Rating. |
| alcohol-tobacco | Rating. |
| all | All ratings. |
| arts-entertainment | Rating. |
| business-economy | Rating. |
| chat-instant-messaging | Rating. |
| cult-occult | Rating. |
| cultural-institutions | Rating. |
| drugs-illegal-drugs | Rating. |
| Rating. | |
| education | Rating. |
| freeware-software-downloads | Rating. |
| gambling | Rating. |
| games | Rating. |
| gay-lesbian-issues | Rating. |
| government | Rating. |
| hacking-proxy-avoidance-systems | Rating. |
| health | Rating. |
| humor-jokes | Rating. |
| illegal-questionable-skills | Rating. |
| information-technology-computers | Rating. |
| internet-auctions | Rating. |
| internet-watch-foundation | Rating. |
| intimate-apparel-swimsuit | Rating. |
| job-search | Rating. |
| kid-friendly | Rating. |
| malware | Rating. |
| military | Rating. |
| multimedia | Rating. |
| news-media | Rating. |
| not-rated | Rating. |
| nudism | Rating. |
| online-banking | Rating. |
| online-brokerage-trading | Rating. |
| other | Rating. |
| pay-to-surf-sites | Rating. |
| personals-dating | Rating. |
| political-advocacy-groups | Rating. |
| pornography | Rating. |
| real-estate | Rating. |
| reference | Rating. |
| religion | Rating. |
| restaurants-dining | Rating. |
| search-engine-portals | Rating. |
| sex-education | Rating. |
| shopping | Rating. |
| social-networking | Rating. |
| society-lifestyle | Rating. |
| sports-recreation | Rating. |
| travel | Rating. |
| usernet-news-groups | Rating. |
| vehicles | Rating. |
| violence-hate-racism | Rating. |
| weapons | Rating. |
| web-communication | Rating. |
| web-hosting | Rating. |
| abortion-advocacy-groups | Rating. |
| adult-mature-content | Rating. |
| advertisement | Rating. |
| alcohol-tobacco | Rating. |
| all | All ratings. |
| arts-entertainment | Rating. |
| business-economy | Rating. |
| chat-instant-messaging | Rating. |
| cult-occult | Rating. |
| cultural-institutions | Rating. |
| drugs-illegal-drugs | Rating. |
| Rating. | |
| education | Rating. |
| freeware-software-downloads | Rating. |
| gambling | Rating. |
| games | Rating. |
| gay-lesbian-issues | Rating. |
| government | Rating. |
| hacking-proxy-avoidance-systems | Rating. |
| health | Rating. |
| humor-jokes | Rating. |
| illegal-questionable-skills | Rating. |
| information-technology-computers | Rating. |
| internet-auctions | Rating. |
| internet-watch-foundation | Rating. |
| intimate-apparel-swimsuit | Rating. |
| job-search | Rating. |
| kid-friendly | Rating. |
| malware | Rating. |
| military | Rating. |
| multimedia | Rating. |
| news-media | Rating. |
| not-rated | Rating. |
| nudism | Rating. |
| online-banking | Rating. |
| online-brokerage-trading | Rating. |
| other | Rating. |
| pay-to-surf-sites | Rating. |
| personals-dating | Rating. |
| political-advocacy-groups | Rating. |
| pornography | Rating. |
| real-estate | Rating. |
| reference | Rating. |
| religion | Rating. |
| restaurants-dining | Rating. |
| search-engine-portals | Rating. |
| sex-education | Rating. |
| shopping | Rating. |
| social-networking | Rating. |
| society-lifestyle | Rating. |
| sports-recreation | Rating. |
| travel | Rating. |
| usernet-news-groups | Rating. |
| vehicles | Rating. |
| violence-hate-racism | Rating. |
| weapons | Rating. |
| web-communication | Rating. |
| web-hosting | Rating. |
| <ACTION_OBJ_NAME> |
Action object name. Example: HTTP Block Page |
| <ACTION_OBJ_NAME> |
Action object name. Example: HTTP Block Page |
| <ACTION_OBJ_NAME> |
Action object name. Example: HTTP Block Page |
| bandwidth-management | Bandwidth management. |
| block-smtp-error-reply | Block SMTP e-mail and send error reply. |
| disable-email-attachment | Disable e-mail attachment and add text. |
| email-add-text | E-mail - add text. |
| ftp-notification-reply | FTP notification reply. |
| http-block-page | HTTP block page. |
| http-redirect | HTTP redirect. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| blue | Blue. |
| red | Red. |
| white | White. |
| yellow | Yellow. |
| per-action | Per action. |
| per-policy | Per policy. |
| bandwidth-object | Clear bandwidth object. |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 1. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| <BANDWIDTH_RULE_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| bandwidth-object | Clear bandwidth object. |
| high | High 2. |
| highest | Highest 1. |
| low | Low 6. |
| lowest | Lowest 1. |
| medium | Medium 4. |
| medium-high | Medium-high 3. |
| medium-low | Medium-low 5. |
| realtime | Realtime 0. |
| <BANDWIDTH_RULE_NAME> |
Bandwidth object name. Example: \"Corp High Priority\" |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_NAME> |
E-mail object name. Example: Marketing E-mail Object |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_NAME> |
E-mail object name. Example: Marketing E-mail Object |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_NAME> |
E-mail object name. Example: Marketing E-mail Object |
| exact | Exact match. |
| partial | Partial match. |
| regex | Regular expression match. |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_CONTENT_ENTRY> |
E-mail object content. Example: administrator@corp.local |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_CONTENT_ENTRY> |
E-mail object content. Example: administrator@corp.local |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| ips | Use IPS Exclusion List. |
| object | Use specified address object for exclusion list. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object Host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Specify name of Address Object. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object Network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Specify IP Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| category | Category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Specify an application. |
| id | App ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | App name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| category | Category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| app | Specify an application. |
| id | App ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | App name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| sig | Specify an signature. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <AC_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Signature name. |
| <AC_SIG_NAME> | Signature name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| disable | Disable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| global-setting | Use Global Setting. |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| all | All. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| none | None. |
| all | All. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object Host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Specify name of Range Address Object. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object Network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Specify IP Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object Host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Specify name of Range Address Object. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object Network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| none | None. |
| range | Specify IP Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| always-on | Always on. |
| days | Schedule Object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule Object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule Object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| all | All. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| none | None. |
| all | All. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group. |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| none | None. |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| always-on | Always on. |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| days | Schedule Object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule Object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule Object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| category-setting | Use Category Setting. |
| filter | Set log redundancy filter in seconds. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| disable | Enable. |
| enable | Enable. |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| all | All. |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| administrator | Built-in administrator. |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| group | Specify local user group. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| guests | Guests. |
| name | Specify local user. |
| <LOCAL_USER_NAME> |
User object name. Example: user1 |
| none | None. |
| all | All. |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| group | Address Object Group |
| <ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Address Object host. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address Object name. |
| <ADDR_RANGE_GROUP> |
Range group address object name. Example: Public Servers Group |
| network | Address Object network. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| none | None. |
| range | Address Object range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| always-on | Always on. |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| days | Schedule Object days. |
| <SCHED_DAYS> |
Days of the week in the form: SU-M-T-W-TH-F-SA. Example: SU-M-TH-SA |
| time | Schedule Object beginning/ending time. |
| <SCHED_TIME_BEGIN> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| <SCHED_TIME_END> |
Time in the form: DD:DD. Example: 12:00 |
| name | Schedule Object name. |
| <SCHED_NAME> |
Schedule object name. Example: Work Hours |
| app-setting | Use App Setting. |
| filter | Set log redundancy filter in seconds. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| inherit | Inherit DNS servers. |
| primary | Specify primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Specify secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| tertiary | Specify tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| tertiary | Clear tertiary DNS server IP address. |
| enable | Enable specified parameter. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | Real-Time Blacklist Service Name. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| enable | Enable specified parameter. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | Real-Time Blacklist Service Name. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| name | RBL service name. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| fqdn | SMTP server Full Qualified Domain Name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | SMTP server host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | SMTP server named host address object. |
| <RBL_ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| range | SMTP server Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| fqdn | SMTP server Full Qualified Domain Name. |
| <RBL_ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | SMTP server host address. |
| <RBL_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | SMTP server named host address object. |
| <RBL_ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| range | SMTP server Range. |
| <RBL_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <RBL_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| fqdn | SMTP server Full Qualified Domain Name. |
| <ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | SMTP server host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | SMTP server named host address object. |
| <RBL_ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| range | SMTP server Range. |
| <ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| fqdn | SMTP server Full Qualified Domain Name. |
| <RBL_ADDR_FQDN> |
FQDN in the form: example.com or *.example.com. Example: example.com |
| host | SMTP server host address. |
| <RBL_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | SMTP server named host address object. |
| <RBL_ADDR_NAME> |
Address object name. Example: Web Server |
| range | SMTP server Range. |
| <RBL_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <RBL_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| open-relay | 127.0.0.2 - Open Relay. |
| dialup-spam-source | 127.0.0.3 - Dialup Spam Source. |
| spam-source | 127.0.0.4 - Spam Source. |
| smart-host | 127.0.0.5 - Smart Host. |
| spamware-site | 127.0.0.6 - Spamware Site. |
| bad-list-server | 127.0.0.7 - Bad List Server. |
| insecure-script | 127.0.0.8 - Insecure Script. |
| open-proxy-server | 127.0.0.9 - Open Proxy Server. |
| block-all | Block All Responses. |
| open-relay | 127.0.0.2 - Open Relay. |
| dialup-spam-source | 127.0.0.3 - Dialup Spam Source. |
| spam-source | 127.0.0.4 - Spam Source. |
| smart-host | 127.0.0.5 - Smart Host. |
| spamware-site | 127.0.0.6 - Spamware Site. |
| bad-list-server | 127.0.0.7 - Bad List Server. |
| insecure-script | 127.0.0.8 - Insecure Script. |
| open-proxy-server | 127.0.0.9 - Open Proxy Server. |
| block-all | Block All Responses. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| categories | Show Intrusion Prevention categories. |
| category | Show Intrusion Prevention category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 1234 |
| name | Category name. |
| <IPS_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: ACTIVEX |
| exclusion-list | Show Intrusion Prevention exclusion list. |
| policies | Show Intrusion Prevention policies. |
| policy | Show Intrusion Prevention policy. |
| <IPS_POLICY_NAME> |
Policy name. Example: ActivePDF WebGrabber ActiveX Instantiation |
| status | Show Intrusion Prevention status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| exclusion-list | Show Gateway Anti-Virus exclusion list. |
| signatures | Show Gateway Anti-Virus signatures. |
| status | Show Gateway Anti-Virus status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show match objects status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <MATCH_OBJ_NAME> |
Match object name. Example: Match FTP |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show action objects status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <ACTION_OBJ_NAME> |
Action object name. Example: HTTP Block Page |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| status | Show e-mail user objects status. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <EMAIL_OBJ_NAME> |
E-mail object name. Example: Marketing E-mail Object |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| application | Show App Control application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| applications | Show App Control applications. |
| categories | Show App Control categories. |
| category | Show App Control category. |
| id | Category ID. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_ID> |
Category ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Category name. |
| <AC_CATEGORY_NAME> |
Category name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| exclusion-list | Show App Control exclusion list. |
| signature | Show App Control signature. |
| app | Specify an App Control application. |
| id | Application ID. |
| <AC_APP_ID> |
Application ID. Example: 123 |
| name | Application name. |
| <AC_APP_NAME> |
Application name. Example: APP-UPDATE |
| sig | Specify a signature. |
| name | Signature name. |
| <AC_SIG_NAME> | Signature name. |
| id | Signature ID. |
| <AC_SIG_ID> |
Signature ID. Example: 123 |
| signatures | Show App Control signatures. |
| status | Show App Control status. |
| custom | Show custom configuration. |
| default | Show system/factory default configuration. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| blacklist | Show RBL blacklist. |
| service | Show Real-Time Blacklist service. |
| <RBL_SERVICE_NAME> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| services | Show Real-Time Blacklist services. |
| statistics | Show Real-Time Blacklist service statistics. |
| whitelist | Show RBL whitelist. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| <CUSTOMER_ID> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| host | IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| network | Network address and subnet mask. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_MASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| host | IP address. |
| <VIRTUAL_ASSIST_DENY_REQUESTS_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| network | Network address and subnet mask. |
| <VIRTUAL_ASSIST_DENY_REQUESTS_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <VIRTUAL_ASSIST_DENY_REQUESTS_NETMASK> |
IPV4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
| sessions | Show virtual assist active customer sessions. |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| policy | Add, edit or enable a VPN policy. |
| enable | Enable a VPN policy. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| group-vpn | Edit group VPN policy. |
| <VPN_GROUP_POLICY_NAME> |
Group VPN policy name. Example: WAN GroupVPN |
| ipv6 | IPv6 vpn policy. |
| site-to-site | Add or edit IPv6 site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_V6_NAME> |
IPv6 Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| site-to-site | Add or edit site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| tunnel-interface | Add or edit tunnel interface VPN policy. |
| <VPN_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| enable | Enable a VPN policy. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| ipv6 | IPv6 vpn policy. |
| site-to-site | Delete IPv6 site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_V6_NAME> |
IPv6 Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| site-to-site | Delete site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| tunnel-interface | Delete tunnel interface VPN policy. |
| <VPN_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| interval | Dead peer detection interval for idle VPN sessions in seconds. |
| <UINT16> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 123 |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| mschap | Use MSCHAP for RADIUS. |
| mschapv2 | Use MSCHAPv2 for RADIUS. |
| 1 | Group 1 modp768. |
| 14 | Group 14 modp2048. |
| 19 | Group 19 ECP random 256-bit. |
| 2 | Group 2 modp1024. |
| 20 | Group 20 ECP random 384-Bit. |
| 21 | Group 21 ECP random 521-Bit. |
| 25 | Group 25 ECP random 192-Bit. |
| 26 | Group 26 ECP random 224-Bit. |
| 5 | Group 5 modp1536. |
| aes-128 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 128 bit. |
| aes-192 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 192 bit. |
| aes-256 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 256 bit. |
| des | Data encryption standard (DES). |
| triple-des | Triple data encryption standard (3DES). |
| md5 | Message-digest algorithm 5 (MD5). |
| sha-1 | Secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1). |
| sha-256 | Secure hash algorithm 256 (SHA-256). |
| sha-384 | Secure hash algorithm 384 (SHA-384). |
| sha-512 | Secure hash algorithm 512 (SHA-512). |
| enable | Enable a VPN policy. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| group-vpn | Edit group VPN policy. |
| <VPN_GROUP_POLICY_NAME> |
Group VPN policy name. Example: WAN GroupVPN |
| ipv6 | IPv6 vpn policy. |
| site-to-site | Delete IPv6 site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_V6_NAME> |
IPv6 Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| site-to-site | Add or edit site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| tunnel-interface | Add or edit tunnel interface VPN policy. |
| <VPN_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| enable | Enable a VPN policy. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| ipv6 | IPv6 vpn policy. |
| site-to-site | Delete IPv6 site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_V6_NAME> |
IPv6 Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| site-to-site | Delete site-to-site VPN policy. |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_NAME> |
Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| tunnel-interface | Delete tunnel interface VPN policy. |
| <VPN_TUNNEL_POLICY_NAME> |
Tunnel interface VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| <VPN_SITE_POLICY_V6_NAME> |
IPv6 Site-to-site VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <HOSTNAME_MIXED> |
IPV4: hostname in the form: D.D.D.D or hostname\nIPV6: host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| certificate | IKE using 3rd party certificates. |
| manual-key | Manual key. |
| shared-secret | IKE using pre-shared secret. |
| certificate | IKE using 3rd party certificates. |
| shared-secret | IKE using pre-shared secret. |
| <VPN_GROUP_POLICY_ENABLE_NAME> |
Group VPN policy name. Example: WAN GroupVPN |
| rcf | Rcf format is required for Global VPN Clients. |
| network | Configure the client access network(s) you wish to export. |
| group | Select the network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| name | Select the network to named address object. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| password | You may encrypt the exported file using a chosen password. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| spd | Spd format is required for VPN Clients 8.x and earlier. |
| ftp | Export using the FTP protocol. |
| <FTP_URL> |
FTP URL in the form: ftp://username:password@hostname/\n Escape character: ':' -> '\\\\:', '@' -> '\\\\@', '/' -> '\\\\/', '\\' -> '\\\\\\\\'. Example: ftp://username:password@hostname/\nftp://username@hostname/\nftp://hostname/ |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| domain-name | Domain name identifier. |
| <VPN_FQDN> |
Domain name in the form: aaa.aa. Example: example.com |
| email-address | E-mail address identifier. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| firewall-id | Firewall identifier. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ipv4 | IP address identifier. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ipv6 | IPv6 address identifier. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| key-id | Key ID identifier. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| domain-name | Clear domain name identifier. |
| email-address | Clear e-mail address identifier. |
| firewall-id | Clear Firewall ID identifier. |
| ipv4 | Clear IPv4 address identifier. |
| ipv6 | Clear IPv6 address identifier. |
| key-id | Clear key ID identifier. |
| domain-name | Domain name identifier. |
| <VPN_FQDN> |
Domain name in the form: aaa.aa. Example: example.com |
| email-address | E-mail address identifier. |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| firewall-id | Firewall ID identifier. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ipv4 | IP address identifier. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| ipv6 | IPv6 address identifier. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| key-id | Key ID identifier. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| domain-name | Clear domain name identifier. |
| email-address | Clear e-mail address identifier. |
| firewall-id | Clear Firewall ID identifier. |
| ipv4 | Clear IPv4 address identifier. |
| ipv6 | Clear IPv6 address identifier. |
| key-id | Clear key ID identifier. |
| <CERT_NAME> |
Certificate name. Example: my_cert |
| default-id | Default ID from the certificate. |
| distinguished-name | Distinguished name (DN). |
| domain-name | Domain name (FQDN). |
| email-id | E-mail ID (userFQDN). |
| ip | IP address (IPV4). |
| distinguished-name | Distinguished name (DN). |
| <DISTINGUISHED_NAME> |
Distinguished name filter in the form: c=*;cn=*;o=*;ou=*; or *. Example: ou=aaa;c=a;* |
| domain-name | Domain name (FQDN). |
| <VPN_FQDN> |
Domain name in the form: aaa.aa. Example: example.com |
| email-id | E-mail ID (userFQDN). |
| <EMAIL> |
E-mail in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| ip | IP address (IPV4). |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| distinguished-name | Clear distinguished name (DN). |
| domain-name | Clear domain name (FQDN). |
| email-id | Clear e-mail ID (userFQDN). |
| ip | Clear IP address (IPV4). |
| distinguished-name | Distinguished name. |
| <DISTINGUISHED_NAME> |
Distinguished name filter in the form: c=*;cn=*;o=*;ou=*; or *. Example: ou=aaa;c=a;* |
| domain-name | Domain name. |
| <VPN_FQDN_FILTER> |
Domain name filter in the form: aabb?*-.aa. Example: example.com |
| email-id | E-mail ID. |
| <VPN_EMAIL_FILTER> |
E-mail filter in the form: aaaaa@bbb.com. Example: support@sonicwall.com |
| any | Any local network. |
| dhcp | Obtain IP addresses using DHCP through this VPN tunnel. |
| group | Configure the local network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Configure the local network to host address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the local network to named address object. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Configure the local network to network address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Configure the local network to range of addresses. |
| <VPN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| any | Use this VPN tunnel as default route for all internet traffic. |
| dhcp | Destination network obtains IP addresses using DHCP through this VPN tunnel. |
| group | Configure the remote network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Configure the remote network to host address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Configure the remote network to named address object. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Configure the remote network to network address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Configure the remote network to range of addresses. |
| <VPN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| authentication | Authentication hashing encryption algorithm. |
| md5 | Message-digest algorithm 5 (MD5). |
| sha-1 | Secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1). |
| sha-256 | Secure hash algorithm 256 (SHA-256). |
| sha-384 | Secure hash algorithm 384 (SHA-384). |
| sha-512 | Secure hash algorithm 512 (SHA-512). |
| dh-group | DH group. |
| 1 | Group 1 modp768. |
| 14 | Group 14 modp2048. |
| 19 | Group 19 ECP random 256-bit. |
| 2 | Group 2 modp1024. |
| 20 | Group 20 ECP random 384-Bit. |
| 21 | Group 21 ECP random 521-Bit. |
| 25 | Group 25 ECP random 192-Bit. |
| 26 | Group 26 ECP random 224-Bit. |
| 5 | Group 5 modp1536. |
| encryption | Encryption algorithm. |
| aes-128 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 128 bit. |
| aes-192 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 192 bit. |
| aes-256 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 256 bit. |
| des | Data encryption standard (DES). |
| triple-des | Triple data encryption standard (3DES). |
| exchange | Exchange. |
| aggressive | Aggressive mode. |
| ikev2 | IKEv2 mode. |
| main | Main mode. |
| lifetime | Life time (seconds). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| authentication | Authentication hashing encryption algorithm. |
| aes-xcbc | Secure hash algorithm AES (AES-XCBC). |
| md5 | Message-digest algorithm 5 (MD5). |
| sha-1 | Secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1). |
| sha-256 | Secure hash algorithm 256 (SHA-256). |
| sha-384 | Secure hash algorithm 384 (SHA-384). |
| sha-512 | Secure hash algorithm 512 (SHA-512). |
| authentication-key | Configure authentication key. |
| <VPN_HEX_STRING64> |
String of hexadecimal (16-64) digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| encryption | Encryption algorithm. |
| aes-128 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 128 bit. |
| aes-192 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 192 bit. |
| aes-256 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - 256 bit. |
| aes-gcm16-128 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GCM16 128 bit. |
| aes-gcm16-192 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GCM16 192 bit. |
| aes-gcm16-256 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GCM16 256 bit. |
| aes-gmac-128 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GMAC 128 bit. |
| aes-gmac-192 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GMAC 192 bit. |
| aes-gmac-256 | Advanced encryption standard (AES) - GMAC 256 bit. |
| des | Data encryption standard (DES). |
| triple-des | Triple data encryption standard (3DES). |
| encryption-key | Configure encryption key. |
| <VPN_HEX_STRING64> |
String of hexadecimal (16-64) digits. Example: 0123456989abcdef |
| in-spi | Configure incoming SPI. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| lifetime | Life time (seconds). |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| out-spi | Configure outgoing SPI. |
| <HEX_UINT32> |
Hexadecimal integer in the form: 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 0xaa55aa55 |
| perfect-forward-secrecy | Enable perfect forward secrecy. |
| dh-group | DH group. |
| 1 | Group 1 modp768. |
| 14 | Group 14 modp2048. |
| 19 | Group 19 ECP random 256-bit. |
| 2 | Group 2 modp1024. |
| 20 | Group 20 ECP random 384-Bit. |
| 21 | Group 21 ECP random 521-Bit. |
| 25 | Group 25 ECP random 192-Bit. |
| 26 | Group 26 ECP random 224-Bit. |
| 5 | Group 5 modp1536. |
| protocol | Protocol. |
| ah | Configure AH. |
| esp | Configure ESP. |
| authentication | None authentication hashing encryption algorithm. |
| authentication-key | Configure authentication key. |
| encryption | None encryption algorithm. |
| encryption-key | Configure encryption key. |
| perfect-forward-secrecy | Disable perfect forward secrecy. |
| always | Always cache. |
| never | No caching. |
| single-session | Cache for single session. |
| dhcp-and-manual | Use DHCP lease or manual configuration. |
| dhcp-only | Use DHCP lease. |
| none | None. |
| all-secured-gateways | All secured gateways. |
| split-tunnels | Split tunnels. |
| this-gateway-only | This gateway only. |
| access-list | Enable apply VPN access control list. |
| disable-acl | Disable apply VPN access control list. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| translated-local | Translated local network. |
| group | Configure the local network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Host IP. |
| <VPN_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Network address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original translated local network. |
| range | Network range. |
| <VPN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| translated-remote | Translated remote network. |
| group | Configure the local network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Host IP. |
| <VPN_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Network address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| original | Original translated remote network. |
| range | Network range. |
| <VPN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| http | Enable HTTP management for VPN policy. |
| https | Enable HTTPS management for VPN policy. |
| snmp | Enable SNMP management for VPN policy. |
| ssh | Enable SSH management for VPN policy. |
| http | Disable HTTP management for VPN policy. |
| https | Disable HTTPS management for VPN policy. |
| snmp | Disable SNMP management for VPN policy. |
| ssh | Disable SSH management for VPN policy. |
| http | Enable VPN policy for HTTP user login. |
| https | Enable VPN policy for HTTPS user login. |
| http | Disable VPN policy for HTTP user login. |
| https | Disable VPN policy for HTTPS user login. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| interface | Bound to interface. |
| <VPN_BOUND_TO_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| zone | Bound to zone. |
| <ZONE_WAN_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| custom | Specify the Local Gateway IP address. |
| <IPV6_HOST> |
IPV6 Address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH. Example: 2000:0000:0000:ff68:0205:62ef:ee8d:f25b |
| primary | Using Primary IP address. |
| 1 | Bound to group 1. |
| 2 | Bound to group 2. |
| 3 | Bound to group 3. |
| 4 | Bound to group 4. |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| allow-unauthenticated | Enable unauthenticated access for VPN policy. |
| group | Configure the remote network to named address object group. |
| <VPN_ADDR_GROUP_NAME> |
Group address object name. Example: Sales Group |
| host | Host IP. |
| <VPN_ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Address object name. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NAME> |
Host/network/range address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Network address. |
| <VPN_ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| range | Network range. |
| <VPN_ADDR_BEGIN> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 starting range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 starting range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.100\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| <VPN_ADDR_END> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 ending range in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 ending range in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.1.150\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:effe\n |
| require-xauth | Enable XAUTH checking for VPN policy. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| <WEB_URL> |
URL in the form: http://host/file. Example: http://www.example.com/products/ |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| primary | Primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Clear primary DNS server IP address. |
| secondary | Clear secondary DNS server IP address. |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| local | Use local L2TP IP pool. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| provided | IP address provided by RADIUS/LDAP Server. |
| <LOCAL_USER_GROUP_NAME> |
User group object name. Example: Limited Administrators |
| central | Configure DHCP over VPN for central gateway. |
| remote | Configure DHCP over VPN for remote gateway. |
| <DHCP_SERVER_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <DHCP_SERVER_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <DHCP_OVER_VPN_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| <STATIC_DEVICE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <STATIC_DEVICE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <STATIC_DEVICE_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <EXCLUDE_DEVICE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| <EXCLUDE_DEVICE_MAC> |
MAC address in the form: HH:HH:HH:HH:HH:HH OR HHHHHHHHHHHH. Example: 00:0C:F1:56:98:AD |
| tunnel | Show an active VPN tunnel. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| tunnels | Show all currently active VPN tunnels. |
| ike | Show ike sa. |
| ipsec | Show ipsec sa. |
| summary | Show vpn sa number. |
| dhcp-over-vpn | Show DHCP over VPN status or configuration. |
| leases | Show DHCP over VPN leases. |
| l2tp-server | Show L2TP server configuration. |
| policies | Show all VPN policies. |
| ipv4 | Show only IPv4 VPN policies. |
| ipv6 | Show only IPv6 VPN policies. |
| policy | Show a VPN policy. |
| <VPN_POLICY_NAME> |
VPN policy name. Example: Remote Office |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |
| <SSLVPN_LOGOUT_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SSLVPN_LOGOUT_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SSLVPN_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <SSLVPN_ZONE_NAME> |
Zone object name. Example: DMZ |
| <IPV4_PORT> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHH. Example: 80 |
| name | Specify certificate. |
| <CERT_NAME> |
Certificate name. Example: my_cert |
| use-self-signed | Use self signed certificate. |
| aes256-sha1 | AES256-SHA1. |
| rc4-md5 | RC4-MD5. |
| triple-des-sha1 | 3DES-SHA1. |
| mschap | Use MSCHAP for RADIUS. |
| mschapv2 | Use MSCHAPv2 for RADIUS. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| custom | Use customed home page message. |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| default | Use default home page message example template. |
| custom | Use customed login message. |
| <ROL> |
Remaining command line input. Example: line... |
| default | Use default login message example template. |
| custom | Enable use custom sonicwall logo. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| default | Enable use default sonicwall logo. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <SSLVPN_INTERFACE> |
Interface name. Example: X0 |
| primary | Primary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary DNS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| inherit | Use the default global DNS settings. |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| primary | Primary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| secondary | Secondary WINS server IP address. |
| <IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| <UINT32> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHHHHHHHH. Example: 123 |
| credentials | Allow saving of user name and password. |
| user-name-only | Allow saving of user name only. |
| host | Add client route of host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Add client route of named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_NAME> |
Host or network address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Add client route of network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| host | Add client route of host address. |
| <ADDR_HOST> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 host address in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 host address in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.168\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:0000:0000:0000:0000:3257:9652\n |
| name | Add client route of named address object. |
| <ADDR_HOST_NETWORK_NAME> |
Host or network address object name. Example: Web Server |
| network | Add client route of network address. |
| <ADDR_NETWORK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 network in the form: D.D.D.D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 network in the form: HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH:HHHH\n. Example: IPV4: 192.168.168.0\nIPV6: 2001:cdba:3257:effe:0000:0000:0000:0000\n |
| <ADDR_MASK> |
IPV4: address object IPv4 netmask in decimal dotted or CIDR form: D.D.D.D OR /D\nIPV6: address object IPv6 netmask in the form: /D\n. Example: IPV4: 255.255.255.0\nIPV6: /64\n |
| <SSLVPN_BOOKMARK> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <SSLVPN_BOOKMARK> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <SSLVPN_BOOKMARK> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <HOSTNAME> |
Hostname in the form: hostname OR a.b.c.d. Example: example.com |
| rdp-activex | Terminal services (RDP5-ActiveX). |
| rdp-java | Terminal services (RDP5-JAVA). |
| sshv1 | Secure shell version 1 (SSHv1). |
| sshv2 | Secure shell version 2 (SSHv2). |
| telnet | Telnet. |
| vnc | Virtual network computing (VNC). |
| 1024x768 | 1024x768. |
| 1280x1024 | 1280x1024. |
| 640x480 | 640x480. |
| 800x600 | 800x600. |
| full-screen | Full screen. |
| 15bit | 15 bit - high color. |
| 16bit | 16 bit - high color. |
| 24bit | 24 bit - high color. |
| 256 | 256 bit. |
| 32bit | 32 bit - highest quality. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| custom | Use custom account credentials. |
| name | Enter login name. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| password | Enter login password. |
| <ENC_PASSWORD> |
Password. Example: secret |
| domain | Enter login domain. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| ssl-vpn | Use SSL-VPN account credentials. |
| <WORD> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| corre | Set CoRRE encoding type. |
| hextile | Set hextile encoding type. |
| raw | Set raw encoding type. |
| rre | Set RRE encoding type. |
| tight | Set tight encoding type. |
| zlib | Set ZLIB encoding type. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| level | Set JPEG image quality level. |
| <UINT8> |
Integer in the form: D OR 0xHH. Example: 123 |
| off | Turn off JPEG image quality. |
| disable | Disable cursor shape updates. |
| enable | Enable cursor shape updates. |
| ignore | Ignore cursor shape updates. |
| bookmark | Show a specified virtual office bookmark. |
| <SSLVPN_BOOKMARK> |
Word in the form: WORD or \"QUOTED STRING\". Example: abc |
| bookmarks | Show all virtual office bookmarks. |
| client | Show client configuration. |
| portal | Show portal configuration. |
| routes | Show client route configuration. |
| server | Show server configuration. |
| sessions | Show all active sessions. |
| statistics | Show statistics for the session associated with the specified NetExtender virtual IP. |
| <SSLVPN_LOGOUT_IPV4_HOST> |
IPV4 Address in the form: a.b.c.d. Example: 192.168.168.168 |
| pending-config | Show pending configuration changes. |
| with-pending-config | View current configuration with pending changes included in the output. |
| json | Format output as JSON. |
| validate | Validate configuration settings. |
| xml | Format output as XML. |