Policies_Anti-Spam_Settings_Snwls
Activating Anti-Spam
To activate the Comprehensive Anti-Spam Service, perform the following steps:
1. Navigate to the Policies > Anti-Spam > Settings page.
2. Select the Enable Anti-Spam Service checkbox to activate the Anti-Spam service.
The Comprehensive Anti-Spam Service is now activated.
Configuring Anti-Spam Settings
You can configure the Comprehensive Anti-Spam Service on the Anti-Spam > Settings page, including installing the Junk Store and configuring email threat categories. See the following sections:
• Configuring the Email Threat Categories
• Configuring Email Domains
• Configuring User Defined Access Lists
• Configuring Advanced Options
• Configuring Anti-Spam Real-Time Black List Filtering
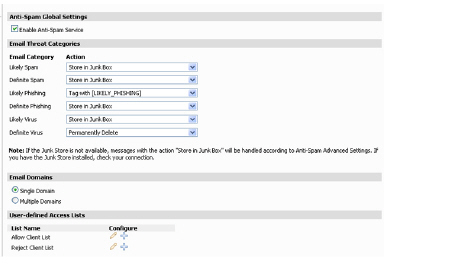
Configuring the Email Threat Categories
The Email Threat Categories section enables the administrator to configure the settings for users’ messages. Choose settings for messages that contain spam, phishing, and virus issues. The default settings are:
• Likely Spam – Store in Junk Box
• Definite Spam – Permanently Delete
• Likely Phishing – Tag with [LIKELY PHISHING]
• Definite Phishing – Store in Junk Box
• Likely Virus – Store in Junk Box
• Definite Virus – Permanently Delete
Use the pull-down options to choose how to to handle messages in each threat category. Your options are:
|
Response
|
Effect
|
|
Filtering off
|
SonicWALL Anti-Spam service will not scan and filter any email, so all email messages in this category are delivered to the recipients without modification.
|
|
Tag With
|
The email is tagged with a term in the subject line, for example, [JUNK] or [Possible Junk?]. Selecting this option allows the user to have control of the email and junk it if it is unwanted.
|
|
Store in Junk Box
|
The email message is stored in the Junk Box. It can be unjunked by users and administrators with appropriate permissions.
|
|
Reject Mail
|
The email message is returned to sender with a message indicating that it was not deliverable.
|
|
Permanently Delete
|
The email message is permanently deleted.
CAUTION: If you select this option, your organization risks losing wanted email.
|
|
Configuring Email Domains
The Comprehensive Anti-Spam Service supports up to 5 domains. If you are using more than one domain, choose the Multiple Domains option and contact SonicWALL or your SonicWALL reseller for more information.
Configuring User Defined Access Lists
User-defined Access Lists designate which clients are allowed to connect to deliver email. You can also set clients to be automatically rejected.
Configuring Advanced Options
Click the down-arrow next to Advanced Options to expand this section.
Advanced options allow you to set the following:
|
Setting
|
Description
|
|
Allow / Reject delivery of unprocessed mails when Comprehensive Anti-Spam Service is unavailable
|
If the Anti-Spam service is not enabled or unavailable for some other reason, you can choose Allow to let all unprocessed emails go through. Spam messages will be delivered to users, as well as good email. If the setting is Reject, no email will be delivered until the Anti-Spam service is re-enabled.
|
|
Tag and Deliver / Reject / Delete emails when SonicWALL Junk Store is unavailable
|
If the SonicWALL Junk Store cannot accept spam messages, you can choose to delete them, reject them, or deliver them with cautionary subject lines such as “[Phishing] Please renew your account”
|
|
Probe Interval
|
Set the number of minutes between messages to the monitoring service.
|
|
Success Count Threshold
|
Set the number of successes required to report a success to the monitoring service.
|
|
Failure Count Threshold
|
Set the number of failures required to report a failure to the monitoring service.
|
|
Server Public IP Address
|
The IP address of the server that is available for external connections.
|
|
Server Private IP Address
|
The IP address of the server for internal traffic.
|
|
Inbound Email Port
|
The port your SonicWALL firewall appliance has open to receive email from outside sources.
|
|
Enable Email System Detection
|
Enables the detection of other anti-spam solutions in the network perimeter.
|
|
